Stem Cell Patches Research represents a cutting-edge field within regenerative medicine, holding immense promise for treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. This innovative approach combines the regenerative power of stem cells with biocompatible materials to create “patches” that can be applied directly to damaged tissues or organs.
What are Stem Cell Patches?
Stem cell patches are essentially bioengineered constructs that deliver a concentrated dose of stem cells directly to the site of injury or disease. These patches act as a scaffold, providing structural support for the stem cells to attach, proliferate, and differentiate into the desired cell types needed for repair.
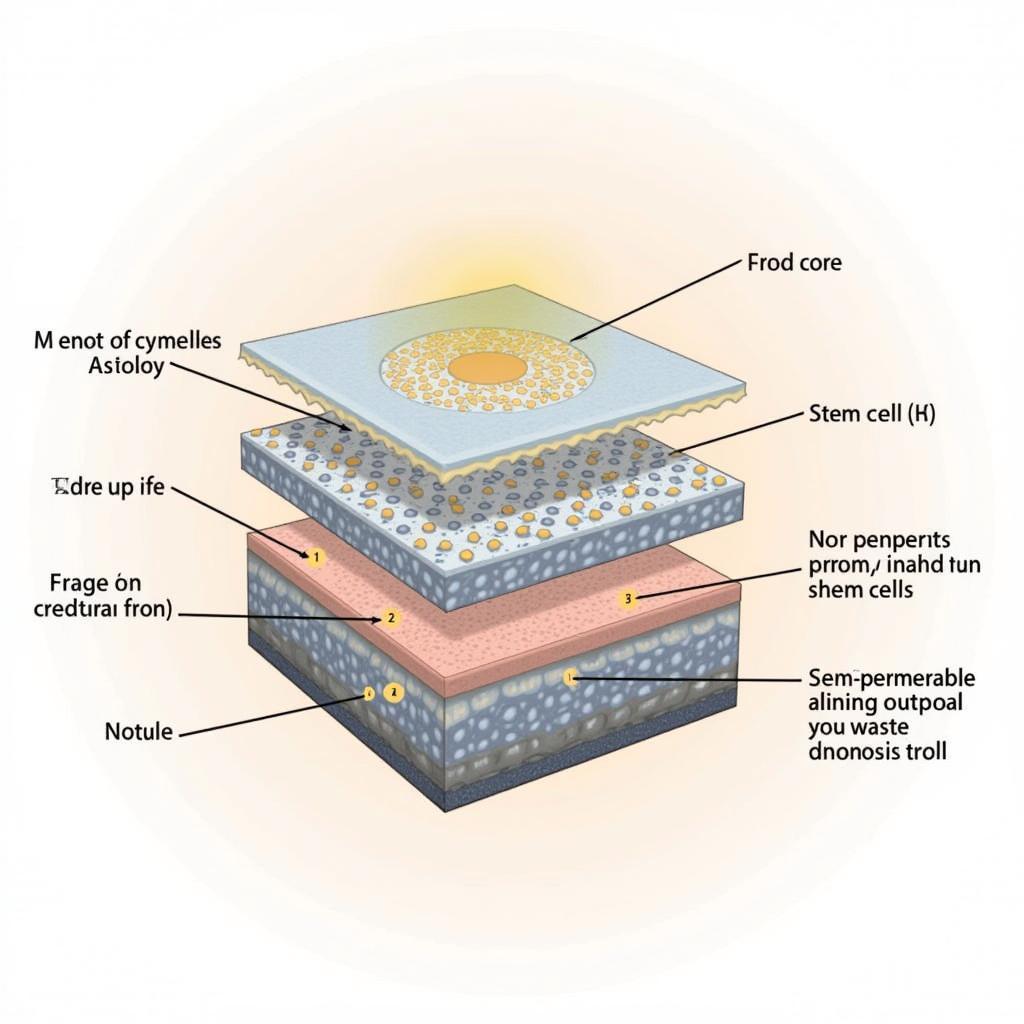 Structure of a Stem Cell Patch
Structure of a Stem Cell Patch
How Do Stem Cell Patches Work?
The mechanism of action of stem cell patches involves a complex interplay of biological processes. Upon application, the stem cells within the patch release a variety of growth factors and cytokines, signaling molecules that stimulate the body’s natural healing response. These signaling molecules recruit endogenous stem cells to the damaged area and promote the formation of new blood vessels, which in turn enhances nutrient supply and waste removal, facilitating tissue regeneration.
Potential Applications of Stem Cell Patches
Stem cell patch research is being explored for a diverse range of medical applications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Stem cell patches are being investigated for their potential to regenerate damaged heart tissue after a heart attack, improving heart function and reducing the risk of heart failure.
- Wound Healing: Patches embedded with stem cells have shown promise in accelerating the healing of chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers and burn injuries.
- Osteoarthritis: Researchers are exploring the use of stem cell patches to repair damaged cartilage in arthritic joints, potentially delaying or even eliminating the need for joint replacement surgery.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Stem cell patches are being investigated for their ability to protect and potentially regenerate damaged nerve cells in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
 Stem Cell Patch Application for Heart Repair
Stem Cell Patch Application for Heart Repair
Advantages of Stem Cell Patch Therapy
Stem cell patch therapy offers several advantages over traditional stem cell transplantation methods, including:
- Targeted Delivery: Patches deliver stem cells directly to the site of injury, maximizing their therapeutic effect and minimizing off-target effects.
- Minimally Invasive: The application of stem cell patches is minimally invasive, often requiring only a small incision or injection, leading to faster recovery times and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery.
- Controlled Release: The patch provides a controlled release of stem cells and growth factors over time, optimizing the healing process.
- Improved Cell Survival: The scaffold structure of the patch provides a protective environment for the stem cells, enhancing their survival and integration into the damaged tissue.
Challenges and Future Directions
While stem cell patch research holds great promise, several challenges remain before this technology can be widely implemented in clinical practice:
- Long-Term Efficacy: Further research is needed to determine the long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell patches in humans.
- Immune Rejection: Strategies to minimize the risk of immune rejection of the patch and the transplanted cells are crucial for long-term success.
- Large-Scale Production: Developing cost-effective methods for the large-scale production of stem cell patches while maintaining quality control is essential for wider accessibility.
“Stem cell patches represent a paradigm shift in regenerative medicine,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in the field. “By harnessing the power of stem cells in a targeted and controlled manner, we have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of a wide range of debilitating diseases.”
Conclusion
Stem cell patch research represents a rapidly evolving field with the potential to transform the landscape of regenerative medicine. As research progresses and these challenges are addressed, stem cell patches are poised to become a powerful tool in the fight against a wide range of diseases and injuries, offering hope for improved treatments and ultimately, a better quality of life for countless individuals.