Doe in estrus is a crucial phase in the wildlife reproductive cycle, a period of sexual receptivity that drives the continuation of deer populations. Understanding this delicate period is paramount for wildlife research, conservation efforts, and population management. This article delves into the fascinating world of doe estrus, exploring its biological intricacies and significance in wildlife research.
The Biology of Doe Estrus
Doe estrus, also known as the “heat” cycle, is a complex interplay of hormonal changes that signal a doe’s readiness to breed. This period is characterized by a surge in estrogen, triggering behavioral and physiological changes that attract bucks. The duration and frequency of estrus vary depending on the species, environmental factors, and individual deer.
Hormonal Orchestration of Estrus
The primary hormone driving estrus is estrogen. As estrogen levels rise, the doe displays specific behaviors indicating her receptivity. These behaviors include increased vocalizations, scent marking, and a general restlessness. Understanding these hormonal changes is crucial for researchers studying deer reproduction.  Hormonal Changes in Doe During Estrus
Hormonal Changes in Doe During Estrus
The Significance of Doe Estrus in Wildlife Research
The study of doe estrus provides valuable insights into deer population dynamics, reproductive success, and overall ecosystem health. Researchers utilize various methods to monitor estrus, including behavioral observations, hormone analysis, and tracking technologies. This data is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and managing deer populations sustainably.
Understanding Population Dynamics
By monitoring estrus cycles, researchers can estimate breeding success and predict population fluctuations. This information is crucial for managing deer populations to prevent overgrazing and maintain a healthy ecosystem balance. Factors such as food availability, environmental stress, and disease can influence estrus and, consequently, population size.
Conservation Implications
Doe estrus research is instrumental in conservation efforts. By understanding the factors that influence breeding success, conservationists can implement strategies to protect vulnerable populations and ensure their long-term survival. This research also aids in understanding the impact of habitat loss and fragmentation on deer reproduction.
How is Doe Estrus Studied in the Wild?
Researchers employ various techniques to study doe estrus in the wild, often requiring meticulous observation and advanced technological tools.
Observational Studies
Researchers spend countless hours in the field, observing deer behavior for signs of estrus. These observations include noting changes in vocalizations, scent marking frequency, and interactions with bucks. While labor-intensive, observational studies provide valuable insights into natural deer behavior during estrus.
Hormone Analysis
Collecting and analyzing fecal samples allows researchers to measure hormone levels, providing a precise indication of estrus. This method offers a non-invasive way to monitor reproductive status and track hormonal changes over time.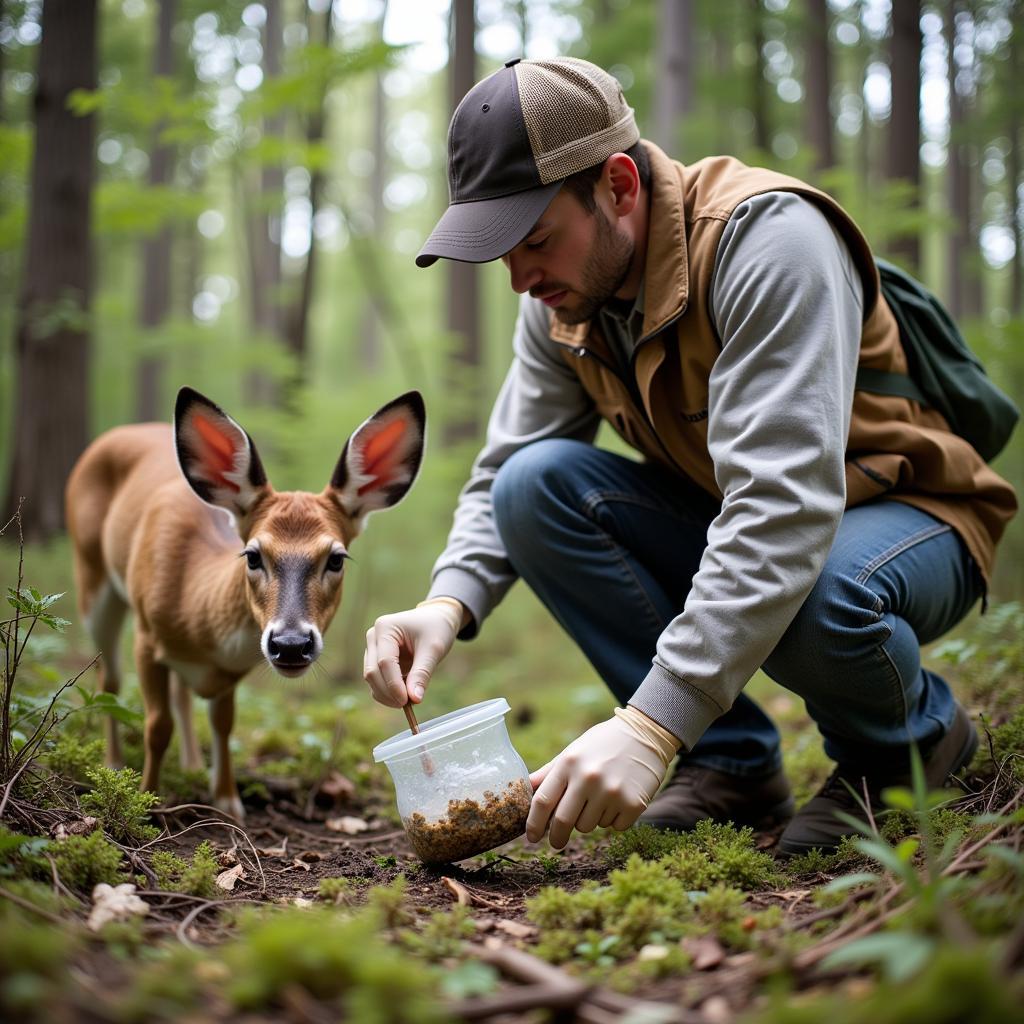  Wildlife Researcher Collecting Fecal Samples
Wildlife Researcher Collecting Fecal Samples
Conclusion
Doe in estrus is a pivotal period in the deer reproductive cycle, holding significant implications for wildlife research and conservation. Understanding the intricacies of estrus provides crucial insights into deer population dynamics, reproductive success, and the overall health of deer populations. By continuing research in this area, we can develop more effective strategies for managing and conserving these magnificent animals.
FAQ
- How long does doe estrus typically last?
- What are the most common signs of doe estrus?
- How does estrus vary between different deer species?
- How do environmental factors influence doe estrus?
- What are the challenges researchers face when studying estrus in the wild?
- How can the study of doe estrus help with conservation efforts?
- What are the ethical considerations involved in researching doe estrus?
Need assistance with wildlife research or have questions about doe estrus? Contact us at Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com Or visit our office at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team available to help.