Juvenile Crime Research delves into the complex factors contributing to criminal behavior in young people. This field of study is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies, intervention programs, and rehabilitation efforts aimed at reducing delinquency and promoting positive youth development.
Unraveling the Multifaceted Nature of Juvenile Crime
Juvenile crime research examines a wide range of offenses, from minor delinquencies like vandalism and shoplifting to more serious crimes such as assault and robbery. Researchers strive to understand the underlying causes of these actions, which can vary significantly depending on individual, familial, socioeconomic, and environmental factors.
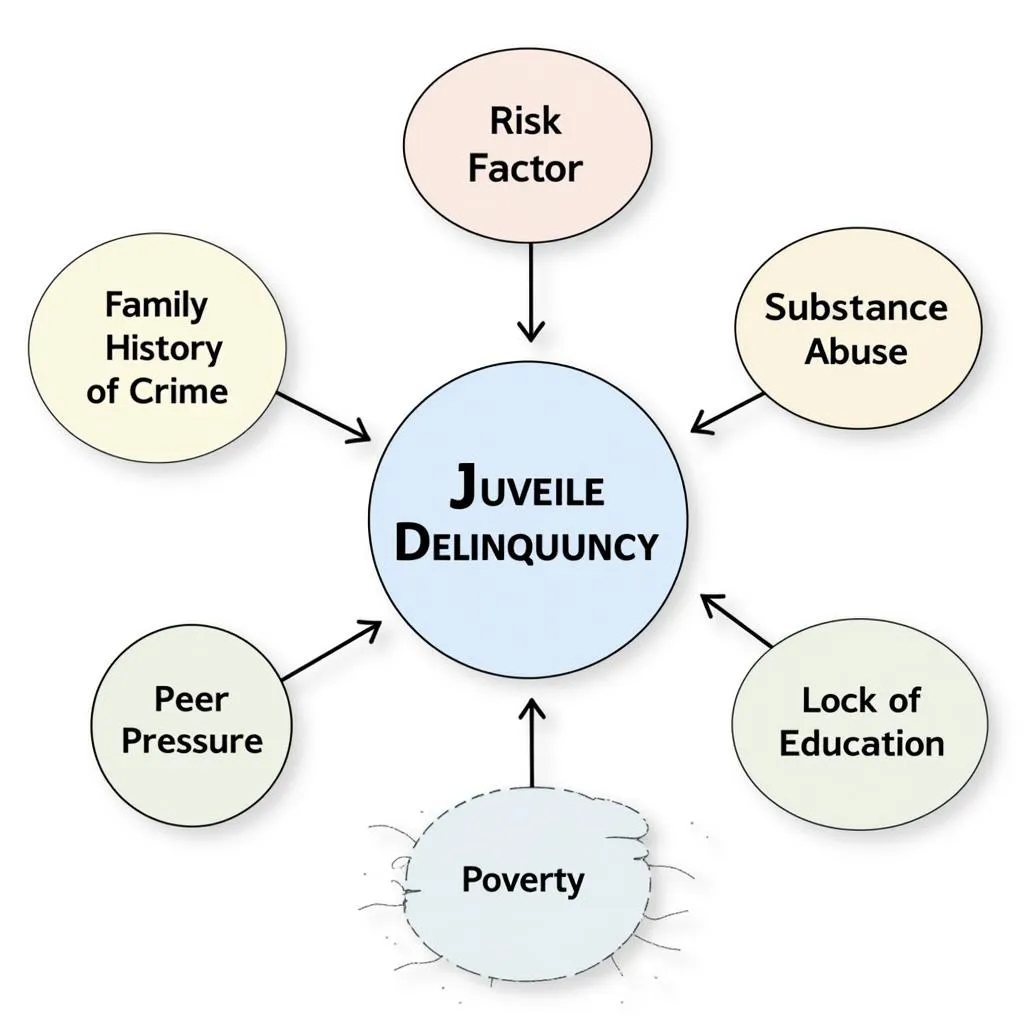 Juvenile Delinquency Risk Factors
Juvenile Delinquency Risk Factors
Key Areas of Focus in Juvenile Crime Research
Several key areas are central to juvenile crime research:
1. Risk and Protective Factors:
This area of research focuses on identifying specific individual, family, school, peer group, and community factors that increase or decrease the likelihood of youth engaging in criminal behavior.
2. Early Intervention and Prevention Programs:
Researchers evaluate the effectiveness of programs designed to address risk factors and promote protective factors in children and adolescents. These programs often target at-risk youth and aim to prevent future criminal involvement.
3. Juvenile Justice System Responses:
Juvenile crime research examines the effectiveness of various juvenile justice system responses, such as detention, probation, and community-based treatment programs, in reducing recidivism and promoting rehabilitation.
The Role of Family, Peers, and Community
Juvenile crime research highlights the significant influence of family, peer groups, and community factors on youth behavior.
- Family dynamics: A lack of parental supervision, family conflict, and exposure to domestic violence are all recognized risk factors for delinquency. Conversely, strong family bonds, consistent discipline, and parental involvement in a child’s life serve as protective factors.
- Peer influence: Association with delinquent peers is a strong predictor of juvenile crime. Youth may engage in risky behavior to gain acceptance or approval from their peer group.
- Community factors: Living in disadvantaged neighborhoods characterized by poverty, high crime rates, and limited access to resources can increase the likelihood of youth becoming involved in criminal activity.
The Importance of Evidence-Based Practices
Juvenile crime research plays a crucial role in developing and evaluating evidence-based practices within the juvenile justice system. By identifying effective interventions and programs, researchers help ensure that resources are allocated to strategies that have the greatest potential to reduce delinquency, rehabilitate young offenders, and enhance public safety.
 Evidence-Based Practices in Juvenile Justice
Evidence-Based Practices in Juvenile Justice
Conclusion: Working Towards a Brighter Future
Juvenile crime research is essential for understanding the complex factors that contribute to youth delinquency and developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By focusing on evidence-based practices and addressing individual, familial, and community risk factors, we can work towards creating a safer and more supportive environment for all young people.
FAQs
1. What are some common misconceptions about juvenile crime?
One common misconception is that juvenile crime is always violent. In reality, a significant portion of juvenile offenses involve property crimes or status offenses, such as truancy.
2. How effective are early intervention programs in preventing juvenile crime?
Research has shown that well-designed early intervention programs, particularly those that focus on family engagement and addressing risk factors, can be effective in reducing delinquency and promoting positive outcomes for youth.
3. What are some alternatives to incarceration for juvenile offenders?
Alternatives to incarceration include community-based treatment programs, restorative justice initiatives, and diversion programs that provide counseling, education, and vocational training.
4. What is the role of schools in addressing juvenile crime?
Schools play a vital role in prevention by fostering positive school climates, implementing anti-bullying programs, and providing support services for students struggling with academic or behavioral challenges.
5. How can I get involved in supporting efforts to prevent juvenile crime?
Consider volunteering with local youth organizations, mentoring programs, or advocacy groups working to improve the lives of young people in your community.
Need Help?
For assistance or further information, please contact us at:
Phone: 0904826292
Email: research@gmail.com
Address: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam
Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to provide support and guidance.