Coding Techniques In Qualitative Research are essential for organizing and analyzing large amounts of textual data. They help researchers identify patterns, themes, and insights from interviews, observations, and other qualitative data sources. This article will delve into various coding techniques, their applications, and best practices to enhance your qualitative research.
For researchers diving into the world of qualitative data, understanding effective coding methods is crucial. See our resources on open ended questions in research. These techniques provide a systematic way to dissect complex information, ultimately leading to a more nuanced understanding of the research topic.
Different Approaches to Coding in Qualitative Research
Several coding techniques exist, each with its own strengths and applications. Choosing the right one depends on your research question and the nature of your data.
In Vivo Coding
In vivo coding involves using the participants’ own words as codes. This method helps preserve the authenticity of the data and provides direct insights into the participants’ perspectives.
Descriptive Coding
Descriptive coding assigns labels to data segments that summarize their content. It’s a basic but effective technique for organizing and categorizing data in the initial stages of analysis.
Process Coding
Process coding captures actions and sequences of events within the data. This is particularly useful when studying dynamic phenomena or change over time.
Pattern Coding
As you analyze data, patterns and recurring themes start to emerge. Pattern coding involves identifying and grouping these recurring themes to develop a higher-level understanding of the data.
Implementing Coding Techniques Effectively
Effective coding requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement coding techniques in your research:
-
Familiarize yourself with the data: Thoroughly read and understand the entire dataset before you start coding.
-
Develop a codebook: Create a list of codes and their definitions. This will ensure consistency and clarity throughout the coding process.
-
Pilot test the codebook: Apply the codes to a small portion of the data to refine the codebook and identify any potential issues.
-
Code the data systematically: Apply the codes consistently to all relevant data segments.
-
Review and refine codes: Regularly review and refine the codes as you progress through the data analysis.
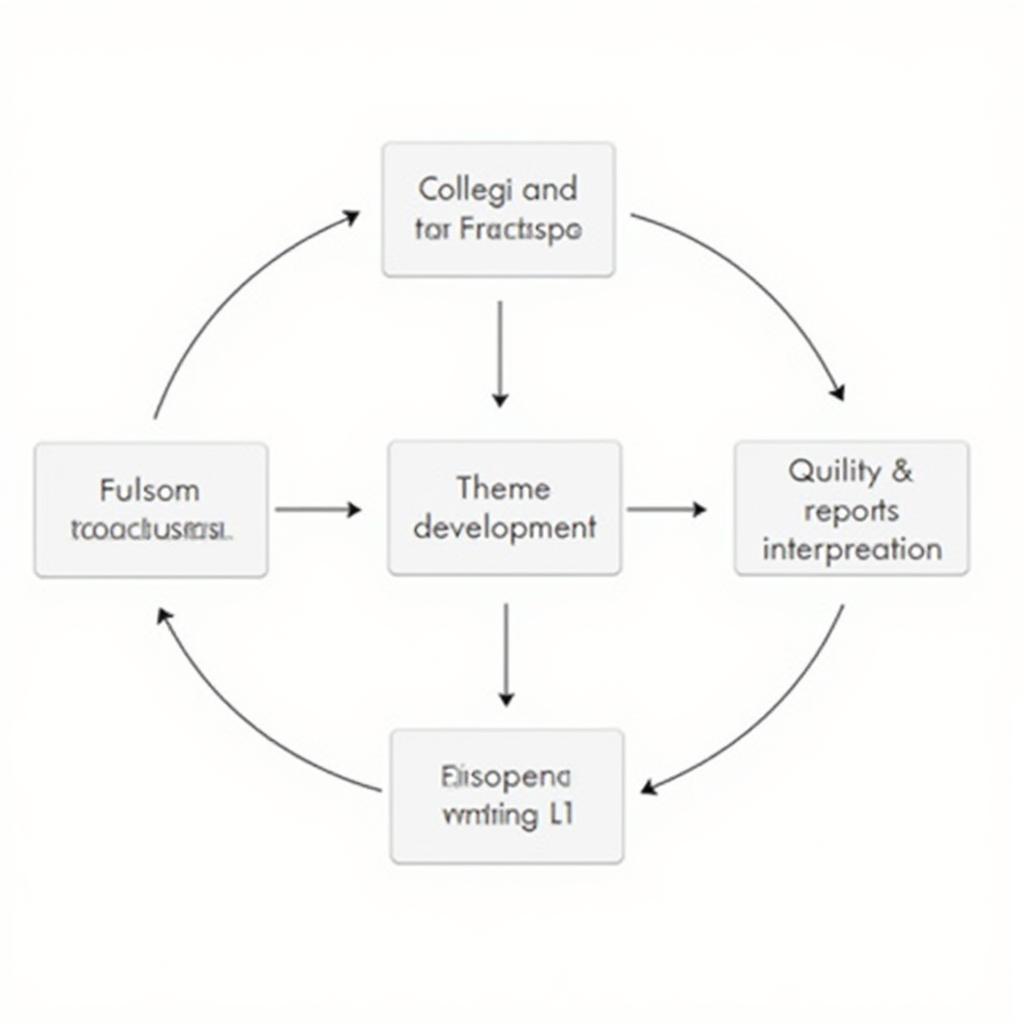 Qualitative Data Analysis Process Flowchart
Qualitative Data Analysis Process Flowchart
Benefits of Using Coding Techniques
Coding techniques offer numerous benefits for qualitative researchers:
-
Organize and manage large datasets: Coding helps break down complex data into manageable units, making it easier to analyze and interpret.
-
Identify patterns and themes: Coding facilitates the identification of recurring patterns and themes within the data, providing insights into the underlying phenomena being studied.
-
