Research Misconduct Definition involves actions that deviate from accepted ethical standards in the research process. This encompasses fabrication, falsification, or plagiarism in proposing, performing, or reviewing research, or in reporting research results. Understanding this definition is crucial for maintaining the integrity of scientific inquiry. Let’s delve deeper into what constitutes research misconduct and explore its implications.
What exactly falls under the umbrella of “research misconduct definition”? It’s important to distinguish between honest errors, differences of opinion, and actual misconduct. Honest errors, while unfortunate, are a part of the learning process in research. Differences of opinion are a natural consequence of scientific debate and exploration. Research misconduct, however, is a deliberate departure from these norms, impacting the reliability and trustworthiness of research findings. This can include actions such as manipulating data, misrepresenting findings, or claiming credit for the work of others. Failing to adhere to ethical research principles can damage reputations, undermine public trust in science, and even have legal repercussions.
Different Forms of Research Misconduct
Research misconduct takes on various forms, each with serious implications for the scientific community. Let’s examine some key examples:
Fabrication
Fabrication in research involves making up data or results and recording or reporting them. This is a blatant violation of research integrity, as it introduces false information into the scientific record.
Falsification
Falsification is manipulating research materials, equipment, or processes, or changing or omitting data or results such that the research is not accurately represented in the research record. This can include selectively reporting data that supports a desired outcome while ignoring contradictory evidence.
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is the appropriation of another person’s ideas, processes, results, or words without giving appropriate credit. This not only disrespects the original author but also undermines the principles of intellectual property and academic honesty.
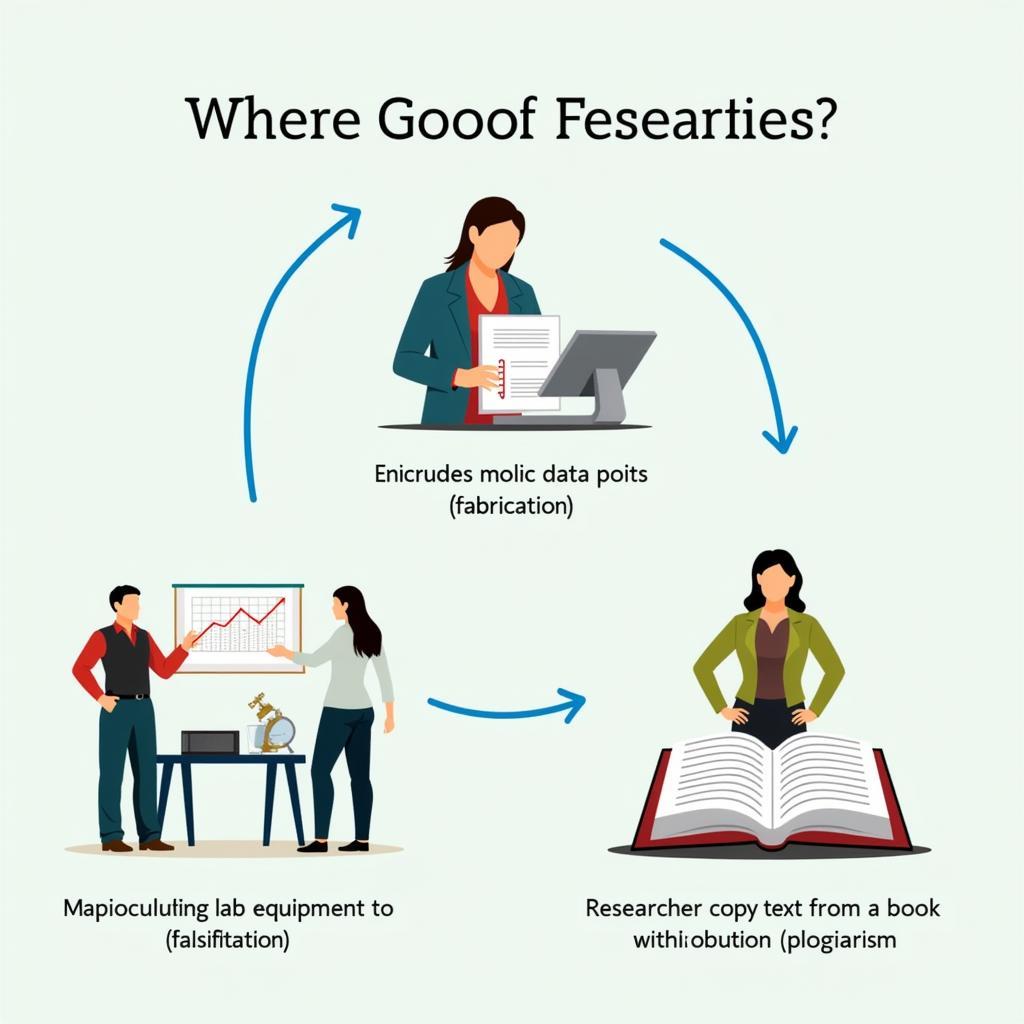 Research Misconduct Types: Fabrication, Falsification, and Plagiarism
Research Misconduct Types: Fabrication, Falsification, and Plagiarism
Ethical research practices are essential for maintaining the credibility of scientific endeavors. For more information on this, you can refer to the ethical research definition.
The Impact of Research Misconduct
Research misconduct has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the individual researcher.
Damage to Reputation and Trust
When research misconduct is uncovered, it can severely damage the reputation of the researcher and the institutions involved. It also erodes public trust in science and the research process. Understanding the definition of impact in research allows us to appreciate the seriousness of these consequences.
Retraction of Publications
