Understanding the nuances of political science often requires diving deep into research. But what does an “Example Of Research Paper In Political Science” actually look like? This guide breaks down the process, providing tangible examples and insights to help you navigate the world of political science research.
Deconstructing the Research Paper
A political science research paper, much like in other academic fields, aims to analyze and interpret information, ultimately contributing new knowledge to the field. It’s not merely a summary of existing literature but a critical examination that pushes the boundaries of understanding.
Key Elements of a Political Science Research Paper
A typical research paper in this domain usually encompasses these key components:
- Introduction: This section sets the stage by introducing the research topic, its relevance, and the central research question(s) the paper seeks to answer.
- Literature Review: Here, you delve into existing academic work related to your topic. This isn’t just listing sources; it’s about critically evaluating them, identifying trends, and highlighting gaps your research aims to fill.
- Methodology: This section outlines your research approach. Are you conducting surveys, analyzing statistical data, or utilizing historical documents? Clearly explain the methods you’ve chosen and justify their suitability for your research question.
- Findings/Analysis: This is where you present the results of your research. This often involves presenting data through charts, graphs, or qualitative descriptions. More importantly, you analyze this data, drawing connections and explaining its significance in relation to your research question.
- Discussion: Here, you interpret your findings, discussing their implications within the broader context of your research topic. Do your findings support or challenge existing theories? What new questions arise from your work?
- Conclusion: Briefly summarize your findings and their implications. Reiterate the importance of your research and suggest avenues for future exploration.
- Bibliography/References: A complete and accurately formatted list of all sources cited in your paper.
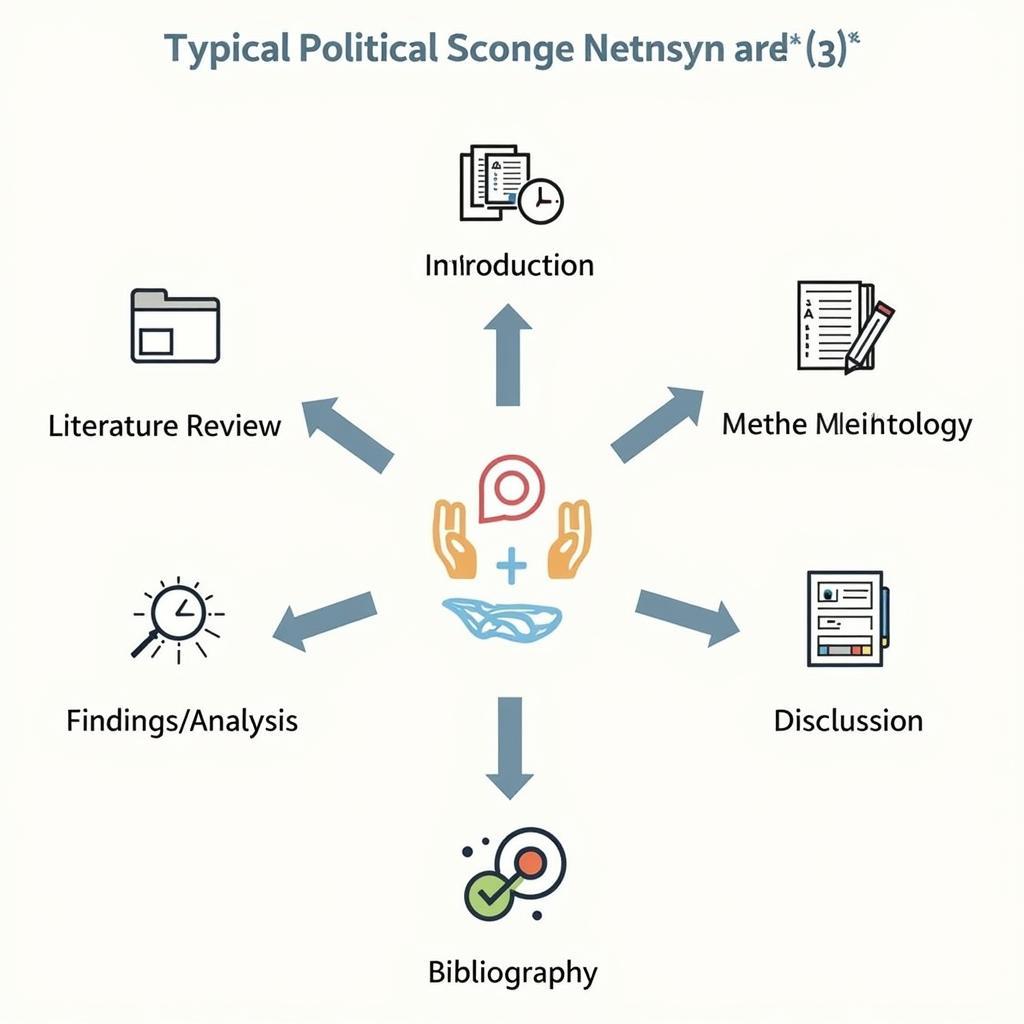 Example of a Political Science Research Paper Structure
Example of a Political Science Research Paper Structure
Choosing a Research Topic: Finding Your Niche
One of the first hurdles is selecting a compelling research topic. A few starting points could be:
- Current Events: Analyze a recent political event, policy change, or social movement.
