The research and development (R&D) tax credit is a valuable incentive offered by the government to encourage businesses to invest in innovation. By offsetting the costs of developing new products, processes, or technologies, the R&D credit helps companies of all sizes stay competitive and drive economic growth. However, navigating the intricacies of Research And Development Credit Calculation can be complex and challenging. This guide aims to demystify the process, providing a clear and concise understanding of how to determine your company’s eligibility and maximize your credit potential.
Understanding the R&D Tax Credit
Before diving into the calculation, it’s crucial to understand what qualifies as a qualified research activity (QRA). The IRS provides specific criteria that must be met for expenses to be eligible for the credit. These activities must be:
- Technological in nature: The research must rely on principles of hard sciences such as engineering, computer science, or biology.
- Aimed at developing a new or improved product, process, or software: This includes modifications that significantly enhance functionality, performance, or quality.
- Subject to technical uncertainty: There must be a significant technical challenge that you are trying to overcome, with no readily available solutions.
- Involve a process of experimentation: You must be actively testing and evaluating different solutions to overcome the technical challenge.
Eligible Expenses for R&D Credit Calculation
Once you’ve determined that your activities qualify as QRAs, you need to identify the associated expenses that are eligible for the credit. These generally fall under four categories:
- Wages: This includes salaries, wages, and benefits for employees directly engaged in qualified research activities.
- Supplies: Materials and supplies used or consumed in the R&D process, such as prototypes, testing equipment, and software.
- Contract research: Payments made to third-party contractors for performing qualified research on your behalf.
- Cloud computing costs: Expenses related to using cloud computing resources for qualified research activities.
R&D Credit Calculation Methods
There are two primary methods for calculating the R&D tax credit:
1. Regular Credit Calculation: This method requires a detailed analysis of your base amount, which is typically your average annual gross receipts for the past four years. You can then claim a credit of 20% of the excess qualified expenses over a calculated base amount.
2. Alternative Simplified Credit (ASC): Introduced to simplify the calculation process, the ASC allows businesses to claim a credit of 14% of the excess qualified expenses over 50% of their average qualified research expenses for the past three years.
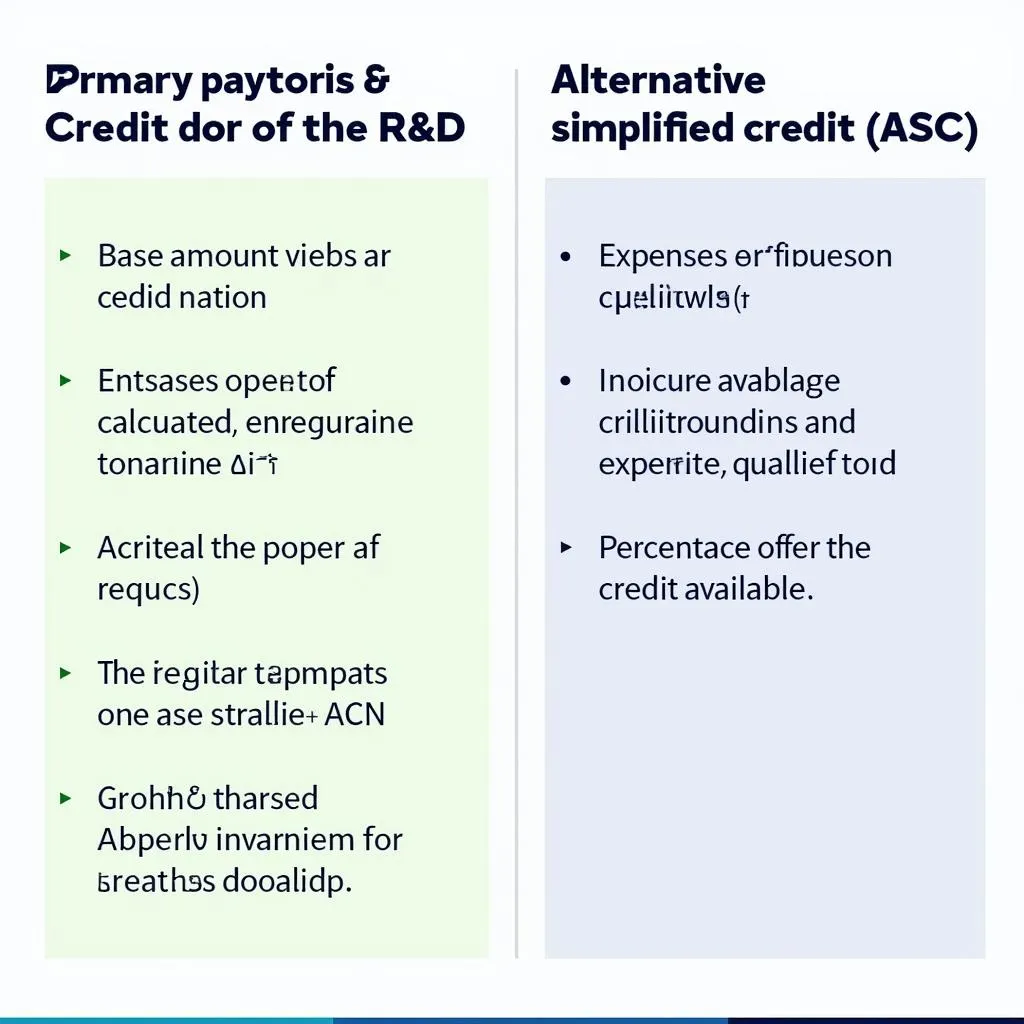 Two distinct methods for calculating R&D tax credits
Two distinct methods for calculating R&D tax credits
The method that yields the larger credit amount is generally the more advantageous option.
Common R&D Credit Calculation Mistakes
Even with a solid understanding of the eligibility criteria and calculation methods, businesses often make costly mistakes that can result in missed opportunities to maximize their credit. Here are some of the most common pitfalls to avoid:
- Overlooking eligible expenses: Many businesses fail to include all qualifying expenses in their calculations, particularly indirect costs associated with R&D activities.
- Inadequate documentation: Maintaining comprehensive records of qualified research activities and related expenses is crucial for substantiating your credit claim in case of an audit.
- Misinterpreting the four-part test: Misunderstanding or misapplying the four criteria for qualified research activities can lead to ineligible expenses being included in the calculation.
 Common pitfalls to avoid when calculating R&D tax credits
Common pitfalls to avoid when calculating R&D tax credits
Maximizing Your R&D Tax Credit
To fully leverage the benefits of the R&D tax credit, consider these strategies:
- Implement robust tracking systems: Establish clear procedures for documenting and tracking all qualified research activities and associated expenses.
- Consult with a tax professional: Navigating the complexities of the R&D tax credit can be challenging. Engaging an experienced tax professional specialized in R&D tax credits can help you optimize your claim and avoid costly mistakes.
- Stay informed about updates and changes: The R&D tax credit landscape is constantly evolving. Stay abreast of any legislative or regulatory changes that may impact your eligibility or calculation methods.
Conclusion
The research and development tax credit is a powerful tool for fostering innovation and driving business growth. By understanding the eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and common pitfalls, companies can effectively leverage this incentive to reduce their tax liability and invest in future advancements. Remember, thorough documentation, accurate calculations, and expert guidance are essential for maximizing the benefits of the R&D tax credit.