The pursuit of knowledge drives both science and pseudoscience. However, the methods employed to acquire and validate that knowledge differ dramatically. Understanding how research functions within these two distinct domains is crucial to discerning fact from fiction. This article contrasts the role of research in science and pseudoscience, highlighting the critical differences in their approaches.
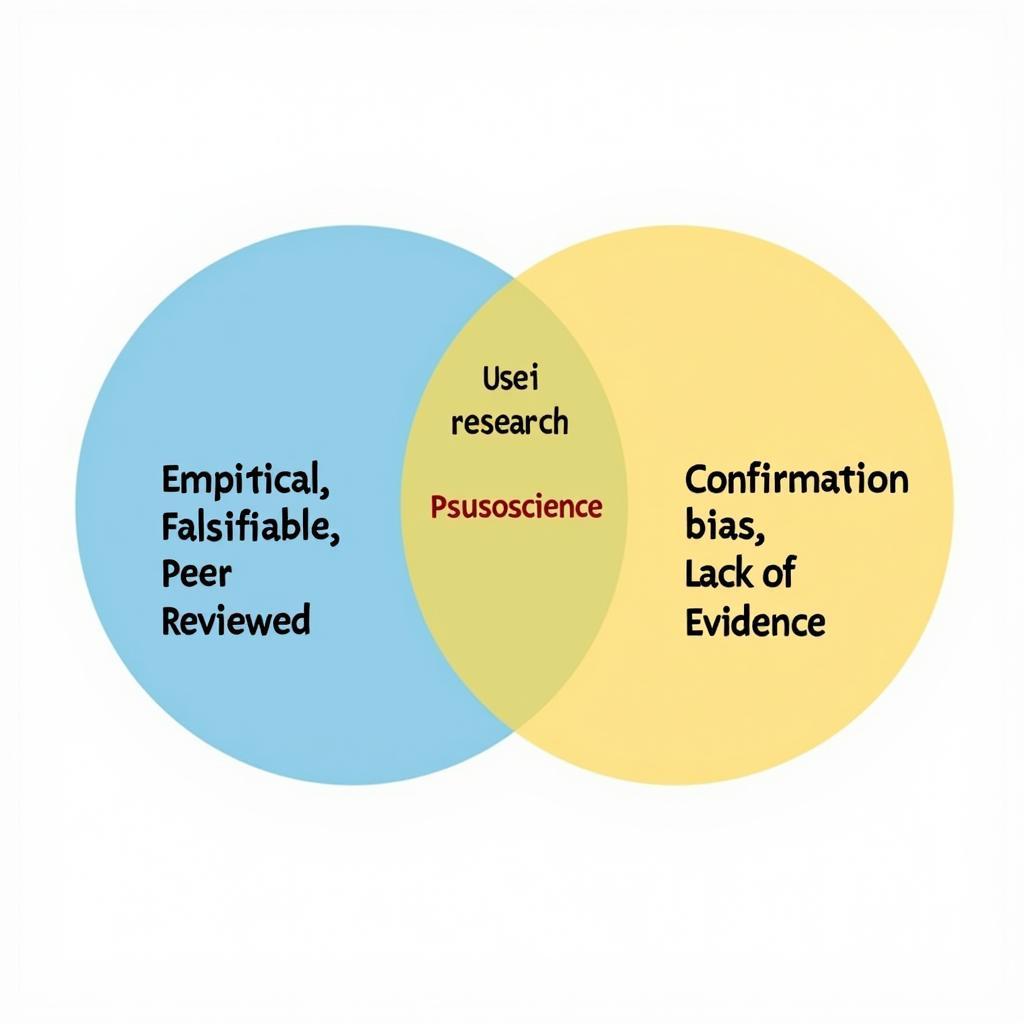 Science vs. Pseudoscience Research Comparison
Science vs. Pseudoscience Research Comparison
The Scientific Method: A Foundation of Rigor
Scientific research is grounded in the scientific method, a systematic process of observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and analysis. This rigorous approach prioritizes empirical evidence, meaning data collected through direct observation or experimentation. A core principle of science is falsifiability – the idea that a scientific theory must be testable and potentially proven wrong.
ast research can even be used to address certain scientific questions.
Hypothesis Testing and Peer Review
Scientists formulate hypotheses, testable predictions based on their observations. These hypotheses are then subjected to rigorous testing through controlled experiments. Results are meticulously documented and analyzed. Crucially, scientific research undergoes peer review, where other experts in the field scrutinize the methodology, data, and conclusions before publication. This process ensures quality control and reduces bias.
Pseudoscience: A Veneer of Legitimacy
Pseudoscience, literally meaning “false science,” often mimics the appearance of scientific inquiry but lacks the substance. While pseudoscientific claims may appear to be based on research, they frequently rely on anecdotal evidence, personal testimonies, and unsubstantiated assertions.
Confirmation Bias and Lack of Falsifiability
One hallmark of pseudoscience is confirmation bias, the tendency to seek out and interpret information that confirms pre-existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence. Pseudoscientific theories are often constructed in a way that makes them unfalsifiable – they cannot be disproven through testing. This makes them immune to scientific scrutiny.
Key Differences in Research Approaches
The table below summarizes the key distinctions between research in science and pseudoscience:
| Feature | Science | Pseudoscience |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Systematic, rigorous, controlled experiments | Anecdotal evidence, lack of control, biased methodologies |
| Evidence | Empirical, measurable, verifiable | Subjective, anecdotal, often unverifiable |
| Falsifiability | Testable and potentially disprovable | Unfalsifiable or resistant to disproof |
| Peer Review | Subjected to rigorous peer review by experts | Often lacks peer review or relies on biased reviews |
| Replicability | Results can be replicated by independent researchers | Results are often difficult or impossible to replicate |
How Can We Identify Pseudoscience?
Identifying pseudoscience can be challenging. Look for red flags such as reliance on anecdotal evidence, extraordinary claims without extraordinary evidence, and resistance to scientific scrutiny. A healthy dose of skepticism and critical thinking are essential tools in navigating the world of information.
Conclusion: Discerning Truth from Deception
Contrasting the role of research in science and pseudoscience reveals fundamental differences in their approaches to knowledge acquisition. While science embraces rigorous testing, peer review, and falsifiability, pseudoscience often relies on flawed methodologies and confirmation bias. Understanding these differences is crucial for discerning truth from deception and making informed decisions based on sound evidence. By recognizing the hallmarks of true scientific research, we can better evaluate the validity of claims and navigate the complex landscape of information in our world.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between science and pseudoscience? The main difference lies in their approach to evidence and testing. Science relies on empirical evidence and testable hypotheses, while pseudoscience often relies on anecdotal evidence and unfalsifiable claims.
- Why is falsifiability important in science? Falsifiability allows scientists to test and refine their theories. If a theory cannot be disproven, it cannot be considered truly scientific.
- Can pseudoscience be harmful? Yes, pseudoscience can be harmful. It can lead to misinformation, misdiagnosis, and rejection of effective treatments.
- How can I tell if something is pseudoscience? Look for red flags like reliance on anecdotal evidence, extraordinary claims without extraordinary evidence, and resistance to scientific scrutiny.
- Is ast research considered pseudoscience? While some aspects of Paranormal Research might fall under pseudoscience, ast research can be conducted with scientific rigor, depending on the methods employed.
- Are all alternative therapies pseudoscience? Not all alternative therapies are pseudoscience. Some have been scientifically studied and shown to be effective, while others lack scientific evidence.
- How can I become more critical of information I encounter? Practice skepticism, evaluate the source of information, look for evidence-based claims, and be aware of your own biases.
For further assistance, please contact us: Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.