RCS research and tirzepatide are two seemingly disparate fields, yet some are exploring a potential link between them. RCS, or Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, is a medical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems in the bile and pancreatic ducts. Tirzepatide, on the other hand, is a novel medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. This article delves into the possibility of a connection, exploring the current research and potential implications.
Understanding RCS Research
RCS is a specialized imaging technique that allows physicians to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts. It involves injecting a contrast dye into these ducts and then taking X-rays. This procedure can help identify blockages, strictures, stones, and other abnormalities. 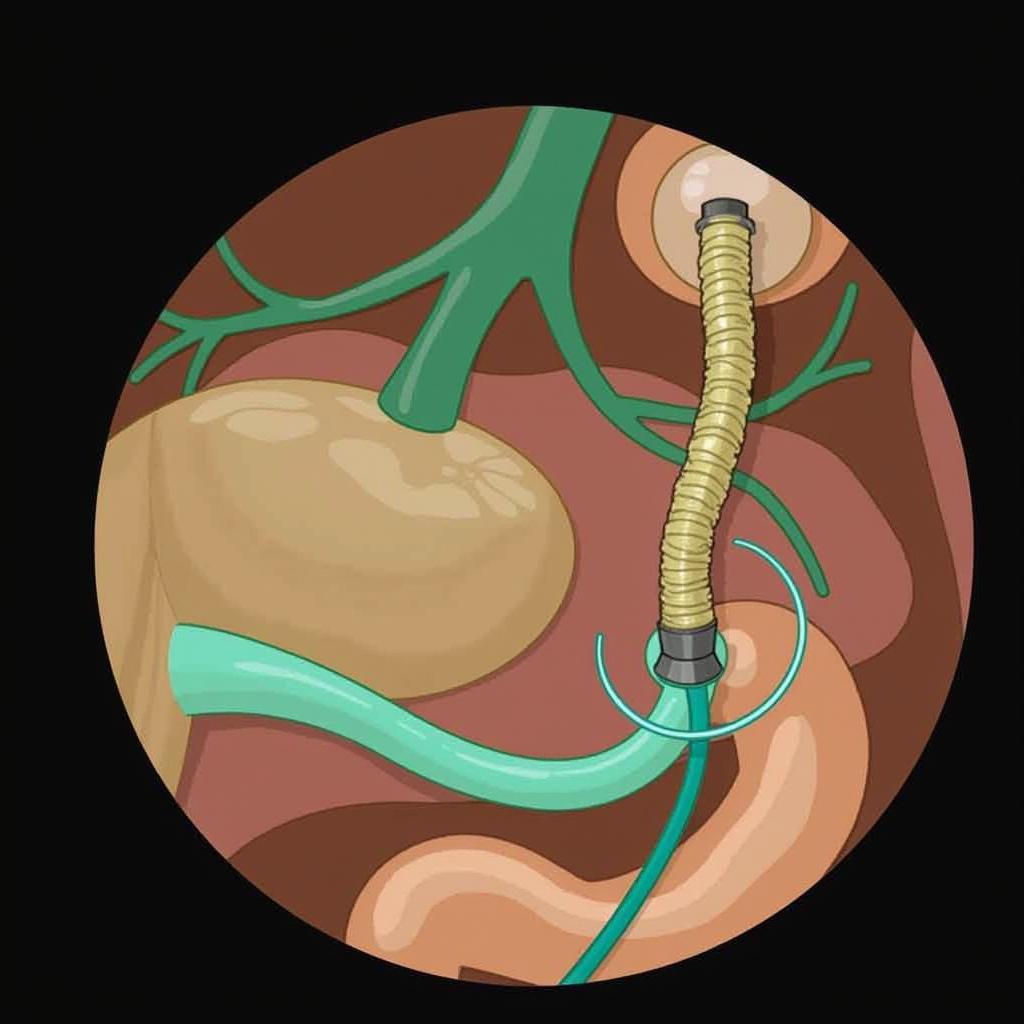 RCS Procedure Visualization RCS is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as gallstones, bile duct cancer, and pancreatitis. Further research is ongoing to improve the technique and expand its applications.
RCS Procedure Visualization RCS is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as gallstones, bile duct cancer, and pancreatitis. Further research is ongoing to improve the technique and expand its applications.
Exploring Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. This means it works by mimicking the effects of two natural hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels. Tirzepatide is a relatively new medication showing promising results in managing type 2 diabetes. It is administered through subcutaneous injection.
The Potential Link Between RCS Research and Tirzepatide
While seemingly unrelated, the potential connection between RCS research and tirzepatide lies in the realm of pancreatitis. Pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas, can sometimes be a side effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists, the class of drugs to which tirzepatide belongs. RCS, being a valuable tool for visualizing the pancreas, could potentially be used to monitor patients on tirzepatide for early signs of pancreatitis. This proactive approach could allow for early intervention and potentially prevent severe complications.
Could RCS Research Help Monitor Tirzepatide Patients?
This is a key question researchers are exploring. While more research is needed, RCS could offer a non-invasive way to assess the pancreas in patients taking tirzepatide.
What are the benefits of early pancreatitis detection?
Early detection allows for prompt treatment and potentially reduces the severity and duration of the condition. It can also prevent long-term complications.
How common is pancreatitis in patients taking Tirzepatide?
The incidence of pancreatitis with tirzepatide is relatively low, but it’s a potential side effect that warrants monitoring.
RCS Research and Tirzepatide: Future Directions
The future of this potential connection lies in further research. Studies are needed to determine the feasibility and efficacy of using RCS to monitor patients on tirzepatide.  Future Research: Tirzepatide and RCS This research will help clarify the role RCS can play in mitigating the risks associated with tirzepatide and optimizing its use in managing type 2 diabetes. research peptides
Future Research: Tirzepatide and RCS This research will help clarify the role RCS can play in mitigating the risks associated with tirzepatide and optimizing its use in managing type 2 diabetes. research peptides
Conclusion
RCS research and tirzepatide may hold a promising connection in the context of pancreatitis monitoring. While more research is needed, the potential for early detection and intervention makes this a valuable area of exploration. Further studies could lead to improved patient safety and outcomes for those using tirzepatide to manage their type 2 diabetes.
FAQ
- What is RCS?
- What is Tirzepatide?
- What is the link between RCS and Tirzepatide?
- How can RCS help monitor Tirzepatide patients?
- What are the benefits of early pancreatitis detection?
For further support, please contact us at Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com, or visit our office at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team available. You can also explore our other articles on research peptides for more related information.