Sampling Techniques In Survey Research are crucial for obtaining reliable and representative data without surveying an entire population. Choosing the right sampling method can significantly impact the accuracy and generalizability of your findings. This article will explore various sampling techniques, their advantages, disadvantages, and best practices for implementing them effectively.
 Different Sampling Techniques in Survey Research
Different Sampling Techniques in Survey Research
One of the most fundamental aspects of conducting sound survey research is selecting an appropriate sampling method. Understanding the different types of sampling methods and their applications can help researchers gather valuable insights from a smaller group that accurately reflects the larger population of interest. social & behavioral research – basic/refresher provides a good overview of basic research principles. By utilizing appropriate sampling strategies, researchers can save time, resources, and still obtain meaningful results.
What are the Different Types of Sampling Techniques?
There are two main categories of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Probability Sampling: Everyone Has a Chance
Probability sampling techniques ensure every member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected. This allows for the generalization of findings to the broader population.
-
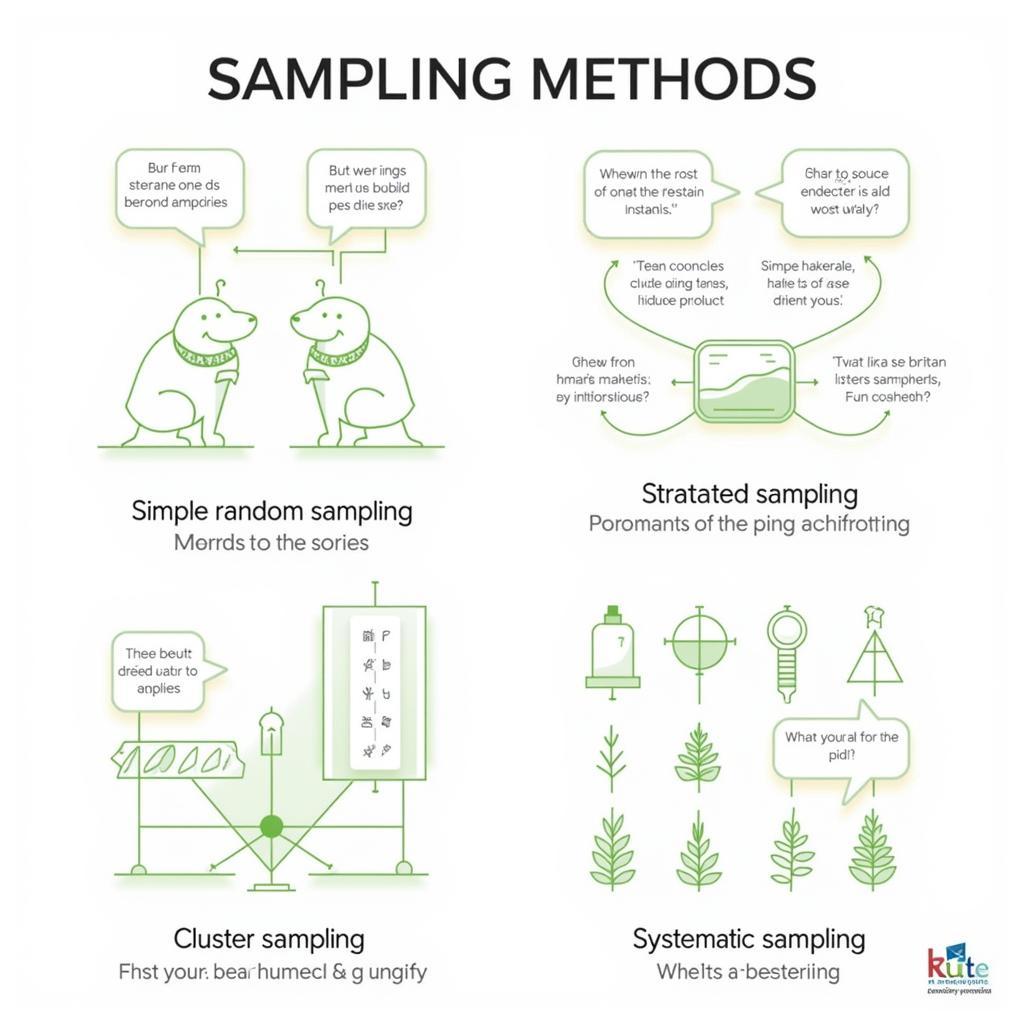
Simple Random Sampling: Every member has an equal chance of selection. This is often achieved using a random number generator.
-
Stratified Sampling: The population is divided into subgroups (strata) based on shared characteristics, and a random sample is drawn from each stratum.
-
Cluster Sampling: The population is divided into clusters, and a random sample of clusters is selected. All members within the selected clusters are included in the sample.
-
Systematic Sampling: Every nth member of the population is selected after a random starting point.
Non-Probability Sampling: Not Everyone Gets a Ticket
Non-probability sampling techniques do not guarantee every member a chance of selection. While less rigorous, these methods are often more practical for exploratory research or when probability sampling is infeasible.
-
Convenience Sampling: Selecting readily available participants. This is often the easiest but least representative method.
-
Quota Sampling: Similar to stratified sampling, but selection within strata is non-random.
-
Snowball Sampling: Existing participants refer new participants, useful for hard-to-reach populations.
-
Purposive Sampling: Researchers handpick participants based on specific criteria relevant to the study.
How to Choose the Right Sampling Technique for Your Survey Research?
Selecting the right technique depends on your research goals, resources, and the characteristics of the population. For instance, if generalizability is paramount, probability sampling is necessary. If you’re exploring a niche topic and accessing specific individuals is critical, purposive sampling might be more suitable. primary research techniques provides further information on different research methods.
