Epidemiological Research Is Research Done to understand the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations, and the application of this study to the control of health problems. In simpler terms, it’s detective work in the world of public health. Imagine yourself as a health detective, piecing together clues to understand why certain diseases occur, who’s at risk, and how to prevent them.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Disease: What Epidemiological Research Seeks to Answer
Epidemiological research tackles a wide range of health-related questions, such as:
- What causes this disease? Epidemiologists investigate risk factors, both genetic and environmental, that contribute to disease development.
- Who is affected by this disease? Understanding how a disease is distributed among different populations (age, gender, location) is crucial for effective interventions.
- How is this disease spreading? By studying disease patterns and transmission routes, epidemiologists can develop strategies to control outbreaks and prevent future ones.
- How effective are public health interventions? Epidemiological research helps evaluate the impact of programs aimed at improving public health and preventing disease.
The Tools of the Trade: Methods Used in Epidemiological Research
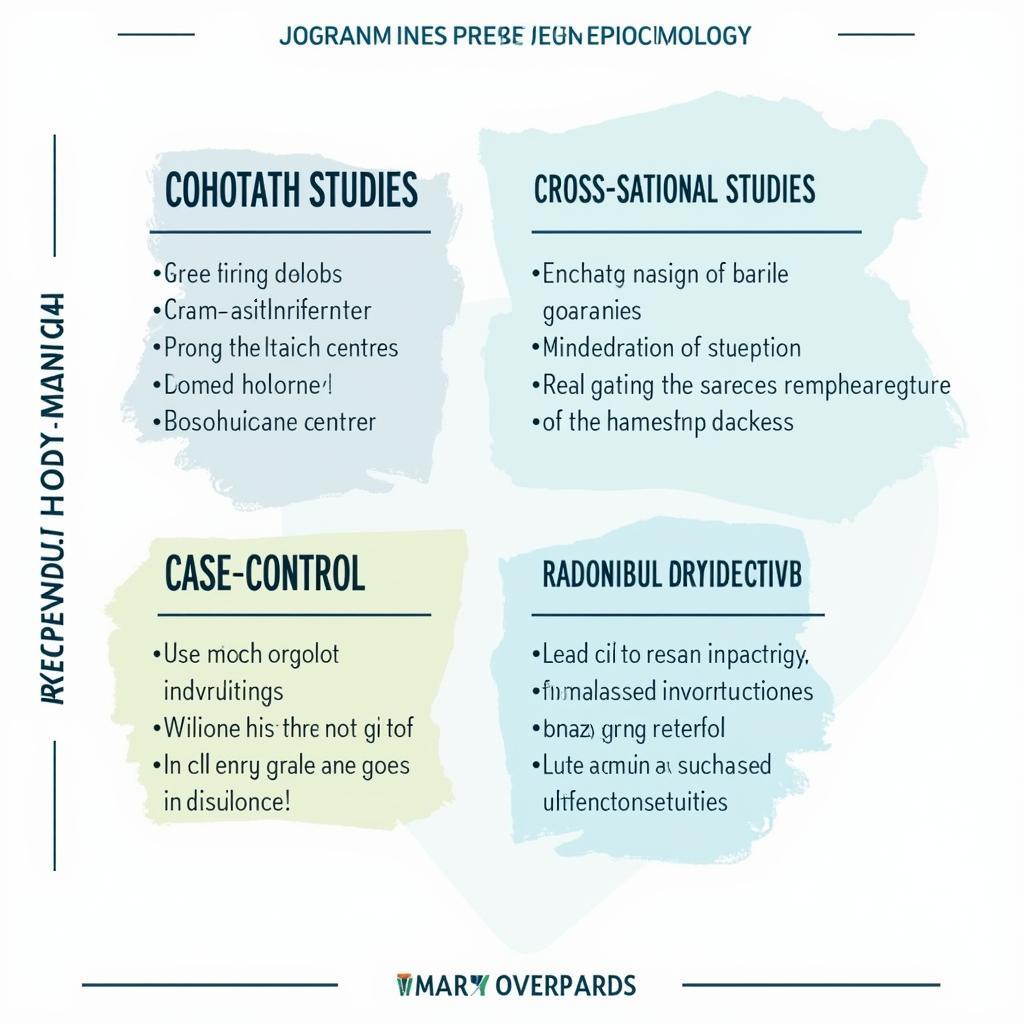 epidemiological research methods chart
epidemiological research methods chart
Epidemiologists use a variety of research methods, often combining approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of a health issue. Here are some common types:
- Cohort Studies: These studies follow a group of people over time to observe the development of disease in relation to different exposures or risk factors.
