Descriptive correlational research design is a powerful tool for exploring relationships between variables without manipulating them. This approach allows researchers to observe phenomena as they naturally occur and identify potential connections, paving the way for further investigation. It’s particularly useful in fields like paranormal research where controlled experiments can be difficult or impossible to conduct. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this research design.
What exactly is a descriptive correlational research design, and how does it fit into the broader landscape of research methods? This design is a non-experimental approach that focuses on describing the relationship between two or more variables without attempting to influence them. Unlike experimental designs, where researchers actively manipulate an independent variable to observe its effect on a dependent variable, descriptive correlational studies simply observe and measure naturally occurring relationships. This is crucial in paranormal research where manipulating alleged paranormal phenomena is often ethically questionable or practically infeasible. It allows us to examine correlations, for example, between reported ghost sightings and specific environmental factors, without intervening in any way. Check out our articles on research method in psychology.
Understanding Descriptive Correlational Research
Descriptive correlational research design aims to identify associations between variables and describe the strength and direction of those relationships. This approach is particularly valuable when exploring complex phenomena where direct manipulation is impractical or unethical, a common scenario in the realm of paranormal investigations. For instance, researchers might investigate the correlation between electromagnetic field fluctuations and reported paranormal experiences in a supposedly haunted location.
Key Characteristics of Descriptive Correlational Studies
- Observational: Researchers do not manipulate any variables but observe and measure them as they exist.
- Non-experimental: No intervention or manipulation is involved, allowing for a naturalistic study of relationships.
- Focus on Relationships: The primary goal is to describe the strength and direction of the relationship between variables.
- No Causation: While correlations can be identified, descriptive correlational studies cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships. A correlation between two variables does not necessarily mean that one causes the other. There may be a third, unmeasured variable influencing both.
 Descriptive Correlational Research Diagram
Descriptive Correlational Research Diagram
Applying Descriptive Correlational Design in Paranormal Research
The descriptive correlational research design is invaluable in paranormal research, enabling exploration of phenomena that defy traditional experimental methods. Consider, for example, the study of alleged psychokinesis. Researchers might examine the correlation between a participant’s reported ability to influence random number generators and their psychological profile.
Examples of Research Questions in Paranormal Studies
- Is there a correlation between lunar cycles and reported paranormal activity?
- What is the relationship between individuals’ belief in the paranormal and their reported experiences?
- Is there a connection between specific historical events and subsequent reports of hauntings at a particular location?
For formulating effective research questions, you can refer to our resources on research questions for psychology and how to formulate quantitative research questions.
 Paranormal Research Correlations
Paranormal Research Correlations
“Descriptive correlational studies offer a powerful lens for exploring the complexities of paranormal phenomena, especially when ethical or practical constraints limit the use of experimental designs,” notes Dr. Evelyn Reed, a leading researcher in parapsychology. “By meticulously observing and analyzing correlations, we can gain valuable insights into the intricacies of the paranormal world.”
Analyzing and Interpreting Correlational Data
The strength and direction of a correlation are quantified using a statistical measure called the correlation coefficient, which ranges from -1 to +1. A positive correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. A negative correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other tends to decrease. A correlation coefficient of 0 indicates no linear relationship between the variables. Understanding the three types of research objectives will be beneficial.
Limitations of Descriptive Correlational Research
While valuable, descriptive correlational research has limitations. Most importantly, it cannot establish causality. Just because two variables are correlated does not mean one causes the other. It’s also susceptible to confounding variables—unmeasured factors that may influence both variables of interest. Review our research study design flowchart to further understand different research approaches.
