Subjective Research, a cornerstone of qualitative studies, delves into the realm of personal experiences, perspectives, and interpretations. It embraces the richness of individual narratives and explores the “why” behind human behavior, offering valuable insights often missed by purely objective approaches. It often plays a key role in fields like psychology, sociology, and even paranormal investigations, where understanding individual experiences is paramount. This exploration of subjective research will uncover its nuances, benefits, challenges, and its vital role in enriching our understanding of the complex human experience. See more about the Qualia Research Institute.
What is Subjective Research?
Subjective research prioritizes individual experiences and perspectives. Unlike objective research which focuses on measurable data and quantifiable facts, subjective research explores the unique realities shaped by personal beliefs, emotions, and interpretations. This approach acknowledges that individuals perceive and interact with the world in diverse ways, offering a rich tapestry of understanding.
For instance, in researching a paranormal event, objective research might focus on recording environmental changes like temperature fluctuations or electromagnetic readings. However, subjective research would explore the witnesses’ personal accounts of the event, their emotional responses, and the meaning they ascribe to the experience. This subjective lens provides valuable context and a deeper understanding of the event’s impact on individuals.
 Subjective Research in Paranormal Investigation
Subjective Research in Paranormal Investigation
Subjective research often relies on qualitative data collection methods such as interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. These methods allow researchers to gather rich, detailed narratives that provide deeper insight into the complexities of human experience.
The Strengths and Limitations of Subjective Research
Like any research methodology, subjective research has both advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these is crucial for effectively utilizing this approach.
The Benefits of Exploring Individual Perspectives
- Depth of Understanding: Subjective research goes beyond surface-level observations, diving into the motivations, beliefs, and feelings that drive human behavior. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
- Generating Hypotheses: By exploring individual experiences, subjective research can unearth patterns and insights that can lead to the development of new hypotheses and research questions for future, potentially objective, study.
- Contextualization: Subjective research provides valuable context for understanding objective data. For instance, statistical data on crime rates can be further illuminated by understanding the lived experiences of individuals affected by crime. See the meaning of subjective and objective data in research meaning.
The Challenges of Subjective Research
- Subjectivity Bias: The inherent subjectivity of this approach can introduce biases, both from the researcher and the participants. Researchers must be mindful of their own preconceptions and employ rigorous methods to minimize bias.
