A well-structured and detailed budget is crucial for any research proposal. It provides a clear overview of the financial resources required to conduct your research effectively. This example of a budget for a research proposal will guide you through the process, ensuring you present a comprehensive and persuasive financial plan to potential funders.
Understanding the Components of a Research Budget
Before diving into the specifics of an example budget, it’s essential to understand the key components:
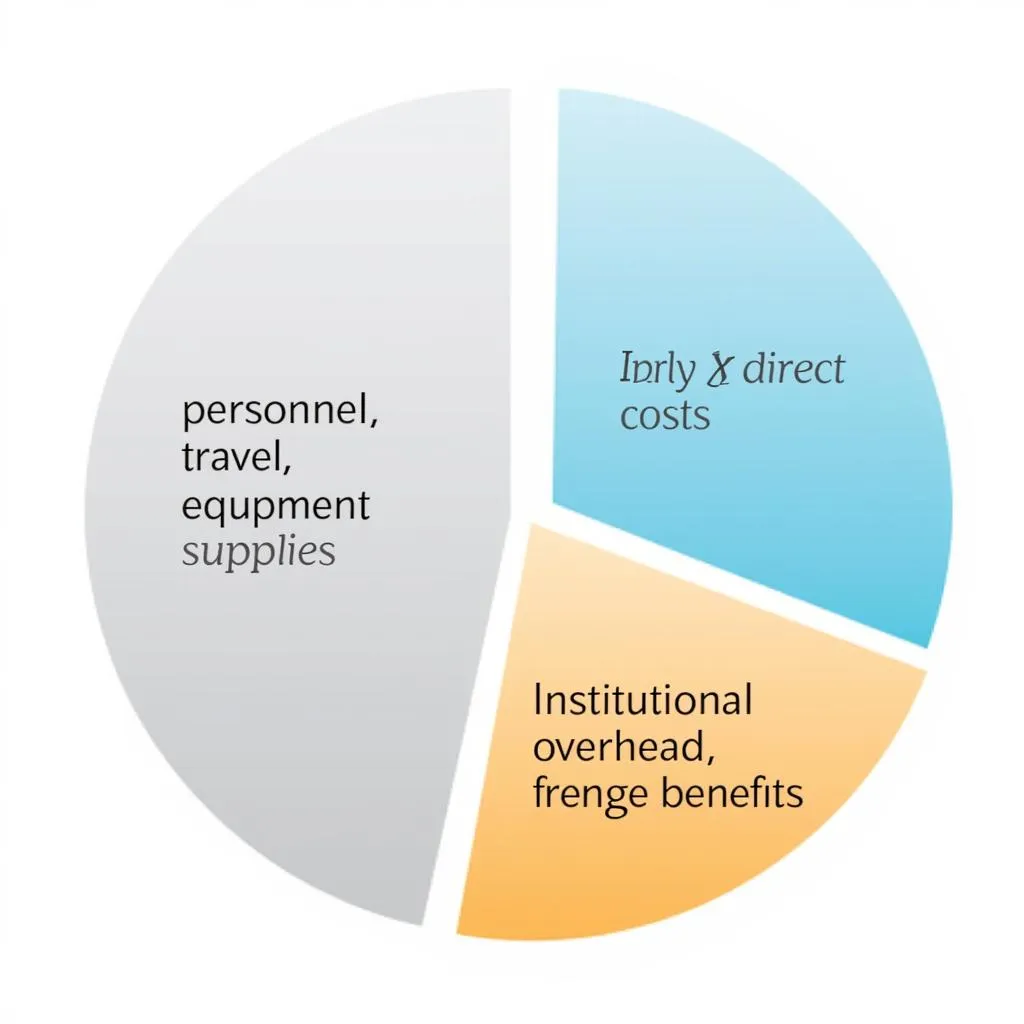
1. Direct Costs:
These are expenses directly related to the research activities, easily traceable to the project.
- Personnel: Salaries, wages, and benefits for researchers, assistants, and any personnel directly involved in the research.
