The seemingly simple letter “n” holds significant weight in the world of research. It represents the sample size, the number of participants or observations included in a study. Understanding what “n” means in research is crucial for interpreting the validity and reliability of any findings. This article delves into the importance of “n,” its influence on research outcomes, and the factors to consider when determining the appropriate sample size for different research designs.
It’s easy to overlook the importance of sample size when evaluating research. However, “n” is a fundamental element that directly impacts the statistical power and generalizability of the findings. A larger “n” generally leads to more reliable results and increases the confidence that the findings accurately reflect the population being studied. A smaller “n,” while sometimes necessary due to resource constraints, can limit the study’s scope and make it more susceptible to bias. Learn more about the core concepts of research by exploring the meaning of research itself at mean in research.
The Significance of “N” in Statistical Analysis
The sample size (“n”) plays a critical role in various statistical calculations. It influences the standard error, confidence intervals, and the ability to detect statistically significant differences. A larger “n” reduces the standard error, leading to narrower confidence intervals and increased statistical power. This means that with a larger sample size, researchers are more likely to detect a true effect if one exists.
How “N” Impacts Research Outcomes
The choice of “n” directly influences the research outcomes. A small “n” can lead to Type II errors (false negatives), where a real effect is missed. Conversely, a very large “n” can sometimes lead to statistically significant results that are not practically significant. Finding the right balance is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
 Sample Size and Statistical Power
Sample Size and Statistical Power
Determining the Appropriate Sample Size
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of what constitutes an appropriate “n.” The ideal sample size depends on several factors, including the research question, the study design, the variability of the data, and the desired level of precision. Researchers often use power analysis to determine the minimum sample size needed to detect a specific effect size with a given level of power. Understanding the implications of research helps researchers make informed decisions regarding sample size.
Factors Influencing Sample Size Selection
Several factors influence the selection of an appropriate sample size:
- Research Question: The complexity of the research question and the number of variables being investigated impact the required sample size.
- Study Design: Different study designs, such as experimental, observational, or qualitative studies, have different sample size requirements.
- Variability of Data: Higher variability within the population requires a larger sample size to capture the full range of responses.
- Desired Level of Precision: A higher desired level of precision requires a larger sample size to reduce the margin of error.
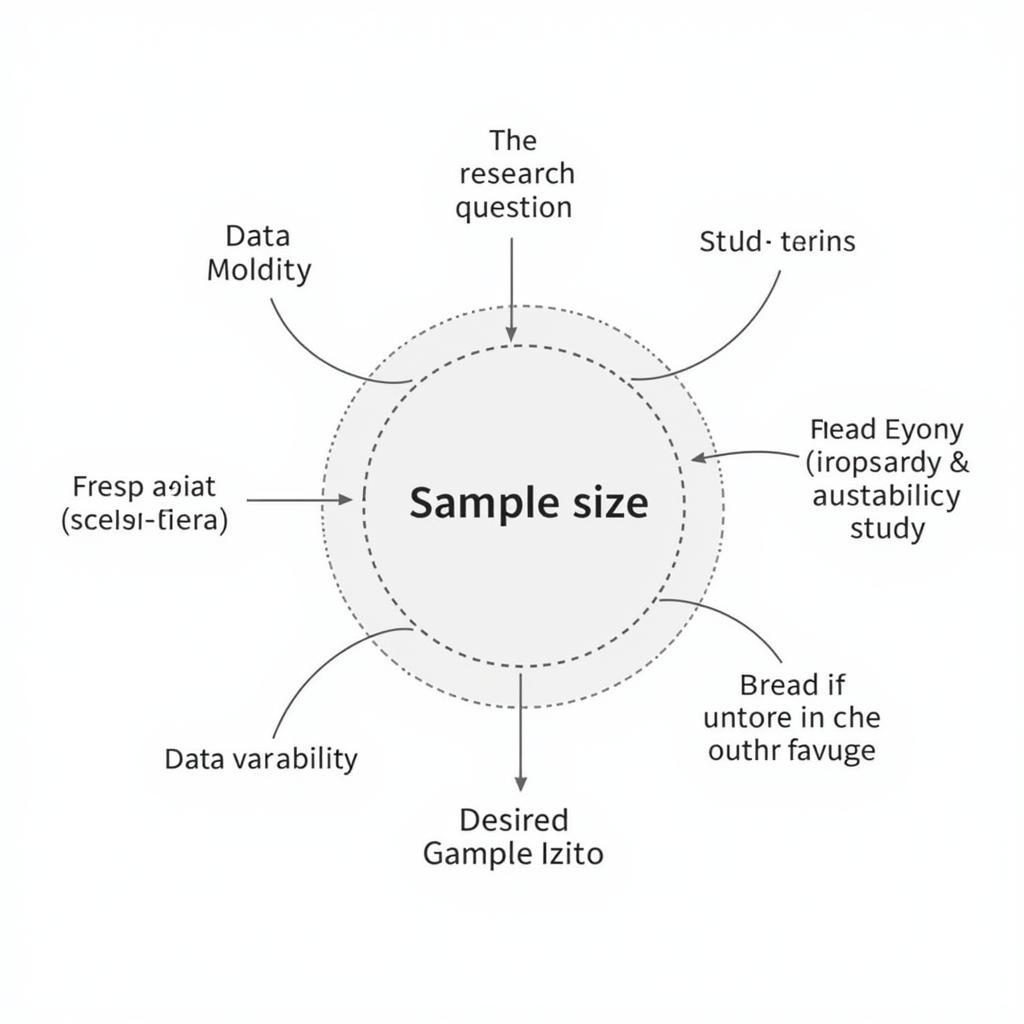 Factors Influencing Sample Size
Factors Influencing Sample Size
