Research and evidence-based practice (EBP) are closely related but distinct concepts. Understanding the difference between research and evidence-based practice is crucial for anyone working in a field that values data-driven decision-making. In the first 50 words of this article, we’ll lay the groundwork for exploring this vital distinction.
What is Research?
Research is a systematic investigation designed to discover new knowledge or validate existing theories. It involves formulating a research question, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Research can take many forms, from basic science research in a laboratory setting to large-scale clinical trials. The goal is to generate new understanding and contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field. Think of research as the process of creating the “evidence” that will later be used in evidence-based practice. Different types of research methodologies exist, including qualitative research which explores experiences and perspectives, and quantitative research which analyzes numerical data. what is original research provides a deeper understanding of the different research categories.
What is Evidence-Based Practice?
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the conscientious and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. It integrates clinical expertise, patient values, and the best available research evidence to inform clinical decision-making. EBP isn’t just about using research findings; it’s about applying those findings in a way that’s tailored to the specific needs and preferences of each patient. EBP acknowledges that while research provides valuable insights, the individual circumstances of each case must also be considered. For instance, while research in speech language pathology may suggest a specific intervention, a speech-language pathologist must tailor that intervention to the individual needs of their client.
How Research Informs EBP
Research plays a critical role in EBP by providing the evidence base for clinical decisions. High-quality research studies, such as randomized controlled trials, offer strong evidence about the effectiveness of different interventions. Systematic reviews, which analyze and synthesize the results of multiple studies, are particularly valuable for EBP. However, it’s important to note that not all research is created equal. EBP emphasizes the use of the best available evidence, which means critically evaluating the quality and relevance of research studies. introduction to research and medical literature for health professionals can offer a good starting point in understanding medical literature.
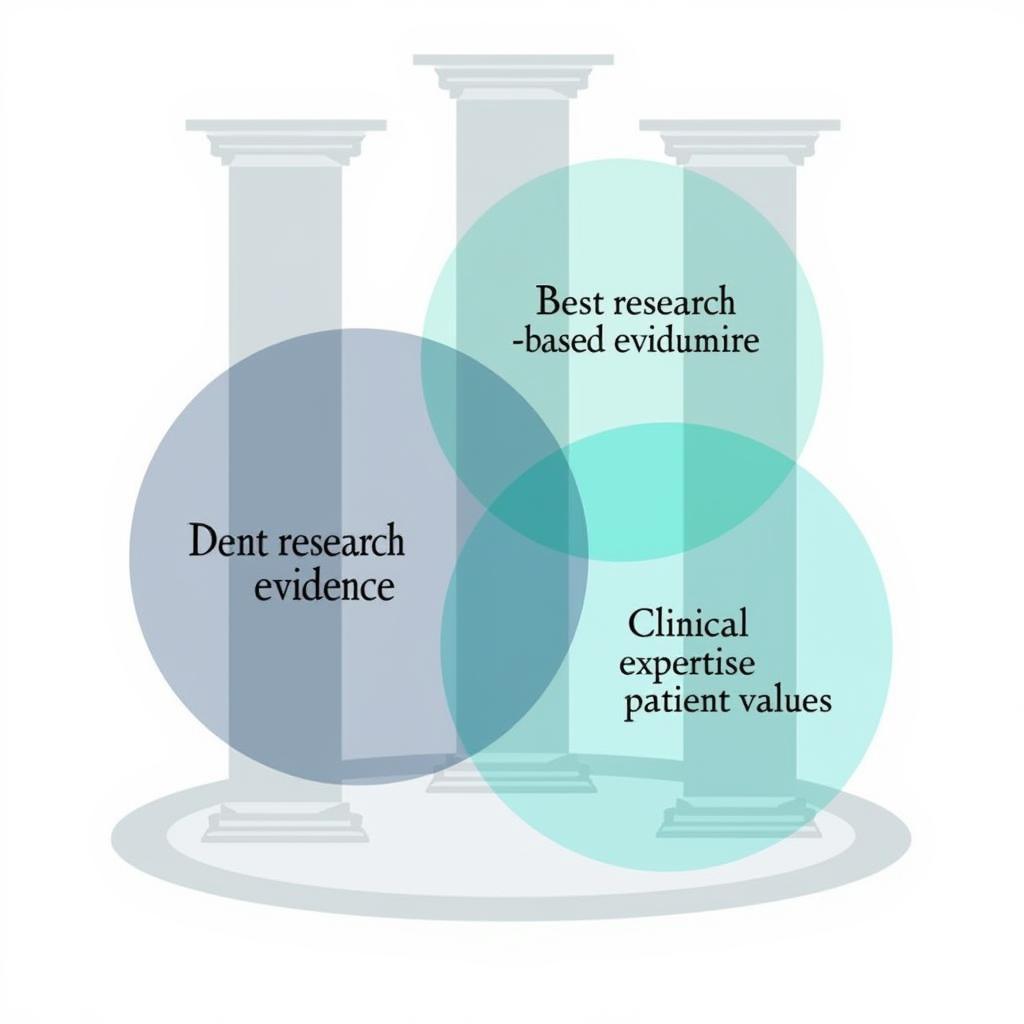 Evidence-Based Practice Model
Evidence-Based Practice Model
Key Differences Between Research and Evidence-Based Practice
While research generates new knowledge, EBP applies that knowledge to real-world clinical settings. Research is focused on discovering new information, while EBP is focused on improving patient outcomes. Research can be theoretical, while EBP is always practical. Understanding this difference between research and evidence-based practice is essential for translating research findings into tangible benefits for patients. clinical problems in nursing for research highlights how research questions originate from practical challenges.
What are some examples of evidence-based practice?
Examples of EBP include using evidence-based guidelines for managing chronic conditions, implementing interventions that have been shown to be effective in research studies, and using shared decision-making to involve patients in their care.
Why is the difference between research and EBP important?
Understanding the difference between research and EBP is crucial for ensuring that clinical practice is informed by the best available evidence. It allows healthcare professionals to critically evaluate research and apply it in a way that benefits patients. example of a results section of a research paper provides insights into how research findings are presented.
Conclusion
The difference between research and evidence-based practice lies in their purpose and application. Research generates new knowledge, while EBP uses that knowledge to improve patient care. Both are essential for advancing healthcare and ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment. By understanding this critical difference between research and evidence-based practice, we can bridge the gap between research and practice, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
FAQ
- What are the steps involved in evidence-based practice?
- How can I find high-quality research evidence?
- What is the role of patient values in EBP?
- How can I integrate research findings into my clinical practice?
- What are some common barriers to implementing EBP?
- What are the benefits of using evidence-based practice?
- How does research contribute to EBP?
Need Help?
Contact us 24/7 for support. Phone: 0904826292, Email: [email protected]. Or visit our office at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.