- Case-Control Studies: These studies compare individuals with a disease (cases) to those without the disease (controls) to identify potential exposures or risk factors associated with the illness.
- Cross-Sectional Studies: These studies look at a snapshot of a population’s health at a specific point in time, providing information about disease prevalence and potential associations.
- Randomized Controlled Trials: Considered the gold standard for research, these studies randomly assign participants to receive an intervention (like a new drug) or a placebo to determine the intervention’s effectiveness.
Epidemiological Research in Action: Real-World Impact
“Epidemiology isn’t just about numbers and statistics,” says Dr. Emily Carter, an epidemiologist at the Center for Disease Control. “It’s about using that information to make real-world changes that improve people’s lives.”
And indeed, epidemiological research has been the driving force behind some of the most significant public health achievements in history. Some notable examples include:
- Eradicating Smallpox: Through global vaccination efforts informed by epidemiological data, smallpox, a deadly disease, was eradicated in 1980.
- Reducing Smoking Rates: Epidemiological research established the link between smoking and lung cancer, leading to public health campaigns that have dramatically reduced smoking rates in many countries.
- Controlling HIV/AIDS: Epidemiological studies have been instrumental in understanding the transmission of HIV and developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Beyond Traditional Disease: The Expanding Scope of Epidemiology
While traditionally focused on infectious diseases, the field of epidemiology has expanded its reach to address a broader spectrum of health issues, including:
- Chronic Diseases: Epidemiologists study the risk factors and patterns of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes to develop effective prevention and management strategies.
- Mental Health: Epidemiological research is shedding light on the prevalence, causes, and consequences of mental health conditions, helping to reduce stigma and improve access to care.
- Environmental Health: This branch of epidemiology investigates how environmental factors, such as air pollution and water contamination, impact human health.
The Future of Epidemiological Research: Emerging Trends and Challenges
 data visualization tools used in epidemiology
data visualization tools used in epidemiology
The field of epidemiology is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the emergence of new health challenges. Some key trends include:
- Big Data and Analytics: The ability to analyze massive datasets is transforming epidemiological research, allowing for more precise identification of risk factors and disease patterns.
- Genomics and Personalized Medicine: Integrating genetic information into epidemiological studies is paving the way for personalized prevention and treatment strategies.
- Global Health Security: In an increasingly interconnected world, epidemiological research plays a crucial role in detecting and responding to emerging infectious diseases and global health threats.
Understanding the “Why” Behind the “What”: The Importance of Epidemiological Research
Epidemiological research is more than just collecting data; it’s about using that data to improve the health and well-being of individuals and populations. By understanding the “why” behind disease patterns and health outcomes, we can develop effective interventions, allocate resources efficiently, and ultimately create a healthier world.
Frequently Asked Questions about Epidemiological Research
1. What is the difference between epidemiology and other public health disciplines?
While epidemiology is a core component of public health, it differs from other disciplines like health education or health administration. Epidemiology specifically focuses on the investigation and analysis of disease patterns and health determinants.
2. What are some career paths in epidemiology?
Epidemiologists work in a variety of settings, including government agencies, research institutions, hospitals, and non-profit organizations. They may specialize in areas like infectious disease control, chronic disease prevention, or environmental health.
3. How can I get involved in epidemiological research?
Opportunities exist for individuals with various backgrounds to contribute to epidemiological research. You can volunteer at a local health department, shadow an epidemiologist, or participate in research studies.
4. Where can I find reliable information about epidemiological research and public health?
Reputable sources of information include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the World Health Organization (WHO), and academic journals like the American Journal of Epidemiology.
5. How does epidemiological research impact my daily life?
From the food we eat to the vaccines we receive, epidemiological research informs numerous aspects of our daily lives. By understanding disease patterns and risk factors, public health policies and recommendations are developed to protect our health and well-being.
Need help with epidemiological research?
Contact us at Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com, or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a dedicated customer support team available 24/7.