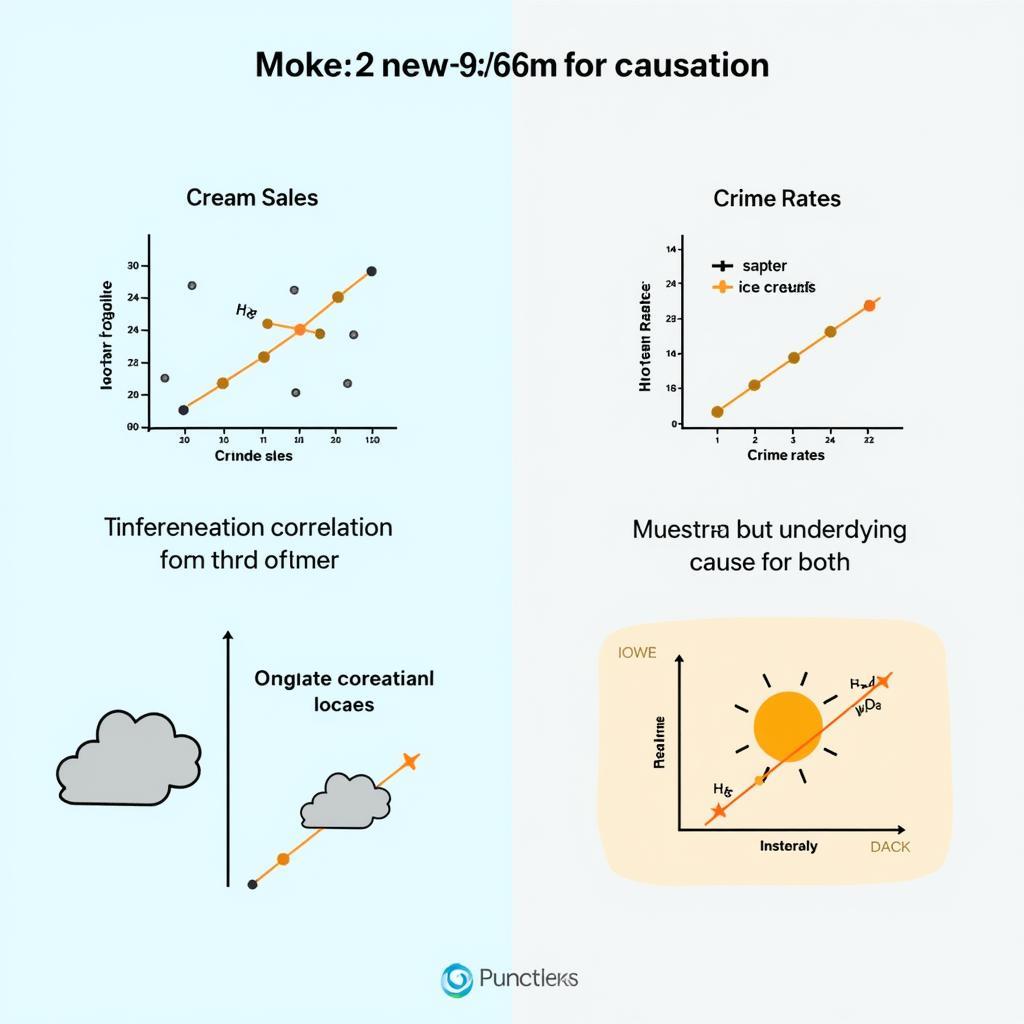 Correlation vs. Causation
Correlation vs. Causation
Conclusion
Descriptive correlational research design is a valuable tool for exploring the often elusive world of paranormal phenomena. By allowing researchers to observe and analyze relationships between variables without manipulation, it opens avenues for investigation where traditional experimental approaches are impractical or impossible. While this design cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships, it provides crucial insights into potential connections, guiding further research and deepening our understanding of the paranormal. Remember, correlation does not equal causation, but it can offer compelling clues in the ongoing quest to understand the unexplained.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between descriptive correlational and experimental research?
- Can descriptive correlational studies prove causation?
- What are some common statistical tests used in correlational research?
- How can I control for confounding variables in a correlational study?
- What are the ethical considerations in conducting paranormal research using a correlational design?
- What are some examples of correlational research in other fields?
- How can I choose the appropriate statistical method for analyzing correlational data?
For any assistance with your Paranormal Research endeavors, please contact us at Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com Or visit our office at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.