Action research and traditional research represent two distinct approaches to understanding and solving problems. While both aim to generate knowledge, their methodologies, purposes, and applications differ significantly. This article delves into the core distinctions between these two research paradigms, exploring their strengths and weaknesses to help you choose the best approach for your needs.
Understanding Traditional Research
Traditional research, often referred to as basic or fundamental research, focuses on expanding the existing body of knowledge. It operates within a structured framework, emphasizing objectivity, rigorous data collection, and statistical analysis. Researchers typically formulate a hypothesis, design experiments to test it, and analyze the results to draw conclusions. The findings are then disseminated through academic publications, contributing to the broader scientific understanding of a particular phenomenon. Traditional research often seeks to establish generalizable principles that apply across various contexts. It prioritizes control over variables and minimizes researcher bias to ensure the validity and reliability of the results.
After this introduction to traditional research, let’s delve into what makes action research unique. traditional research vs action research will further clarify the differences.
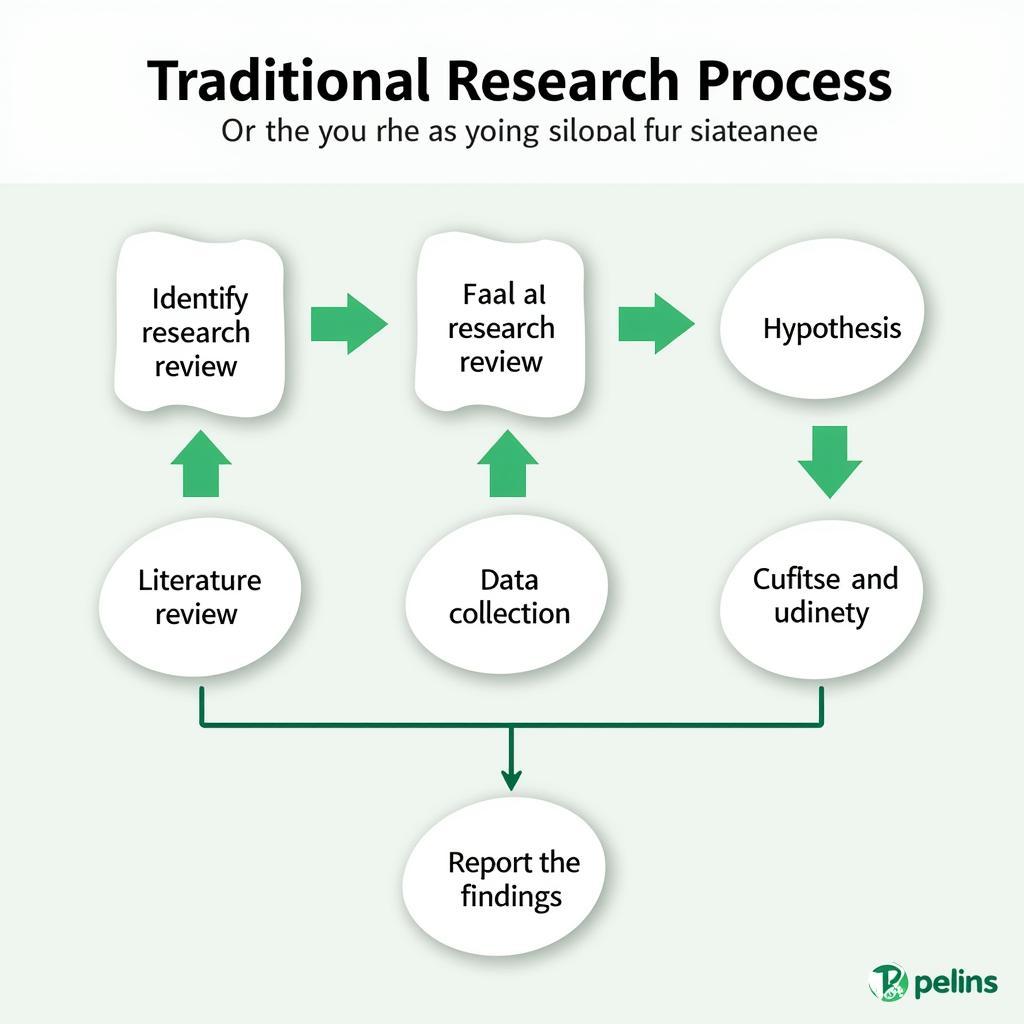 Traditional Research Process Diagram
Traditional Research Process Diagram
Exploring Action Research
Action research, in contrast, is a more participatory and iterative process. It aims to address specific practical problems within a particular context. Researchers actively collaborate with stakeholders throughout the research process, from identifying the problem to implementing and evaluating solutions. This collaborative approach ensures that the research findings are directly relevant and applicable to the real-world situation. Action research emphasizes continuous reflection and learning, allowing researchers to adapt their strategies based on the ongoing feedback and data collected. It’s a cyclical process involving planning, acting, observing, and reflecting, repeated until the desired outcome is achieved.
