The Cross-sectional Approach To Developmental Research Compares different groups of individuals at a single point in time. This method allows researchers to quickly gather data and identify potential relationships between variables across various age groups or developmental stages. It provides a snapshot of development at a specific moment, offering valuable insights into how certain characteristics or behaviors may vary across different cohorts.
What is a Cross-Sectional Study?
A cross-sectional study is a type of observational research design that analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time. It’s like taking a photograph of different groups and comparing the images to see how they differ. This approach is commonly used in developmental research to examine how certain variables, such as cognitive abilities, social behaviors, or physical characteristics, change across the lifespan. The cross-sectional approach to developmental research compares individuals of different ages simultaneously, making it a relatively efficient method for studying age-related differences.
Advantages of the Cross-Sectional Approach
The cross-sectional approach offers several advantages, making it a popular choice for developmental researchers. Firstly, it’s relatively quick and cost-effective. Data collection occurs only once, eliminating the need for lengthy follow-up periods. This efficiency allows researchers to explore a wider range of variables and study larger populations. Secondly, cross-sectional studies can identify potential associations between variables, paving the way for future research using more rigorous designs.
Limitations of the Cross-Sectional Approach
While the cross-sectional approach is valuable, it also has limitations. The most significant limitation is the inability to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Because data is collected at a single point in time, researchers cannot determine whether changes in one variable actually cause changes in another. Another limitation is the potential for cohort effects. Differences between age groups may not be solely due to developmental changes but could be influenced by the unique experiences or historical events shared by individuals born within the same period.
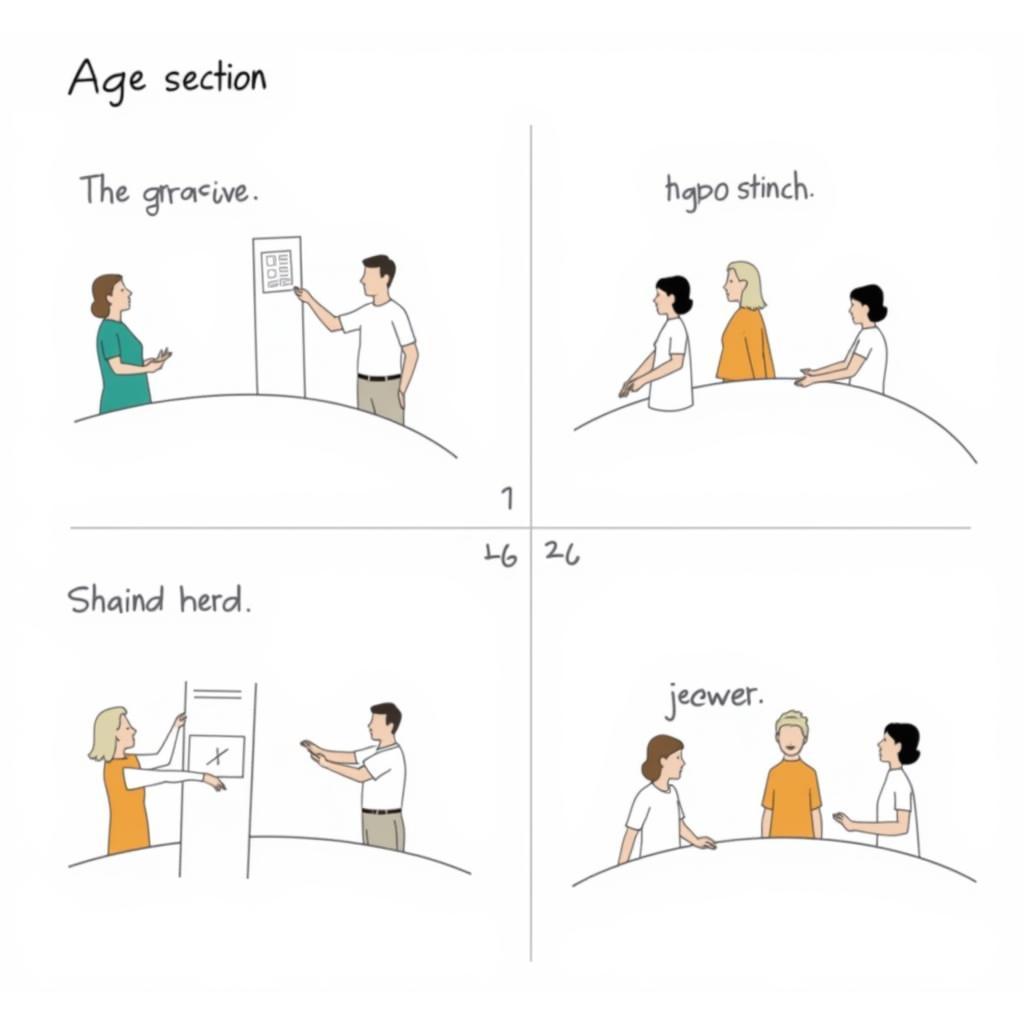 Cross-Sectional Study Design Example
Cross-Sectional Study Design Example
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Studies
The cross-sectional approach is often contrasted with the longitudinal approach, which follows the same group of individuals over an extended period. While longitudinal studies can establish cause-and-effect relationships and control for cohort effects, they are more time-consuming and expensive. The choice between a cross-sectional and longitudinal design depends on the research question and the available resources.