 Choosing the Correct Sampling Technique for Survey Research
Choosing the Correct Sampling Technique for Survey Research
“The key to successful survey research lies in choosing a sampling technique that aligns with your research question and allows you to draw meaningful conclusions,” says Dr. Amelia Hernandez, a renowned statistician specializing in survey methodology. “Understanding the nuances of each method is essential for ensuring the validity and reliability of your findings.”
Why is Sample Size Important?
Sample size directly affects the precision of your results. A larger sample size generally leads to greater precision and reduces the margin of error. However, increasing sample size also increases costs and time. Finding the optimal balance between precision and practicality is crucial.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Sampling
Several common pitfalls can compromise the integrity of your survey research. These include:
-
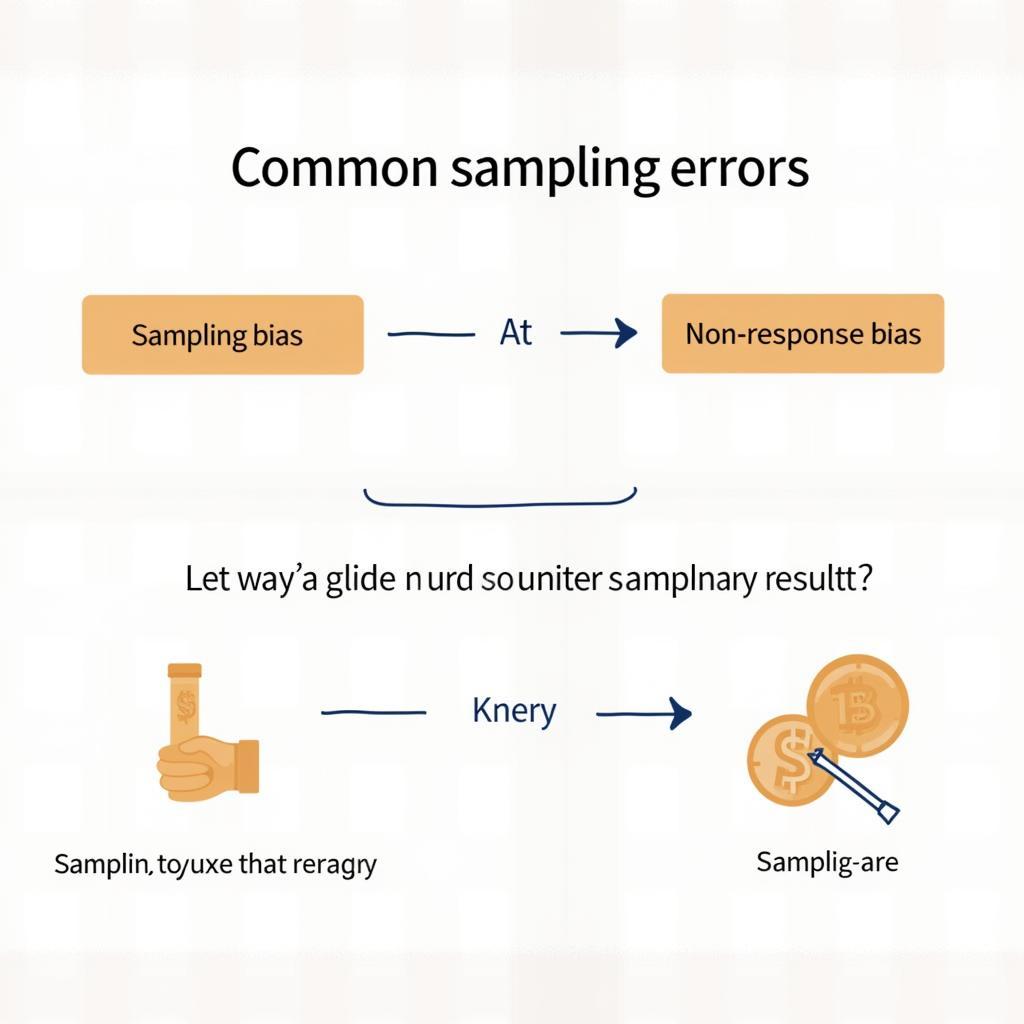
Sampling Bias: When certain members of the population are systematically over- or under-represented in the sample.
-
Non-Response Bias: When a significant portion of the selected sample doesn’t participate, potentially skewing the results.
-
Measurement Error: Errors arising from flaws in the survey instrument or data collection process.
Professor David Lee, a leading expert in research methodology, advises, “Researchers must be vigilant in mitigating potential biases in their sampling procedures. Careful planning and execution are crucial for ensuring the quality and trustworthiness of survey data.”
 Common Sampling Pitfalls in Survey Research
Common Sampling Pitfalls in Survey Research
alan bryman social research methods offers valuable insights on navigating these complexities. Ensuring your sampling technique is robust and accurately represents the target population is fundamental to obtaining reliable and meaningful results.
Conclusion
Mastering sampling techniques in survey research is essential for conducting effective and impactful studies. By carefully considering the various methods available and choosing the one best suited to your specific needs, you can gather valuable data and draw accurate conclusions. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technique and avoiding common pitfalls will help ensure the integrity and validity of your research findings. Using appropriate sampling techniques ultimately leads to more reliable and insightful survey results.
FAQ
- What is the difference between probability and non-probability sampling?
- What is the best sampling technique for a small population?
- How do I calculate the appropriate sample size for my survey?
- How can I minimize sampling bias in my research?
- What are the benefits of using stratified sampling?
- When should I use cluster sampling?
- What are the limitations of convenience sampling?
Need help with your research? Contact us! Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com. Visit us at: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We’re here 24/7!