Published research found to be based on misconduct is often retracted from scientific journals. This removes the flawed information from the public record, but it can also create gaps in scientific knowledge and hinder future research efforts.
Legal and Funding Implications
In some cases, research misconduct can lead to legal action and the loss of research funding. This can have significant financial and career consequences for those involved. For a deeper understanding of the process of conducting research, you can refer to process research definition.
Preventing Research Misconduct
Several measures can be taken to prevent research misconduct and promote research integrity.
Education and Training
Researchers should receive comprehensive training on responsible conduct of research (RCR). This training should cover the definition of research misconduct, as well as strategies for ethical data management and publication practices. You can learn more about research misconduct rcr basic principles.
Mentoring and Supervision
Effective mentoring and supervision are crucial for ensuring that researchers, especially those at the beginning of their careers, understand and adhere to ethical research practices.
Institutional Policies and Procedures
Research institutions should establish clear policies and procedures for handling allegations of research misconduct. These policies should include mechanisms for reporting misconduct, investigating allegations, and taking appropriate disciplinary action. Learn more about maintaining what is research integrity within academic institutions.
Understanding the “research misconduct definition” is fundamental to ensuring the integrity of scientific research. By promoting ethical conduct, fostering a culture of responsibility, and implementing effective oversight mechanisms, we can protect the credibility of research and its contribution to society.
Conclusion
Research misconduct, by definition, represents a severe breach of trust within the scientific community. Understanding this definition, its various forms, and its consequences is essential for every researcher. By adhering to ethical principles, promoting transparency, and embracing a culture of integrity, we can uphold the highest standards of research and safeguard its vital role in advancing knowledge. Remember, maintaining research integrity is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a commitment to the pursuit of truth and the responsible advancement of scientific knowledge.
FAQ
- What is the difference between research misconduct and an honest error?
- What are the potential consequences of plagiarism in research?
- How can research institutions promote a culture of research integrity?
- What are some resources available for researchers who want to learn more about responsible conduct of research?
- What should a researcher do if they suspect research misconduct?
- Where can I find more information on the definition of research misconduct according to specific funding agencies?
- What role does peer review play in preventing research misconduct?
For any assistance, contact us at Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.