- Comparative Politics: Compare and contrast political systems, institutions, or processes across different countries.
- Political Theory: Explore the works of renowned political philosophers, analyzing their ideas and relevance in contemporary society.
- Public Policy: Analyze a specific public policy, examining its effectiveness, unintended consequences, and potential for improvement.
- International Relations: Investigate global conflicts, diplomacy efforts, or the role of international organizations.
 Brainstorming Research Topics in Political Science
Brainstorming Research Topics in Political Science
Examples of Research Questions
The research question is the compass guiding your entire paper. Here are a few examples to illustrate:
- How has social media impacted political campaigns and elections in the 21st century?
- What are the main factors influencing voter turnout in newly democratized countries?
- To what extent does economic inequality contribute to political polarization?
- How effective are international sanctions in achieving foreign policy objectives?
- What are the ethical implications of artificial intelligence in political decision-making?
These are just starting points; your specific research question will become more refined as you delve deeper into your chosen topic.
Engaging with Existing Research: The Literature Review
A robust literature review is essential for positioning your research within the broader academic discourse. Utilize databases like JSTOR, Google Scholar, and your university library to access relevant scholarly articles, books, and government publications.
As you read, ask yourself:
- What are the key arguments and findings of each source?
- Are there any conflicting viewpoints or interpretations?
- What are the strengths and limitations of the existing research?
- Where are the gaps in knowledge that your research can address?
Remember, your literature review shouldn’t merely summarize sources; it should critically analyze them, identifying trends, contradictions, and areas requiring further investigation.
 Navigating the Literature Review Process
Navigating the Literature Review Process
From Theory to Practice: Methodology Matters
Your methodology section details how you plan to answer your research question. Common methods in political science include:
- Quantitative Research: Analyzing numerical data using statistical methods. This could involve surveys, polls, or analyzing existing datasets.
- Qualitative Research: Exploring in-depth, non-numerical data, such as interviews, focus groups, or historical documents, to understand complex social phenomena.
- Case Studies: In-depth analysis of a specific event, country, or policy to understand broader trends or patterns.
The method you choose depends entirely on your research question and the type of data you need to collect and analyze.
Crafting a Compelling Research Paper
Writing a strong research paper requires clarity, conciseness, and a logical flow of ideas.
- Structure: Follow the structure outlined earlier, ensuring each section smoothly transitions to the next.
- Clarity: Use precise language and avoid jargon. Define key terms and concepts to ensure your reader can follow your arguments.
- Evidence: Support all claims and assertions with evidence from your research. Properly cite all sources using footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography.
- Objectivity: Maintain a neutral tone and avoid personal opinions or biases. Present a balanced view of the evidence and acknowledge limitations.
- Proofreading: Thoroughly proofread your paper for any grammatical errors, typos, or inconsistencies in formatting.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can craft a compelling and well-researched paper that contributes meaningfully to the field of political science.
Need More Guidance? Explore Further!
For those seeking more in-depth information and resources, consider exploring the following links on our website:
- Political research questions
- Topics for research paper in English language
- Research topics in politics
Remember, writing a research paper is a journey of discovery. Embrace the process, be open to new ideas, and let your curiosity guide you.