Research in psychology often utilizes visual aids like pie charts to represent data effectively. Pie charts are particularly useful for showcasing the proportional distribution of different categories within a specific dataset. Understanding how to interpret and use pie chart data representation is crucial for researchers and students alike. This article delves into the application of pie charts in psychological research, exploring best practices, common uses, and interpreting results. After reading this, you will be more confident in your ability to present and understand research findings presented in this visual format.
Utilizing Pie Charts in Psychological Studies
Pie charts can simplify complex data and make it easily digestible for both academic audiences and the general public. In psychology, they are frequently used to display data from surveys, experiments, and observational studies. For example, a study on stress management techniques might utilize a pie chart to illustrate the percentage of participants who preferred different methods like mindfulness, exercise, or therapy. Using visuals can enhance the overall understanding of complex datasets, particularly helpful when sharing information with a broader audience.
One area where pie charts shine is in illustrating the prevalence of different psychological conditions within a population. This visual representation offers a quick and easy way to compare the relative proportions of various conditions, aiding in public health awareness and resource allocation. See our [graphs in research paper] for more visual data representation techniques.
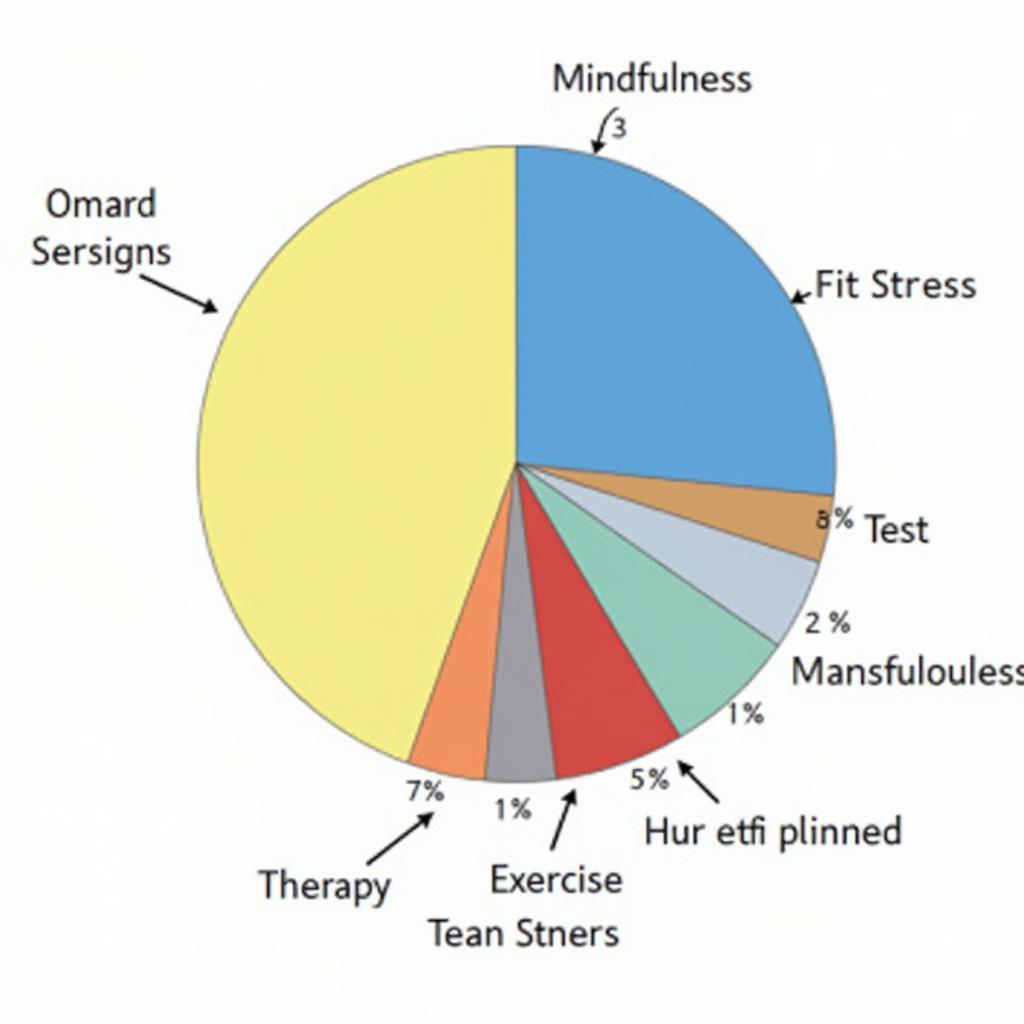 Pie Chart Illustrating Stress Management Techniques Preference
Pie Chart Illustrating Stress Management Techniques Preference
Interpreting Pie Chart Data: Key Considerations
While pie charts are visually appealing, it’s important to interpret them carefully. One common pitfall is misinterpreting the size of the segments, especially when the percentages are close. For optimal clarity, ensure that the segments are clearly labeled with the corresponding percentages and include a legend explaining what each segment represents. This careful labeling helps avoid misinterpretations and facilitates accurate understanding of the data. [Experimental research topics psychology] offers more insight into how these charts might be used in research.
Another critical aspect is the sample size. A pie chart based on a small sample may not accurately represent the larger population. Always consider the representativeness of the sample when drawing conclusions from pie chart data. Furthermore, avoid using 3D pie charts as they can distort the perception of segment sizes and lead to inaccurate interpretations.
Best Practices for Pie Chart Creation in Research
Creating effective pie charts involves several key considerations. Firstly, limit the number of segments. Too many segments can make the chart cluttered and difficult to interpret. Ideally, stick to a maximum of five or six segments for optimal clarity. If you have more categories, consider grouping smaller ones into an “other” category or using a different chart type altogether.
Secondly, ensure the colors used are distinct and easy to differentiate. Avoid using similar shades that might make it hard to distinguish between segments. Finally, clearly label each segment with its corresponding percentage or value and provide a comprehensive legend. This clear labeling enhances readability and allows for quick and accurate interpretation of the presented data. You can explore further on [research paper in psychology with pie chart data representation].
When a Pie Chart is Not the Best Choice: Alternatives
While pie charts are useful, sometimes they aren’t the best option. If your data involves numerous categories or requires displaying small percentage differences, bar graphs or line graphs might be more suitable. These alternatives offer better visual clarity when dealing with complex datasets and subtle variations.
Conclusion: Effectively Using Pie Chart Data Representation
Pie charts offer a valuable tool for researchers in psychology to represent data in a clear and concise manner. When used effectively, they can enhance understanding and communication of research findings. However, mindful creation and interpretation are crucial for accurate data representation. Considering best practices, limitations, and potential alternatives can help researchers choose the most suitable visualization method for their data and research objectives, ultimately enhancing the overall impact of their work.
FAQ
- What is the main purpose of using a pie chart in research?
- What are some limitations of using pie charts?
- What are some alternatives to pie charts?
- How can I make my pie chart more accessible?
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a pie chart?
- How can I interpret the data presented in a pie chart?
- What software can I use to create pie charts?
 Best Practices for Data Visualization in Psychology Research
Best Practices for Data Visualization in Psychology Research
Need help with your research? Contact us! Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.