3.06 Research And Citations are crucial for academic integrity and producing high-quality work. Understanding how to effectively research and properly cite sources is essential for anyone engaging in academic writing, professional reports, or even blog posts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of research and citation, offering practical tips and strategies for conducting thorough research and accurately attributing your sources.
Mastering the Art of 3.06 Research
Effective research goes beyond simply finding information; it involves a systematic approach to gathering, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant data. When embarking on your 3.06 research journey, consider the following steps:
- Define your research question: What are you trying to find out? A clearly defined research question will guide your entire process.
- Identify credible sources: Utilize academic databases, reputable journals, books, and websites to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your information.
- Evaluate your sources: Not all sources are created equal. Consider the author’s expertise, publication date, and potential biases.
- Take thorough notes: Keep track of your sources and key findings to avoid plagiarism and streamline the citation process. Always note the publication details, including author, title, date, and publisher.
Properly citing sources is not just about avoiding plagiarism; it’s about giving credit where credit is due and allowing readers to verify your information.
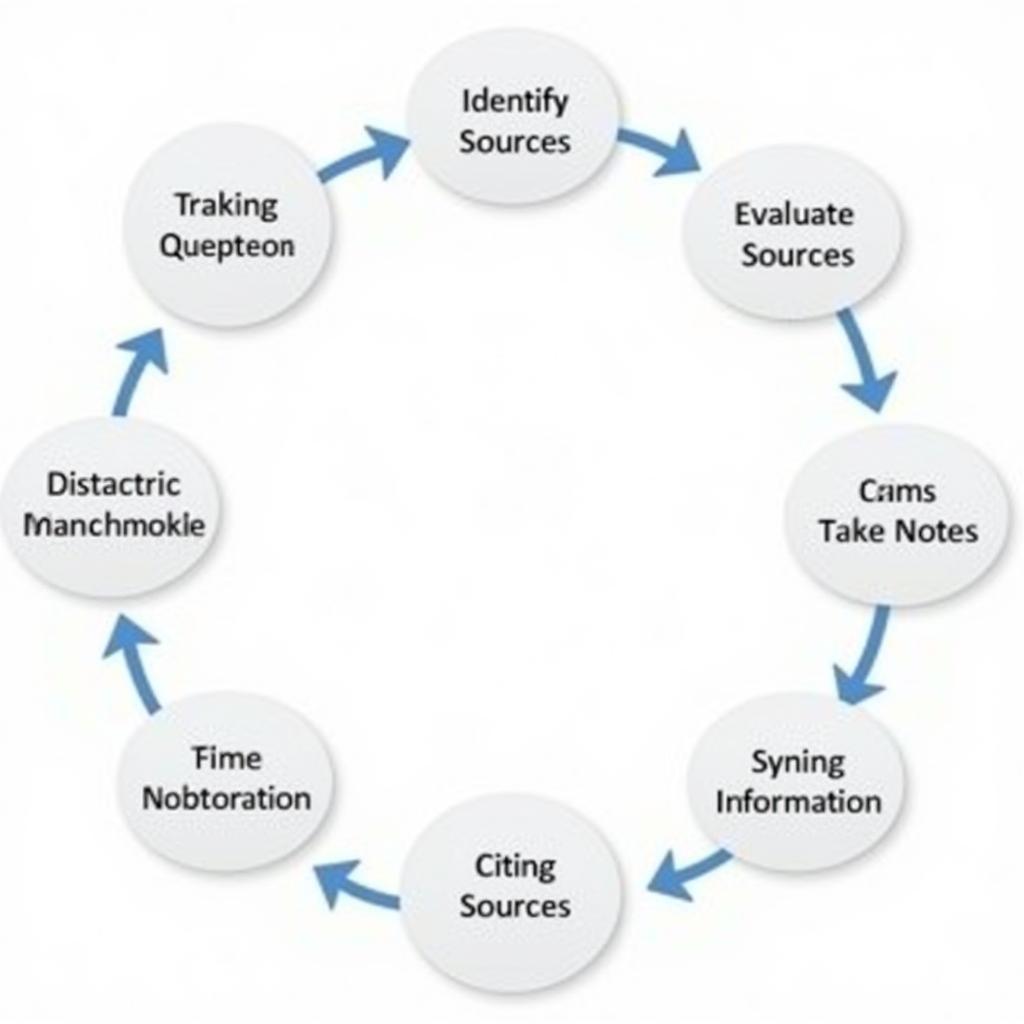 The 3.06 Research and Citation Process
The 3.06 Research and Citation Process
Different Citation Styles for 3.06 Research
There are various citation styles, each with its own set of rules and conventions. Some of the most common styles include MLA, APA, Chicago, and Harvard. Understanding the nuances of each style is crucial for accurate citation.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): Commonly used in the humanities.
- APA (American Psychological Association): Frequently used in the social sciences.
- Chicago Manual of Style: Often used in history and publishing.
- Harvard: Widely used in the humanities and social sciences internationally.
Choosing the appropriate style depends on the specific requirements of your assignment or publication. Consult your instructor or style guide for guidance.
3.06 Research and Citations: Avoiding Plagiarism
Plagiarism, the act of presenting someone else’s work as your own, is a serious academic offense. Even unintentional plagiarism can have significant consequences. By understanding how to properly quote, paraphrase, and summarize information, you can avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity.
- Quoting: Reproducing someone else’s words verbatim, enclosed in quotation marks.
- Paraphrasing: Restating someone else’s ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning.
- Summarizing: Condensing a larger piece of information into a shorter overview.
Always cite your sources, even when paraphrasing or summarizing.
Why are 3.06 Research and Citations Important?
3.06 research and citations are fundamental to academic honesty and intellectual property. They demonstrate respect for other researchers’ work and contribute to the overall body of knowledge. Accurate citations allow readers to trace the origins of your information and further explore the topic.
 The Importance of Research and Citations
The Importance of Research and Citations
Conclusion: The Power of 3.06 Research and Citations
3.06 research and citations are essential tools for anyone engaging in academic or professional writing. By mastering these skills, you can produce high-quality, credible work that contributes to the ongoing conversation in your field. Remember to define your research question, choose appropriate sources, and cite your work accurately to maintain academic integrity and enhance the value of your research.
FAQs about 3.06 Research and Citations
-
What is the difference between a bibliography and a works cited page? A works cited page lists only the sources you directly cited in your paper, while a bibliography includes all sources you consulted, even if you didn’t cite them directly.
-
How do I cite online sources? Include the author, title, website name, publication date, and URL.
-
What is a DOI? A DOI (Digital Object Identifier) is a persistent link to an online source.
-
How do I cite a source with multiple authors? List all authors according to the specific citation style you are using.
-
What is the difference between a primary and secondary source? A primary source is an original document or artifact, while a secondary source analyzes or interprets primary sources.
-
What if I can’t find the author of a source? Use the title of the work in place of the author.
-
Where can I find more information on specific citation styles? Consult style guides such as the MLA Handbook, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, or The Chicago Manual of Style.
Need help with your research? Contact us! Phone: 0904826292, Email: [email protected] or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.