The CAPA process, or Corrective and Preventive Action, is a crucial part of ensuring the quality and integrity of clinical research. It plays a vital role in identifying, analyzing, and correcting deviations from approved protocols and regulations. This systematic approach aims to prevent recurrence and improve overall research processes. Let’s explore the intricacies of CAPA in clinical research.
psychology research opportunities for undergraduates
What is CAPA in Clinical Research?
CAPA in clinical research is a structured process used to address and mitigate issues that arise during the conduct of a clinical trial. These issues, also known as deviations or non-conformances, can range from minor administrative errors to significant protocol violations. The CAPA process is not simply about fixing problems; it’s about learning from mistakes and implementing preventive measures to avoid similar issues in the future. The ultimate goal is to protect the rights and welfare of study participants and ensure the reliability and validity of research data.
Why is the CAPA Process Important?
The importance of the Capa Process In Clinical Research cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental element of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and is required by regulatory agencies worldwide. A robust CAPA system helps build trust and confidence in the research process, demonstrating a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Effective CAPA implementation leads to improved data integrity, reduced risks to participants, and increased efficiency in clinical trials.
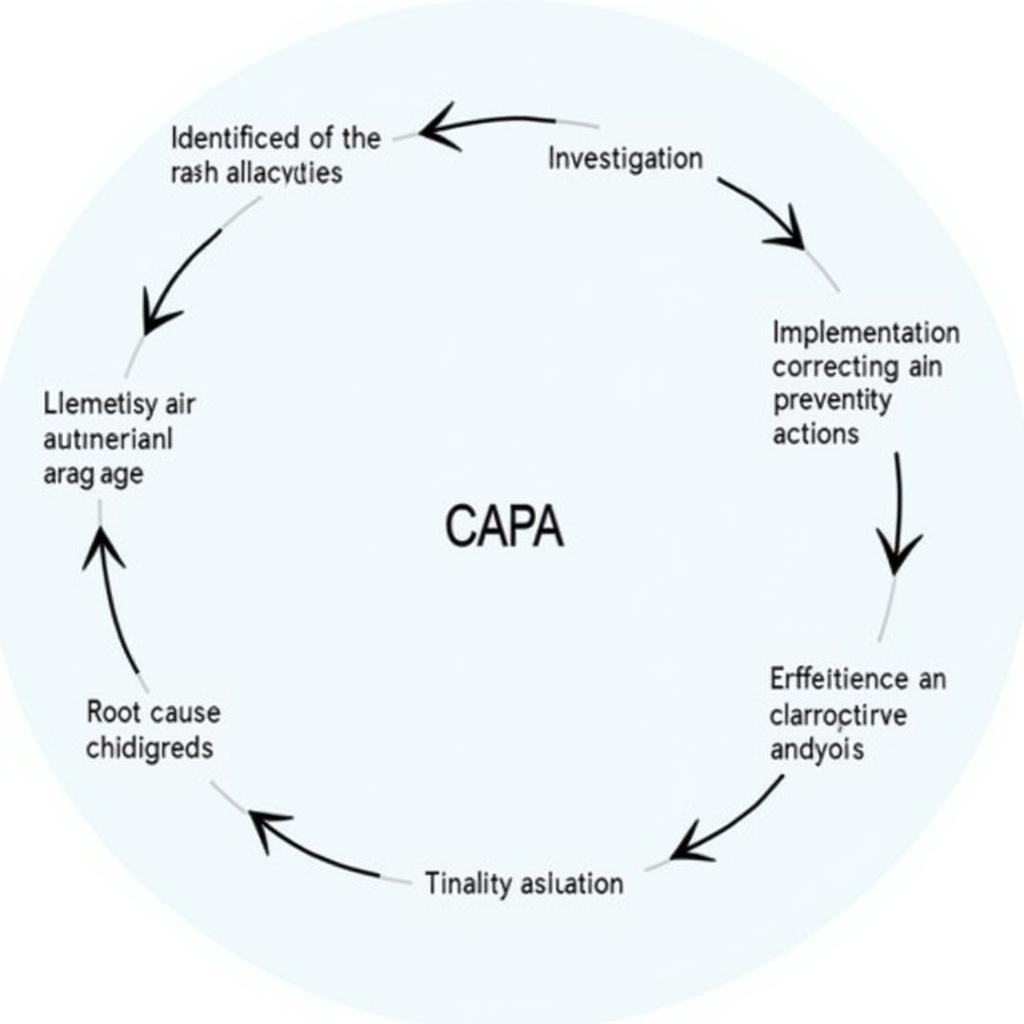 CAPA Process Flowchart in Clinical Research
CAPA Process Flowchart in Clinical Research
Key Steps in the CAPA Process
The CAPA process typically involves the following steps:
- Identification of a Deviation: This step involves recognizing and documenting any deviation from the approved protocol, standard operating procedures (SOPs), or applicable regulations.
