The 7 Levels Of Evidence In Nursing Research provide a hierarchical framework for evaluating the strength and reliability of research findings. This system helps nurses determine the best available evidence to inform their clinical practice and improve patient care. Understanding these levels is crucial for evidence-based nursing.
What are the 7 Levels of Evidence?
The 7 levels of evidence are typically arranged in a pyramid, with Level I at the top representing the highest quality evidence and Level VII at the bottom representing the lowest. This structure reflects the decreasing rigor and potential for bias as you move down the levels. Let’s break down each level:
-
Level I: Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: These combine the results of multiple high-quality studies, providing a comprehensive overview of the current evidence. They offer the strongest evidence for interventions and best practices.
-
Level II: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs): RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. They randomly assign participants to either an intervention group or a control group, minimizing bias and allowing for cause-and-effect relationships to be established.
-
Level III: Controlled Trials Without Randomization: These trials compare interventions, but participants aren’t randomly assigned to groups, increasing the risk of bias.
-
Level IV: Cohort and Case-Control Studies: These observational studies follow groups of people over time (cohort studies) or compare groups with and without a specific outcome (case-control studies). They can identify associations but not definitive cause-and-effect relationships.
-
Level V: Systematic Reviews of Descriptive and Qualitative Studies: These reviews synthesize findings from studies that explore phenomena and experiences, providing valuable insights into patient perspectives and complex healthcare issues.
-
Level VI: Single Descriptive or Qualitative Study: This level includes individual studies that describe characteristics or explore experiences, offering rich details but limited generalizability.
-
Level VII: Opinion of Authorities and/or Reports of Expert Committees: This level represents the lowest level of evidence and relies on expert opinion rather than empirical research. While valuable, it’s important to consider potential biases.
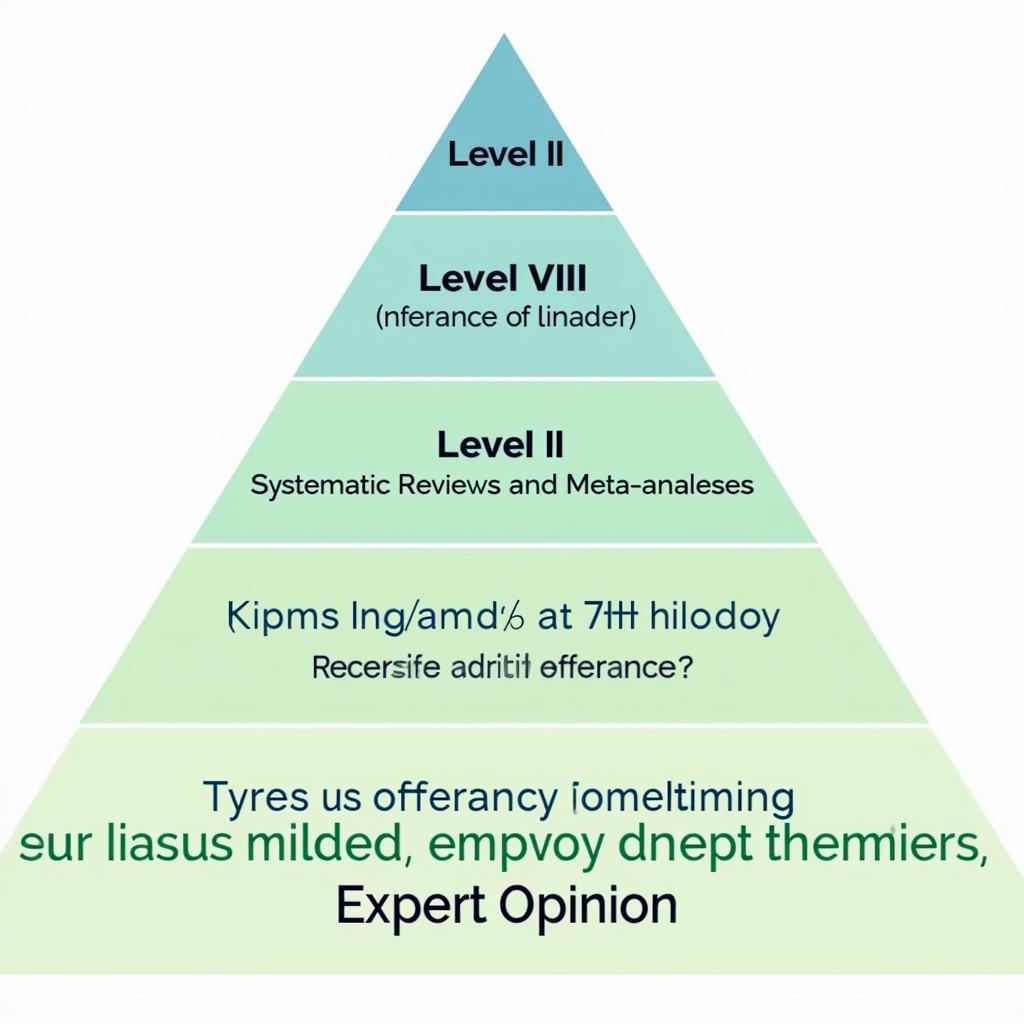 7 Levels of Evidence Pyramid in Nursing Research
7 Levels of Evidence Pyramid in Nursing Research
How are the 7 Levels of Evidence Used in Nursing?
Understanding these levels empowers nurses to critically evaluate research and make informed decisions. For example, when considering a new treatment approach, a nurse might prioritize evidence from a Level I systematic review or a Level II RCT over a Level VII expert opinion. This evidence-based approach ensures that patient care is grounded in the strongest available research. Interested in learning more about the importance of research in nursing? Visit our page on research importance in nursing.
Why is Understanding the Levels of Evidence Important?
Understanding the levels of evidence is fundamental to evidence-based practice, which is crucial for providing high-quality patient care. It enables nurses to discern the strength and reliability of various research designs, ensuring they base their decisions on the best available evidence.
How Can I Find High-Quality Nursing Research?
Numerous resources can help nurses locate high-quality research, such as databases like PubMed and CINAHL. Additionally, professional organizations like the Southern Nursing Research Society provide valuable resources and networking opportunities. Learn more about the southern nursing research society. You might also be interested in exploring specific nursing research topics for pediatrics.
Expert Insights on the 7 Levels of Evidence
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading nursing researcher, emphasizes the importance of using high-quality evidence: “Relying on the strongest available evidence is not just best practice; it’s essential for providing safe and effective patient care.” Another expert, Professor John Davis, adds, “Understanding the 7 levels of evidence empowers nurses to be critical consumers of research and contribute to the advancement of the profession.” Seeking funding for nursing research is crucial for advancing the field. For those interested in STEM education research, there are specific journal for stem education research available.
Conclusion
The 7 levels of evidence in nursing research provide a crucial framework for evaluating research and making informed decisions about patient care. By understanding these levels, nurses can effectively apply research findings to improve practice and contribute to the advancement of the nursing profession. This knowledge is key to ensuring that patient care is based on the most robust and reliable evidence available.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.