Memory consolidation, the process by which our brains transform new experiences into long-term memories, is a fascinating and complex phenomenon. Research Has Shown That The Consolidation Of Memories is not a simple act of storage, but rather a dynamic and ongoing process involving multiple brain regions and intricate molecular mechanisms. Understanding how this process works is crucial not only for comprehending the nature of memory itself, but also for developing treatments for memory disorders and enhancing learning strategies.
The Intricacies of Memory Consolidation: A Deeper Dive
Memory consolidation isn’t instantaneous. It unfolds over time, sometimes taking days, weeks, or even years to fully cement a memory. This gradual process allows for the integration of new information with existing knowledge, shaping our understanding of the world. research on memory focuses mostly on the biological and psychological factors influencing this process.
How Does Sleep Impact Memory Consolidation?
Sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation. During sleep, our brains replay experiences, strengthening the neural connections associated with those memories. This replay process is thought to be essential for transferring memories from short-term storage in the hippocampus to long-term storage in the cortex.
The Role of Emotions in Memory Consolidation
Emotions significantly influence which memories are consolidated and how vividly they are retained. Highly emotional experiences, both positive and negative, tend to be remembered more clearly and persistently than mundane events. This is likely due to the involvement of the amygdala, the brain’s emotional center, which interacts with the hippocampus during memory formation. a researcher claims that the epinephrine signaling pathway controls the strength of memory consolidation.
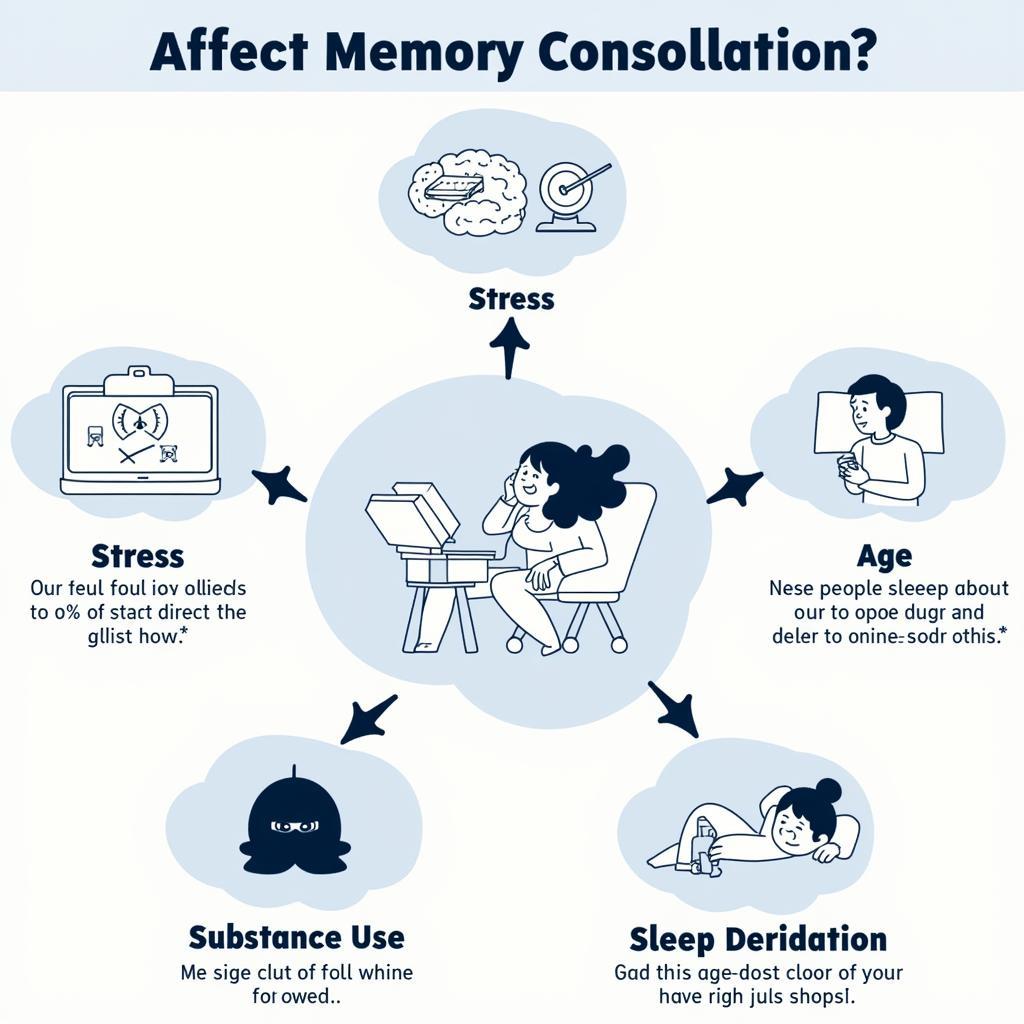
Factors Affecting Memory Consolidation
Several factors can impact the effectiveness of memory consolidation. These include:
- Stress: While moderate stress can enhance memory, chronic stress can impair it.
- Age: Memory consolidation can become less efficient with age.
- Substance use: Alcohol and certain drugs can interfere with memory consolidation.
- Sleep deprivation: Lack of sleep hinders the crucial replay process during sleep.
 Factors Impacting Memory Consolidation
Factors Impacting Memory Consolidation
Enhancing Memory Consolidation: Practical Strategies
Research has shown that the consolidation of memories can be boosted through specific strategies:
- Active recall: Testing yourself on newly learned material strengthens memory traces.
- Spaced repetition: Reviewing information at increasing intervals optimizes long-term retention.
- Meaningful learning: Connecting new information to existing knowledge facilitates integration and consolidation. research on memory construction indicates that making connections between new and old information is vital for consolidation.
How can I improve my memory consolidation?
Engage in activities that promote active recall, spaced repetition, and meaningful learning. Ensure adequate sleep, manage stress levels, and avoid substance abuse.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Journey of Memory
Research has shown that the consolidation of memories is a dynamic and complex process, crucial for learning, adaptation, and our sense of self. By understanding the factors that influence this process, we can develop strategies to enhance our memory and address memory-related challenges.
FAQ
- What is memory consolidation?
- How long does memory consolidation take?
- What is the role of sleep in memory consolidation?
- How do emotions affect memory consolidation?
- What factors can impair memory consolidation?
- How can I improve my memory consolidation?
- What are the different stages of memory consolidation?
Need support? Contact us 24/7 at Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.