Which approach is better for developmental research?
The “better” approach depends on the research question. Cross-sectional is faster and cheaper, while longitudinal provides more in-depth information over time.
How can cohort effects impact cross-sectional studies?
Cohort effects can lead to misinterpretations of age-related differences, as the observed variations may be due to shared experiences rather than developmental changes.
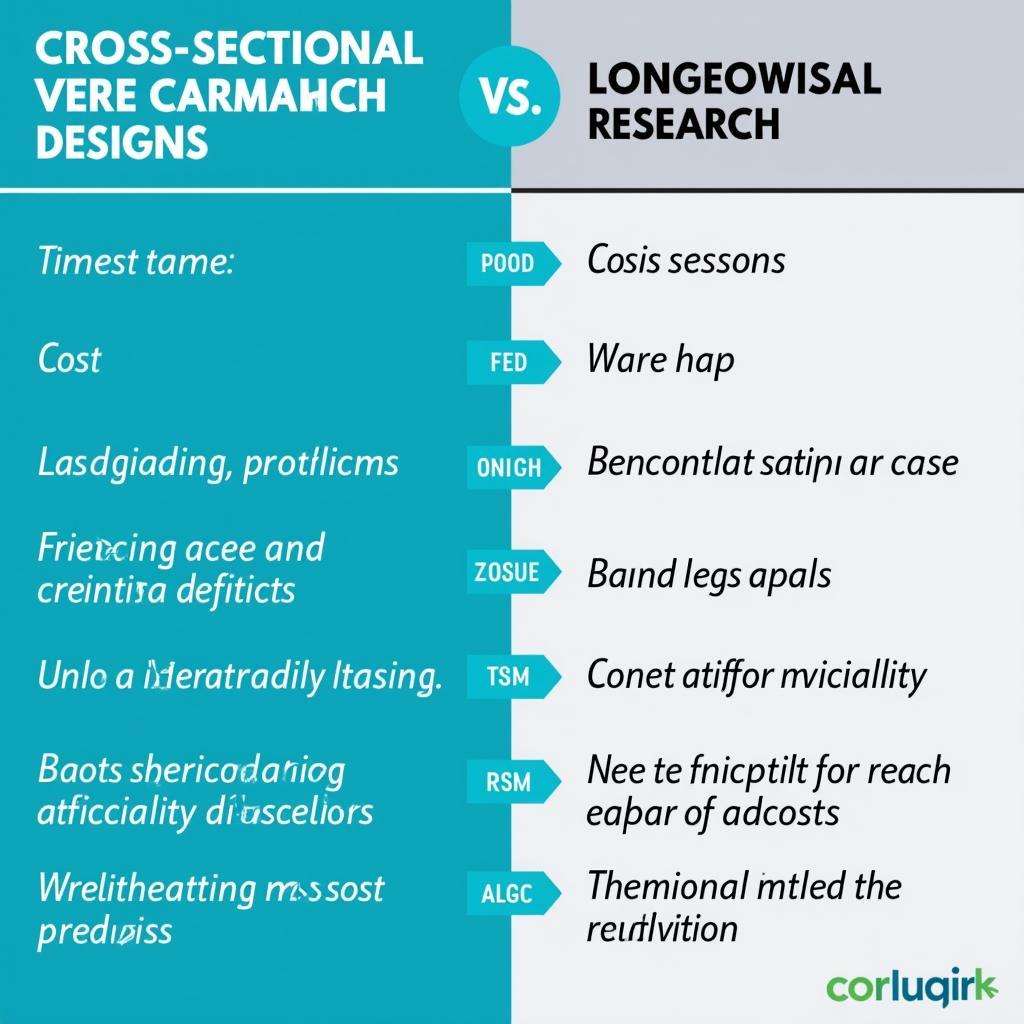 Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research
Applying the Cross-Sectional Approach in Different Fields
The cross-sectional approach isn’t limited to developmental psychology. It’s also used in fields like sociology, public health, and marketing. For example, a cross-sectional study could examine the prevalence of certain health behaviors across different socioeconomic groups or analyze consumer preferences for different products based on demographic characteristics.
“Cross-sectional studies are invaluable tools for exploring relationships between variables across different populations. They provide a quick and efficient way to gather preliminary data, which can then inform more in-depth research,” says Dr. Amelia Carter, a leading researcher in developmental psychology.
Conclusion
The cross-sectional approach to developmental research compares different age groups at a single point in time, offering a snapshot of development. While it has limitations regarding causality and cohort effects, its efficiency and ability to identify potential associations make it a valuable tool for researchers. Choosing the right research design requires careful consideration of the research question and the resources available.
