ECB research reveals a concerning trend: rising housing costs disproportionately impact low-income households. This issue, driven by various factors, including inflation, limited housing supply, and increased demand, has significant economic and social ramifications.
The Unequal Impact of Rising Housing Costs
 Impact of Rising Housing Costs on Low-Income Households
Impact of Rising Housing Costs on Low-Income Households
While rising housing costs affect everyone, low-income households are particularly vulnerable. With a larger portion of their income allocated to housing, even a slight increase in rent or mortgage payments can strain their budgets, leading to difficult choices between basic necessities like food, healthcare, and housing.
Factors Contributing to the Housing Crisis
Several factors contribute to the current housing crisis, exacerbating the challenges faced by low-income families:
- Inflation: Soaring inflation rates across the globe have resulted in increased costs for essential goods and services, including housing.
- Limited Housing Supply: A shortage of affordable housing options in many areas further intensifies competition and drives up prices.
- Increased Demand: Growing populations and urbanization trends contribute to a higher demand for housing, putting upward pressure on prices.
The Domino Effect: Consequences of Housing Instability
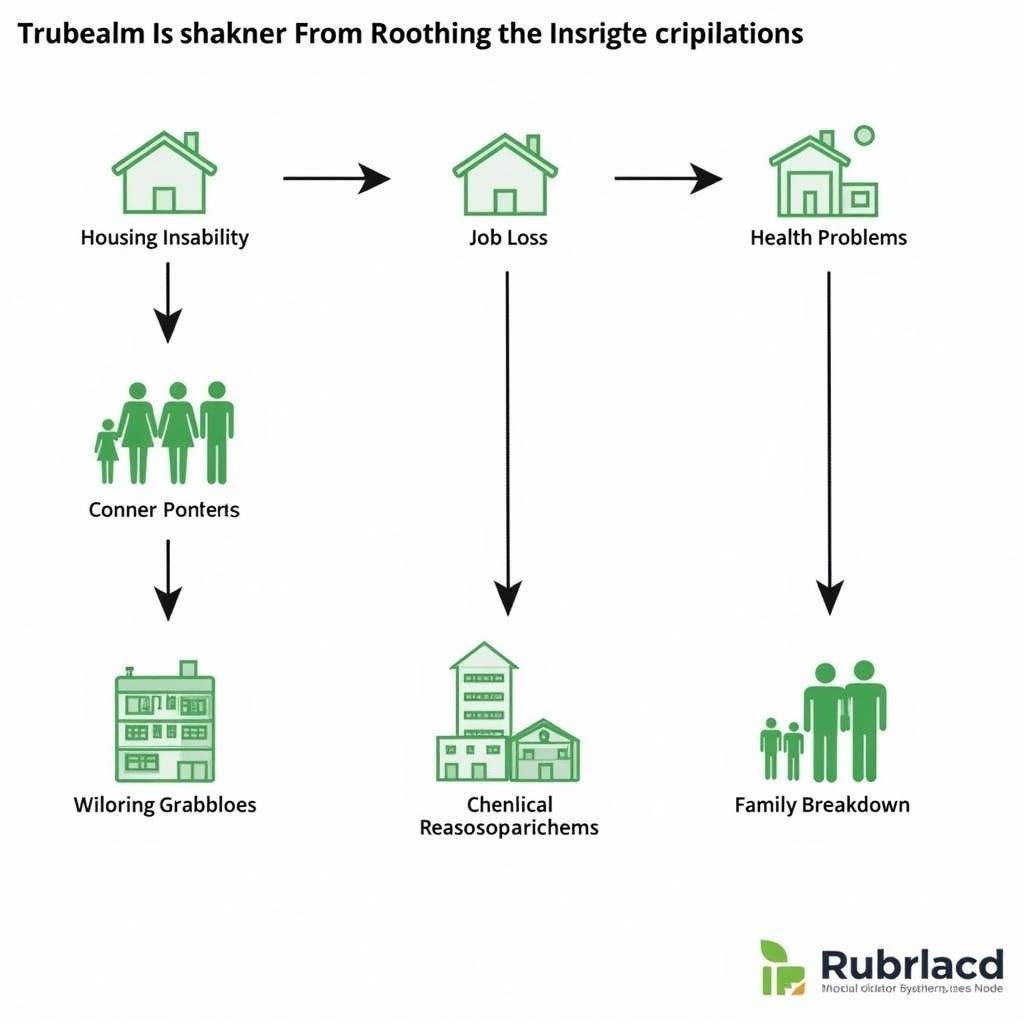 Consequences of Housing Instability on Families and Individuals
Consequences of Housing Instability on Families and Individuals
The consequences of housing instability extend far beyond financial strain, impacting various aspects of life for low-income households:
- Reduced Access to Opportunities: Housing instability can lead to frequent moves, disrupting education and employment opportunities for both adults and children.
- Health Implications: Living in overcrowded or substandard housing can negatively impact physical and mental health, leading to chronic illnesses and increased healthcare costs.
- Increased Poverty Risk: The financial burden of high housing costs can trap families in a cycle of poverty, making it challenging to escape and achieve financial stability.
Addressing the Crisis: Potential Solutions and Support Systems
Addressing this multifaceted issue requires a collaborative effort from policymakers, communities, and individuals:
- Government Initiatives: Policies promoting affordable housing development, rent control measures, and housing subsidies can help alleviate the burden on low-income households.
- Community Support: Local organizations and charities play a vital role in providing emergency housing assistance, financial counseling, and job training programs.
- Financial Literacy: Equipping individuals with financial management skills can empower them to make informed decisions, budget effectively, and navigate challenging economic situations.
Conclusion
The ECB research underscores the urgent need to address rising housing costs and their disproportionate impact on low-income households. Failure to do so will have far-reaching consequences, perpetuating poverty, inequality, and social instability. Collaborative efforts focusing on increasing affordable housing options, providing financial assistance, and empowering communities are crucial to mitigate this growing crisis and ensure everyone has access to safe, stable, and affordable housing.