“A well-chosen sample size is the cornerstone of robust research. It’s like choosing the right lens for a camera – it determines the clarity and focus of your results,” explains Dr. Amelia Vance, a leading statistician at the Institute of Quantitative Sciences.
Practical Considerations for “N”
While statistical calculations provide a starting point, practical considerations also play a role in determining “n.” These considerations include budget constraints, time limitations, and the availability of participants. Researchers must balance the ideal sample size with the feasibility of data collection. Researching unknown callers, like getting a text from McGuire Research, can sometimes involve unique sampling considerations.
Balancing Statistical Power and Practical Constraints
Balancing statistical power and practical constraints is often a challenge in research. Researchers must carefully consider the trade-offs between a larger sample size and the resources available. In some cases, a smaller sample size may be acceptable if the effect size is large or the research question is exploratory. Sometimes, research conclusions, like a closed research case, can be reached with smaller sample sizes if the data is compelling.
“Researchers should always strive for the largest feasible sample size, but they also need to be pragmatic and consider the limitations of their resources,” advises Dr. David Miller, a seasoned research methodologist at the University of Statistical Analysis.
In conclusion, “n,” the sample size, is a fundamental aspect of research methodology. It influences the reliability, validity, and generalizability of research findings. Understanding what “n” means in research and the factors influencing its determination is crucial for conducting and interpreting any research study. By carefully considering the statistical and practical implications of “n,” researchers can ensure that their studies are well-powered and produce meaningful results. Developing research literacy is essential for understanding and critically evaluating the role of “n” in research studies.
FAQ
- What does a small “n” indicate in research? A small “n” can limit the generalizability of the findings and increase the risk of Type II errors.
- How is “n” determined in qualitative research? In qualitative research, “n” is often determined by data saturation, when new data no longer provides new insights.
- Can a large “n” guarantee accurate results? While a large “n” increases statistical power, it doesn’t guarantee accurate results if the study design is flawed or the data is biased.
- What is the role of power analysis in determining “n”? Power analysis helps researchers determine the minimum sample size needed to detect a specific effect size with a given level of power.
- What are the practical limitations in achieving a large “n”? Practical limitations include budget constraints, time limitations, and the availability of participants.
- Is “n” the only factor determining the validity of research? No, other factors like study design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques also contribute to the validity of research.
- How does “n” relate to the concept of statistical significance? “n” directly influences the calculation of p-values, which determine statistical significance.
If you need any assistance, please contact Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com Or visit us at: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.