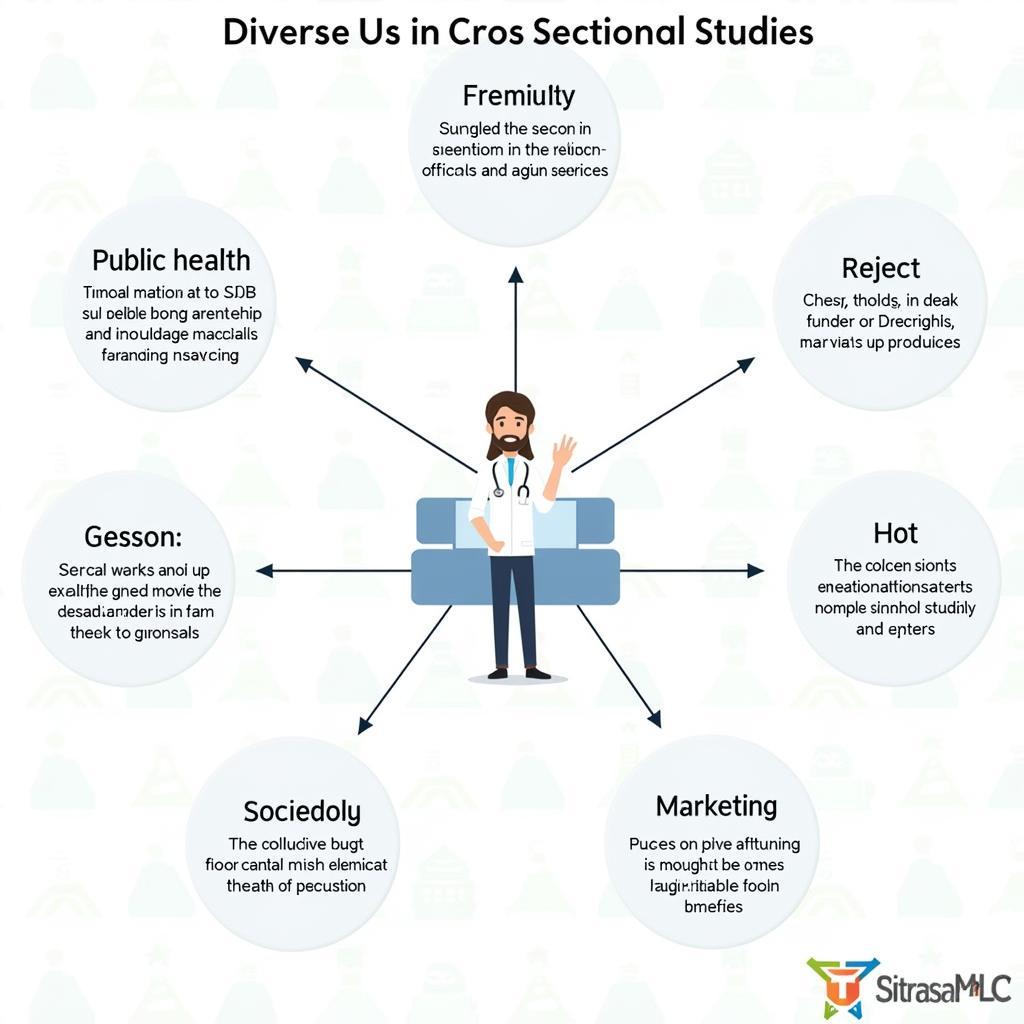 Cross-Sectional Study Applications
Cross-Sectional Study Applications
FAQ
- What are the limitations of the cross-sectional approach? (Inability to establish causality and susceptibility to cohort effects.)
- What is the main advantage of the cross-sectional approach? (Efficiency and cost-effectiveness.)
- How does the cross-sectional approach differ from the longitudinal approach? (Cross-sectional examines different groups at one time, while longitudinal follows the same group over time.)
- Can the cross-sectional approach be used outside of developmental research? (Yes, in fields like sociology, public health, and marketing.)
- What is a cohort effect? (Differences between age groups due to shared experiences rather than developmental changes.)
- What type of research design is a cross-sectional study? (Observational research design)
- What are some examples of variables studied using the cross-sectional approach in developmental research? (Cognitive abilities, social behaviors, and physical characteristics)
Common Situations and Questions:
- Scenario: A researcher wants to study the impact of social media use on self-esteem in adolescents. A cross-sectional study could compare self-esteem levels in different age groups of adolescents who report varying levels of social media use.
- Question: Can a cross-sectional study determine if social media use causes low self-esteem? No, correlation does not equal causation.
Related Articles:
- Longitudinal Research in Developmental Psychology
- Understanding Cohort Effects in Research
- Choosing the Right Research Design for Your Study
Need further assistance? Contact us:
Phone: 0904826292
Email: research@gmail.com
Address: No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.