- Generalizability: Findings from subjective research may not be generalizable to larger populations. Because it focuses on individual experiences, it may not be representative of the broader population.
- Difficulty in Replicating: Due to its reliance on unique personal experiences, replicating subjective research can be challenging. This can make it difficult to verify the findings and build upon existing research. An example of phenomenological research further illustrates this point.
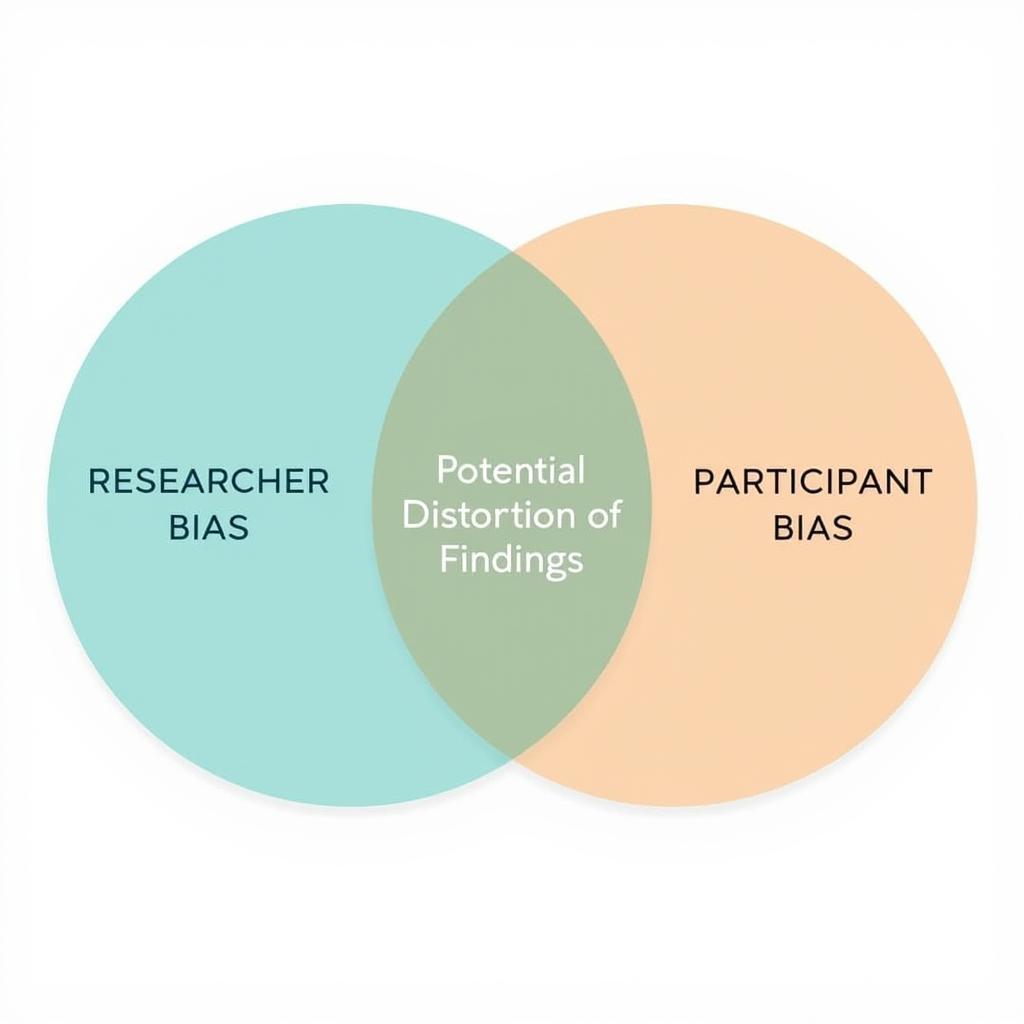 Challenges of Subjective Research
Challenges of Subjective Research
When to Utilize Subjective Research
Subjective research is particularly valuable when exploring complex social phenomena, understanding individual perspectives, and generating hypotheses. It is a powerful tool in fields like:
- Psychology: Understanding mental health conditions, exploring therapeutic approaches, and studying human behavior.
- Sociology: Investigating social issues, exploring cultural differences, and understanding group dynamics.
- Marketing: Gaining consumer insights, understanding brand perception, and developing targeted advertising campaigns.
- Paranormal Research: Exploring individual experiences of unexplained phenomena, understanding the psychological impact of these experiences, and generating hypotheses for further investigation. See Black Lodge research.
Subjective Research: A Powerful Tool for Understanding
Subjective research, while presenting certain challenges, provides a valuable perspective that complements objective research. By embracing the richness of individual experiences, it offers a deeper, more nuanced understanding of the human condition and the world around us. The results from research have been known to produce valuable insights.
Conclusion
Subjective research, though sometimes challenging, provides invaluable insights into the human experience. By understanding its strengths and limitations, researchers can leverage its power to unlock a deeper understanding of complex issues and enrich our knowledge.
FAQ
- How does subjective research differ from objective research? Subjective research focuses on individual perspectives and interpretations, while objective research emphasizes measurable data and facts.
- What are the limitations of subjective research? Subjectivity bias, difficulty in generalizing findings, and challenges in replication are some limitations.
- When is subjective research most useful? Subjective research is particularly valuable when exploring complex social phenomena, understanding individual perspectives, and generating hypotheses.
- What are some examples of subjective research methods? Interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys are commonly used.
- Can subjective and objective research be used together? Yes, they can complement each other to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research topic.
- How can bias be minimized in subjective research? Researchers should be mindful of their own preconceptions and employ rigorous data collection and analysis methods.
- What are some examples of fields where subjective research is commonly used? Psychology, sociology, marketing, and Paranormal Research are just a few examples.
For support, please contact us at Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.