Biological Trace Element Research explores the fascinating interplay between minute quantities of elements and living organisms. These trace elements, often present in concentrations of less than one part per million, play crucial roles in various biological processes, influencing everything from enzyme activity to immune function. Understanding their impact is vital for advancing our knowledge of health, disease, and the intricate workings of life itself.
The Significance of Biological Trace Element Research
Biological trace element research encompasses a wide range of disciplines, from nutritional science and toxicology to environmental science and medicine. This interdisciplinary field seeks to unravel the complex mechanisms by which trace elements exert their effects on biological systems. By studying the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of these elements, researchers gain insights into their essential functions, potential toxicity, and impact on overall health.
Essential Trace Elements and Their Roles
Several trace elements are considered essential for human health, meaning that our bodies require them in small amounts for optimal functioning. These include:
- Iron: Crucial for oxygen transport and red blood cell production.
- Zinc: Plays a vital role in immune function, wound healing, and cell growth.
- Copper: Essential for iron metabolism, nerve function, and connective tissue formation.
- Selenium: A powerful antioxidant that protects against cellular damage.
- Iodine: Necessary for thyroid hormone production, which regulates metabolism.
- Manganese: Involved in bone formation, wound healing, and metabolism.
- Chromium: Enhances insulin action and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Molybdenum: A component of several enzymes involved in detoxification and metabolism.
Deficiencies in these essential trace elements can lead to a variety of health problems, ranging from anemia and impaired immune function to growth retardation and developmental delays.
Investigating the Toxicity of Trace Elements
While essential in trace amounts, some elements can become toxic at higher concentrations. Biological trace element research plays a crucial role in understanding the mechanisms of toxicity and developing strategies for prevention and treatment. Elements like lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium can disrupt cellular processes, damage organs, and even cause cancer.
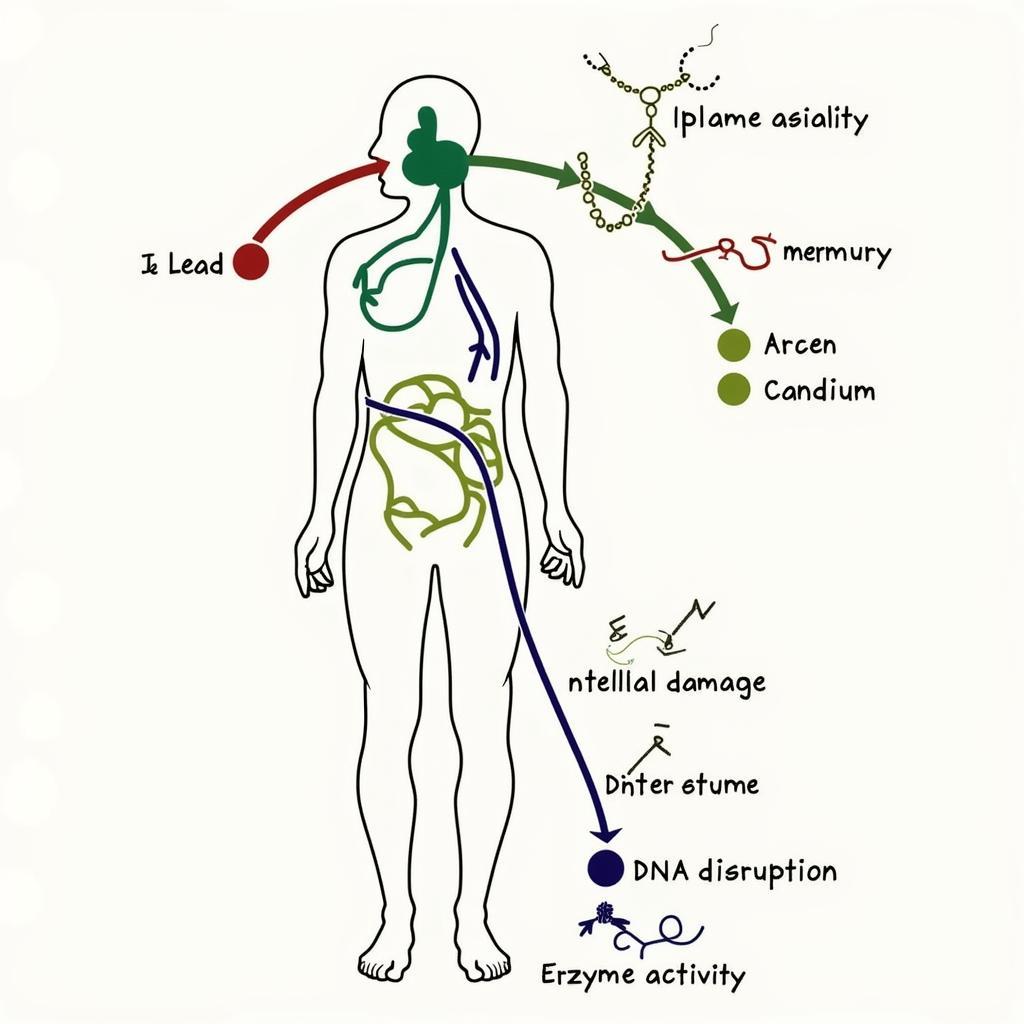 Trace Element Toxicity Pathways
Trace Element Toxicity Pathways
Analytical Techniques in Biological Trace Element Research
Advanced analytical techniques are essential for accurately measuring trace element concentrations in biological samples. These techniques include:
- Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS): Measures the absorption of light by atoms in a sample.
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS): A highly sensitive technique that can detect multiple elements simultaneously.
- Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA): Uses neutron irradiation to induce radioactivity in a sample, allowing for the identification and quantification of trace elements.
How is Biological Trace Element Research Conducted?
Researchers meticulously design studies, collect samples, and analyze data to understand the intricate role of trace elements in living organisms. They often employ sophisticated laboratory equipment and statistical methods to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their findings.
The Future of Biological Trace Element Research
Biological trace element research continues to evolve, driven by advancements in analytical technologies and a growing understanding of the complex interplay between trace elements and biological systems. This field holds immense promise for developing new diagnostic tools, personalized therapies, and strategies for preventing and treating diseases related to trace element imbalances.
In conclusion, biological trace element research is a vital field that sheds light on the crucial roles of these minute but mighty elements in maintaining health and well-being. By continuing to explore the intricate interplay between trace elements and living organisms, researchers pave the way for new discoveries and advancements in healthcare.
FAQ
- What are trace elements?
- Why are trace elements important for human health?
- What are some examples of essential trace elements?
- How can I ensure I am getting enough trace elements in my diet?
- What are the risks of trace element deficiencies?
- Can trace elements be toxic?
- How are trace elements measured in biological samples?
Need support? Contact us at Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com Or visit us at: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.