Enhance the rigor and transparency of the research: Systematic coding enhances the rigor and transparency of the research process, making the findings more credible and trustworthy. For a deeper dive into research design, check out our qualitative research textbook.
“Coding is like detective work,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned qualitative researcher at the Institute of Social Sciences. “It helps you uncover hidden clues within the data and piece them together to form a coherent story.”
Common Challenges and Solutions in Coding
While coding can be a powerful tool, it also presents some challenges:
-
Inter-coder reliability: Ensuring consistency in coding between multiple researchers can be difficult. Using a well-defined codebook and conducting regular inter-coder reliability checks can mitigate this issue.
-
Code drift: Codes can evolve and change over time, leading to inconsistencies in the analysis. Regularly reviewing and refining the codebook can help prevent code drift. Our guide on qualitative research a guide to design and implementation can be helpful here.
“One common pitfall is creating too many codes,” warns Professor Michael Davis, an expert in qualitative research methodology. “It’s important to strike a balance between granularity and manageability.”
 Example of a Codebook in Qualitative Research
Example of a Codebook in Qualitative Research
Conclusion
Coding techniques are indispensable tools in qualitative research, enabling researchers to analyze complex data and uncover valuable insights. By mastering these techniques, researchers can enhance the rigor, transparency, and impact of their qualitative studies. Effectively implementing coding techniques in qualitative research unlocks the rich narratives within your data, leading to a deeper understanding of your research area. You can further explore grounded theory in our resource on the discovery of grounded theory strategies for qualitative research.
FAQ
-
What is the purpose of coding in qualitative research?
-
What are the different types of coding techniques?
-
How do I create a codebook?
-
What is inter-coder reliability and why is it important?
-
How can I address the challenge of code drift?
-
What are some common software tools used for qualitative data analysis?
-
What are the advantages of using coding techniques in qualitative research?
Common Coding Scenarios
-
Analyzing interview transcripts: Coding can be used to identify key themes and patterns in interview data.
-
Studying social media posts: Coding can help researchers understand online conversations and identify emerging trends.
-
Analyzing observational data: Coding can be used to categorize and interpret behaviors observed in fieldwork.
Further Reading: Explore Creswell’s Research Design
For a deeper understanding of research design, you might consider our resource on creswell research design pdf.
Need Help with Your Research?
Contact us for support: Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit our office at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We offer 24/7 customer support.