Emotion Researchers Today Agree That emotions are complex, multifaceted experiences that play a crucial role in human behavior and well-being. They are not simply fleeting feelings but rather intricate processes involving physiological changes, cognitive appraisals, and behavioral responses. Understanding these processes is essential for navigating the complexities of human interaction, mental health, and even societal dynamics.
The Building Blocks of Emotion: What Emotion Researchers Today Agree On
One area where emotion researchers today agree is on the core components of emotion. These components typically include subjective experience (what it feels like to be happy, sad, or angry), physiological responses (changes in heart rate, breathing, and hormone levels), cognitive appraisals (how we interpret situations and events), and behavioral tendencies (our urges to approach, avoid, or attack). These elements work together to shape our emotional landscape and influence our actions. paid research studies miami This integrated view acknowledges the dynamic interplay between our minds, bodies, and the environment in shaping our emotional world.
Unveiling the Neuroscience of Emotion: How the Brain Processes Feelings
Emotion researchers today agree that specific brain regions, such as the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, play vital roles in emotional processing. The amygdala, for instance, is often considered the emotional hub, responsible for rapidly detecting and responding to potential threats. The hippocampus contributes to emotional memory, while the prefrontal cortex is involved in regulating emotions and making decisions based on emotional information. Understanding the neural circuitry of emotions provides crucial insights into how and why we experience feelings in the way we do.
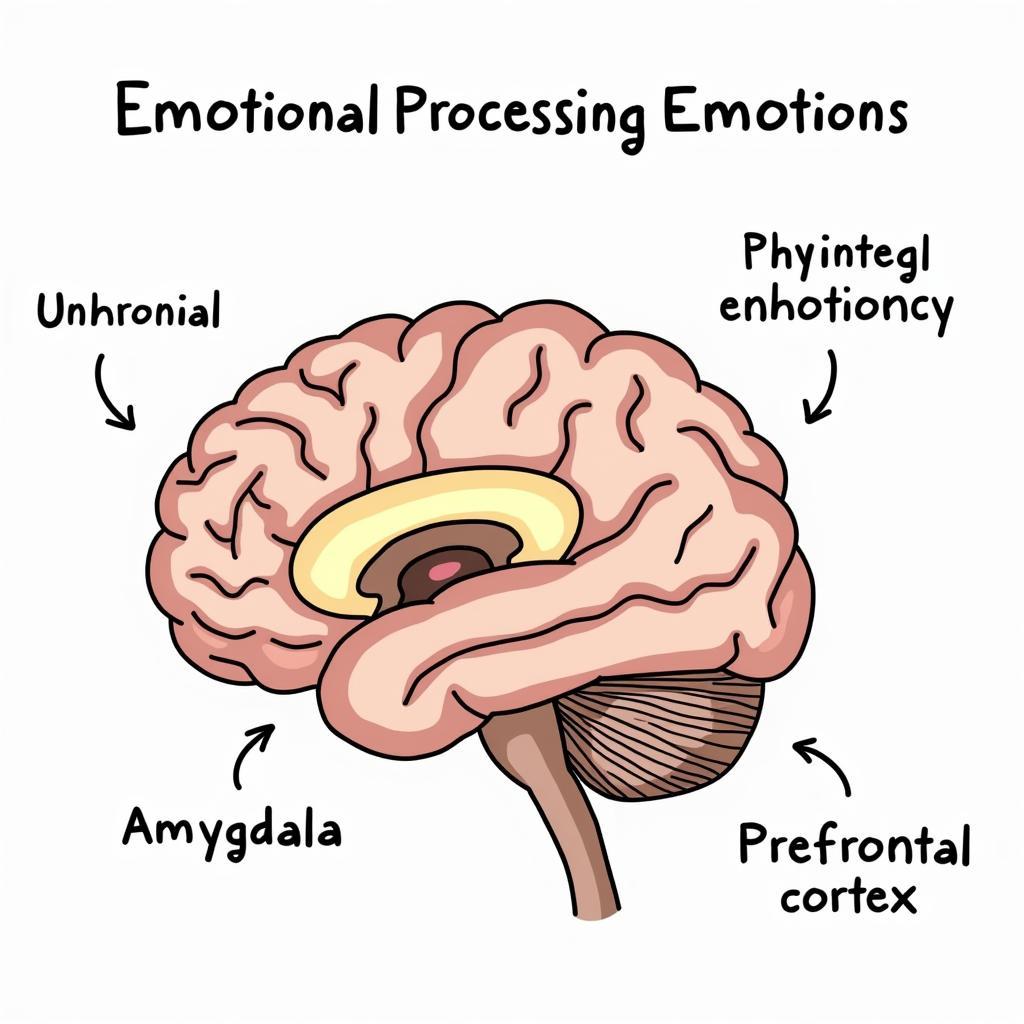 The Neuroscience of Emotion: Brain Regions and Emotional Processing
The Neuroscience of Emotion: Brain Regions and Emotional Processing
The Universality vs. Cultural Specificity of Emotions: A Balancing Act
While emotion researchers today agree that certain basic emotions, such as joy, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust, appear to be universally recognized across cultures, there is ongoing debate about the extent to which emotions are shaped by cultural factors. Some researchers argue that culture significantly influences the expression, regulation, and even the experience of emotions. For instance, while sadness might be universally experienced, how it is expressed publicly might vary considerably across different cultures.
How Culture Shapes Emotional Expression: Navigating Social Norms
Emotion researchers today agree that cultural norms and values dictate how emotions are displayed and managed in social contexts. In some cultures, expressing anger openly is considered acceptable, while in others, it is seen as inappropriate and discouraged. These cultural variations highlight the complex interplay between individual emotional experience and societal expectations.
The Role of Emotions in Decision Making: Beyond Rationality
Emotion researchers today agree that emotions are not simply disruptive forces that interfere with rational thought, but rather integral components of the decision-making process. Emotions can provide valuable information about potential risks and rewards, guiding our choices in ways that pure logic cannot. For instance, feelings of anxiety might warn us of potential danger, while feelings of excitement can motivate us to pursue opportunities.
Emotional Intelligence: Harnessing the Power of Feelings
Emotion researchers today agree that emotional intelligence, which involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions and those of others, is a crucial skill for navigating the complexities of interpersonal relationships and achieving success in various domains of life. Individuals with high emotional intelligence are often better equipped to build strong relationships, resolve conflicts effectively, and make sound decisions.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Field of Emotion Research
Emotion researchers today agree that the study of emotions is a dynamic and evolving field with ongoing exploration of the intricate connections between our feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. As research continues to shed light on the complex mechanisms underlying emotional experiences, we can gain a deeper understanding of what it means to be human and develop more effective strategies for promoting emotional well-being and fostering positive relationships. Emotion researchers today agree that this journey of discovery promises to unlock even more profound insights into the human condition.
FAQ
- What is the amygdala’s role in emotion? (The amygdala processes fear and other strong emotions.)
- How does culture influence emotional expression? (Culture shapes how we display and manage emotions socially.)
- What is emotional intelligence? (It’s the ability to understand and manage your own and others’ emotions.)
- How do emotions affect decision making? (Emotions provide valuable information, guiding choices beyond logic.)
- Are all emotions universal? (Some basic emotions are universally recognized, but culture influences their expression.)
- What are the main components of emotion? (Subjective experience, physiological responses, cognitive appraisals, and behavioral tendencies.)
- Why is emotional research important? (It helps us understand human behavior, mental health, and societal dynamics.)
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.