- Investigation: A thorough investigation is conducted to determine the root cause of the deviation. This may involve interviewing personnel, reviewing documentation, and analyzing data.
- Root Cause Analysis: This crucial step aims to identify the underlying cause of the deviation. Various techniques, such as the 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams, can be used to facilitate this process.
- Corrective Actions: These actions are implemented to address the immediate deviation and prevent its recurrence. They are specific to the identified issue and designed to rectify the current situation.
- Preventive Actions: These actions are designed to prevent similar deviations from occurring in the future. They address the systemic issues that contributed to the deviation.
- Effectiveness Check: After implementing corrective and preventive actions, an effectiveness check is performed to verify their success and ensure that the deviation has been effectively addressed.
- CAPA Closure: Once the effectiveness check is complete and the deviation is deemed resolved, the CAPA is formally closed.
Common Examples of CAPAs in Clinical Research
Some common examples of CAPAs in clinical research include:
- Protocol deviations related to informed consent: Implementing revised consent forms or retraining staff on proper consent procedures.
- Deviations related to data entry errors: Implementing data validation checks within electronic data capture systems.
- Deviations related to inadequate training of research personnel: Developing and implementing comprehensive training programs and competency assessments.
 CAPA Documentation Example
CAPA Documentation Example
Best Practices for Effective CAPA Implementation
To ensure effective CAPA implementation, consider the following best practices:
- Establish clear procedures and responsibilities: Define roles and responsibilities for each step of the CAPA process.
- Use a standardized CAPA form: This ensures consistency and facilitates tracking and trending of deviations.
- Ensure adequate training on CAPA procedures: All research staff should be trained on the CAPA process and their respective roles.
- Conduct regular reviews of the CAPA system: This helps to identify areas for improvement and ensure the system remains effective.
“A robust CAPA system is not just about fixing problems; it’s about building a culture of quality and continuous improvement within the research environment,” says Dr. Amelia Hernandez, a seasoned clinical research expert. “By proactively addressing deviations and implementing preventive measures, we can enhance the reliability and integrity of clinical trials.”
Conclusion
The CAPA process is a critical component of clinical research, ensuring data quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. By implementing a robust and effective CAPA system, research organizations can minimize risks, improve processes, and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge. Implementing CAPA effectively helps organizations learn from their mistakes and strive for continuous improvement in clinical research.
 CAPA Training Session in Clinical Research
CAPA Training Session in Clinical Research
FAQ
- What is the difference between corrective and preventive actions?
- Who is responsible for implementing CAPAs?
- How often should the CAPA system be reviewed?
- What are some common tools used for root cause analysis?
- How does CAPA contribute to GCP compliance?
- What is the role of documentation in the CAPA process?
- What are the benefits of an effective CAPA system?
Situations involving common questions
Here are some typical situations and the corresponding questions that might arise regarding CAPA:
- Incorrect data entry: What procedures are in place to prevent future data entry errors?
- Protocol deviation: How was the deviation identified and what steps were taken to address it?
- Adverse event: What corrective and preventive actions were implemented to mitigate the risk of similar adverse events?
Further Resources
- See our page on MFS Research Fund for related information on research funding.
- Learn more about the evolution of research in physical therapy in our article on How Has Research Changed in Physical Therapy?.
Contact Us
Need help with your research? Contact us 24/7. Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.