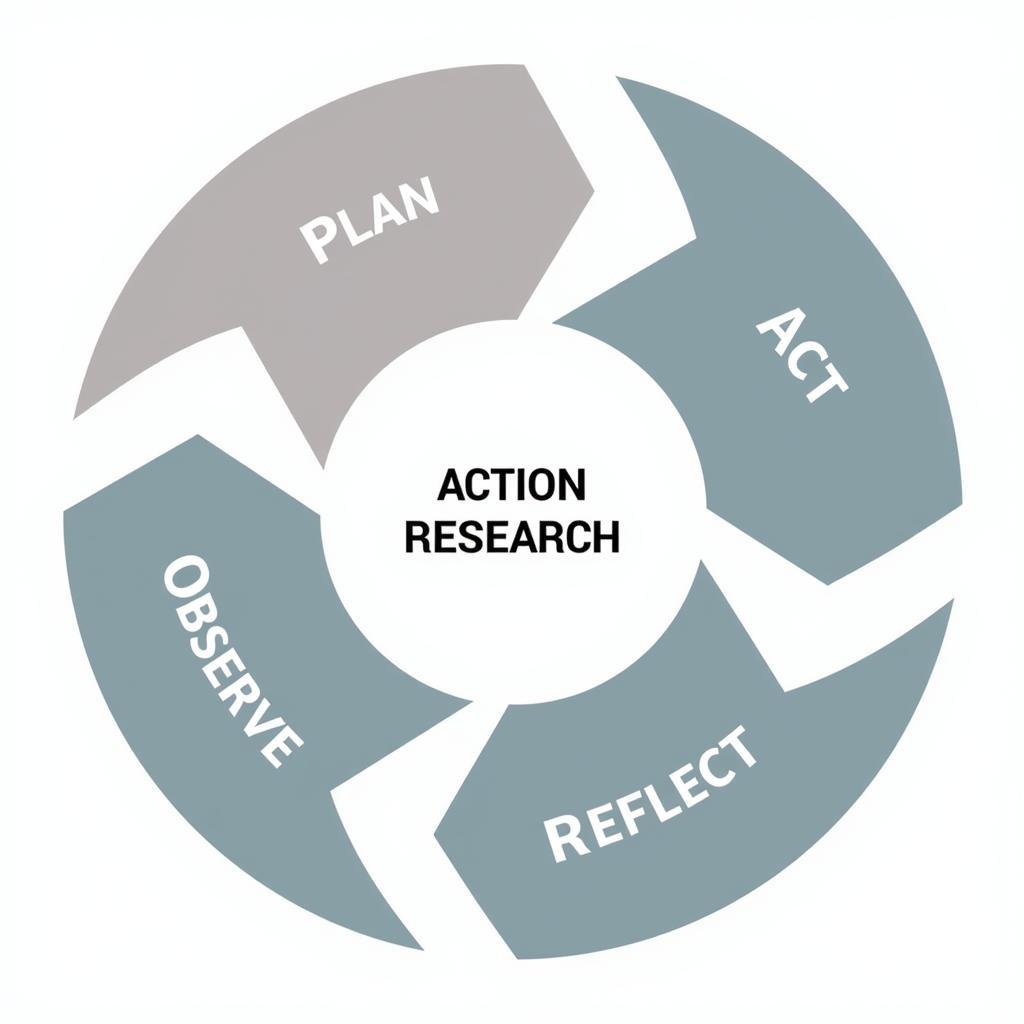 Action Research Cycle Diagram
Action Research Cycle Diagram
For a deeper understanding of how action research can be applied in organizational development, explore this resource on the action research model in od.
Key Differences between Action Research vs Traditional Research
One of the key distinctions between the two methodologies lies in the researcher’s role. In traditional research, the researcher remains detached and objective, aiming to minimize their influence on the research process. In action research, the researcher becomes an active participant, working collaboratively with stakeholders to address the problem at hand. This involvement introduces a level of subjectivity but also enhances the relevance and applicability of the findings.
To better understand the nuances of researcher involvement and reflection, researchers reflexivity provides valuable insights.
Which Approach is Right for You?
Choosing between action research and traditional research depends on your research goals and the specific context. Traditional research is suitable when seeking generalizable knowledge and testing theoretical hypotheses. Action research is more appropriate when addressing specific practical problems within a particular context and requiring stakeholder involvement.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Action Research Vs Traditional Research is crucial for selecting the most effective methodology for your research endeavors. By considering the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, you can tailor your research design to achieve your specific goals and contribute meaningful insights to your field. While traditional research seeks to expand general knowledge, action research focuses on solving practical problems within specific contexts.
FAQ
- What is the primary goal of traditional research? To expand the general body of knowledge.
- What is the primary goal of action research? To solve specific problems within a context.
- Is action research collaborative? Yes, it involves stakeholders throughout the process.
- Is traditional research objective? Yes, it aims for objectivity and minimizes researcher bias.
- Which research type uses a cyclical process? Action research.
- What is the role of the researcher in traditional research? Detached observer.
- What is the role of the researcher in action research? Active participant.
Considering escalent research and other specialized fields can further expand your understanding of various research approaches. Examining field of research examples can offer practical applications of these research methodologies.
Need help with your research project? Contact us! Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you.