Hermann Ebbinghaus Research Would Most Likely Predict That forgetting occurs rapidly at first and then levels off over time. His groundbreaking work on memory and the “forgetting curve” has had a profound impact on how we understand learning and retention. This article will delve into the specifics of Ebbinghaus’s research, explore its implications for modern learning strategies, and discuss how his findings can be applied to improve memory and retention.
Understanding Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve
Ebbinghaus conducted meticulous experiments on himself, memorizing lists of nonsense syllables to isolate the effects of time on memory. He carefully tracked how long it took him to relearn the lists after varying intervals. What he discovered was a predictable pattern of forgetting: the majority of information is lost within the first few hours, then the rate of forgetting gradually slows. This pattern became known as the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve.
Implications for Modern Learning
Ebbinghaus’s research has significant implications for modern learning strategies. Understanding the forgetting curve allows us to develop more effective methods for retaining information. By spacing out review sessions strategically, we can combat the natural tendency to forget.
- Spaced Repetition: This technique involves reviewing material at increasing intervals, aligning with the natural forgetting curve.
- Active Recall: Instead of passively rereading material, actively trying to retrieve the information from memory strengthens the neural pathways associated with that information.
- Interleaving: Mixing different subjects or topics during study sessions can improve long-term retention.
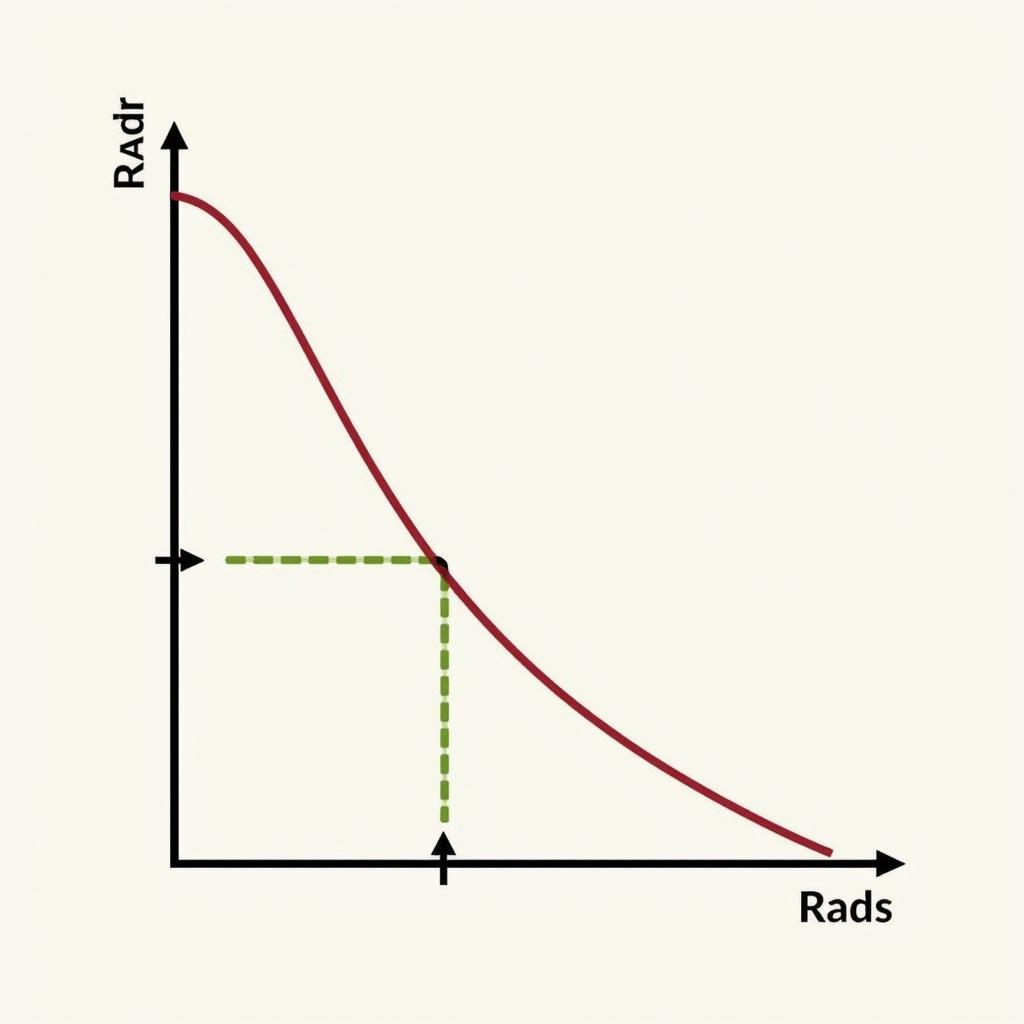 Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve Illustration
Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve Illustration
Applying Ebbinghaus’s Findings to Improve Memory
The principles discovered by Ebbinghaus can be applied in various settings, from academic studies to professional development. Here are some practical tips:
- Review Regularly: Don’t cram! Regular, short review sessions are far more effective than marathon study sessions.
- Test Yourself: Quizzing yourself or using flashcards forces active recall, strengthening memory.
- Connect New Information to Existing Knowledge: Relating new concepts to what you already know creates a stronger memory trace.
- Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is crucial for consolidating memories.
The Importance of Meaningful Material
While Ebbinghaus used nonsense syllables, his findings are relevant to learning meaningful material as well. However, meaningful information is generally retained better than arbitrary information.
- Mnemonics: Memory aids, such as acronyms or rhymes, can help make information more memorable.
- Visualizations: Creating mental images of concepts can enhance retention.
- Storytelling: Weaving information into a narrative can make it more engaging and easier to remember.
 Spaced Repetition Schedule Example
Spaced Repetition Schedule Example
“Ebbinghaus’s work underscores the importance of active engagement with the material,” says Dr. Amelia Carter, a cognitive psychologist specializing in memory. “Passive learning is simply not as effective as actively retrieving and applying information.”
Beyond the Forgetting Curve: Modern Perspectives
While Ebbinghaus’s research provides a valuable foundation, modern cognitive psychology has expanded our understanding of memory.
The Role of Context and Emotion
Context and emotion play a significant role in memory formation and retrieval. Information learned in a specific environment is often easier to recall in that same environment. Similarly, emotionally charged events are typically remembered more vividly.
“Emotional connections can significantly enhance memory,” adds Dr. Carter. “Finding ways to connect with the material on an emotional level can make a big difference in retention.”
 Various Memory Techniques
Various Memory Techniques
Conclusion
Hermann Ebbinghaus research would most likely predict that forgetting is a natural process, but one that can be managed effectively. By applying his findings and incorporating modern learning strategies, we can significantly improve our ability to retain information and achieve our learning goals.
FAQ
- What is the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve?
- How can I use spaced repetition to improve my memory?
- What are some effective memory techniques?
- How does sleep affect memory?
- Why is active recall important for learning?
- What is the role of emotion in memory?
- How can I apply Ebbinghaus’s research to my studies?
See also: “Boosting Your Memory Power: Proven Techniques and Strategies” and “Understanding the Science of Learning: A Comprehensive Guide”.
For support, contact us at Phone: 0904826292, Email: [email protected] or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.