- Travel: Costs associated with research-related travel, including transportation, accommodation, and per diem expenses.
- Equipment: Purchase or rental costs for any equipment necessary for your research, such as computers, software, lab instruments, etc.
- Supplies: Consumable materials used in the research, like chemicals, office supplies, and experimental materials.
- Other Direct Costs: This category includes expenses like publication fees, participant incentives, and data analysis costs.
2. Indirect Costs (F&A):
These are expenses that are not directly tied to specific research activities but are necessary for the overall operation of the research institution.
- Institutional Overhead: Covers expenses such as building maintenance, utilities, and administrative support.
- Fringe Benefits: Includes costs associated with employee benefits like health insurance and retirement contributions.
 Research Budget Breakdown
Research Budget Breakdown
Building Your Budget: A Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to create a comprehensive budget for your research proposal:
- Identify Personnel Needs: Determine the required personnel, their roles, estimated time commitment, and salary rates.
- Estimate Travel Expenses: Calculate travel costs based on the research location, duration, mode of transportation, and accommodation requirements.
- List Necessary Equipment and Supplies: Create a detailed list of all equipment and supplies, including specifications, quantity, and estimated costs.
- Factor in Other Direct Costs: Consider any additional direct expenses, such as publication fees, participant incentives, or data analysis services.
- Calculate Indirect Costs: Consult with your institution to determine the applicable indirect cost rate.
- Present a Clear and Organized Budget: Use tables or spreadsheets to present your budget clearly, separating direct and indirect costs, and providing detailed justifications for each item.
Example Budget Table:
| Category | Item | Description | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | Research Assistant | Data collection and analysis | 1 | $25/hour | $10,000 |
| Travel | Conference Attendance | Presentation of research findings | 2 people | $2,000/person | $4,000 |
| Equipment | Laptop | Data processing and analysis | 1 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Supplies | Software | Statistical analysis software | 1 | $500 | $500 |
| Other Direct Costs | Publication Fees | Open-access publication in a reputable journal | 1 | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| Total Direct Costs: | $18,000 | ||||
| Indirect Costs (F&A) @ 50% of Direct Costs | $9,000 | ||||
| Total Project Cost: | $27,000 |
 Budget Justification Example
Budget Justification Example
Tips for Creating a Persuasive Budget
- Be Realistic and Justify Your Expenses: Ensure your budget accurately reflects the actual costs involved in your research and provide clear justifications for each item.
- Consider Cost-Sharing Opportunities: Explore potential cost-sharing arrangements with collaborating institutions or organizations.
- Consult with Experienced Researchers: Seek guidance from experienced researchers in your field to validate your budget estimates.
- Proofread Carefully: Thoroughly review your budget for any errors or inconsistencies before submitting your proposal.
Conclusion
Crafting a comprehensive budget is essential for securing funding and successfully executing your research project. By understanding the key components, following a systematic approach, and presenting your budget clearly, you can increase your chances of obtaining the necessary resources. Remember, a well-prepared budget reflects your professionalism and strengthens the overall impact of your research proposal.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a direct and indirect cost?
Answer: Direct costs are directly tied to the research activities (salaries, travel), while indirect costs support the research institution as a whole (utilities, administration).
2. How do I determine the indirect cost rate for my institution?
Answer: Contact your institution’s research administration office; they will provide the applicable indirect cost rate.
3. What should I do if my research project requires unexpected expenses?
Answer: It’s crucial to communicate with your funding agency and seek approval for any significant budget modifications.
4. Can I use my research grant for personal expenses?
Answer: No, research funds are strictly for project-related expenses. Using them for personal purposes is unethical and can have serious consequences.
Need Assistance with Your Research Budget?
We understand that creating a detailed budget can be challenging. If you need any help or have further questions, don’t hesitate to contact us:
Phone: 0904826292
Email: research@gmail.com
Address: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam
Our team of experts is available 24/7 to provide you with personalized guidance and support throughout your research journey.