Cancer Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (CER) research plays a pivotal role in understanding and combating various types of cancer. This complex field of study focuses on the epidermal growth factor receptor, a protein found on the surface of many cells, which plays a crucial role in cell growth and differentiation. When this receptor malfunctions, it can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, contributing to the development of cancer.
The study of CER has opened up new avenues for targeted therapies, allowing for more personalized treatment approaches. This article delves into the intricacies of Cer Research, exploring its significance in cancer treatment and the ongoing advancements in this critical field. We will examine the mechanisms of CER, its role in different cancer types, and the promising therapeutic strategies that have emerged from this research.
Understanding the Importance of CER Research
CER research is crucial because it has fundamentally changed our understanding of cancer development and progression. By identifying CER as a key driver in several cancers, researchers have been able to develop drugs that specifically target this receptor. This targeted approach aims to minimize damage to healthy cells while maximizing the effectiveness of the treatment.
Research into the different mutations and variations of CER has further enhanced the development of personalized medicine. By analyzing the specific CER profile of a patient’s tumor, clinicians can tailor treatment plans to ensure the highest chance of success. This personalized approach is revolutionizing cancer care, moving away from a “one-size-fits-all” model towards targeted and individualized therapies. You can learn more about specific cancer research efforts, such as those at the Joe Arrington Cancer Research and Treatment Center.
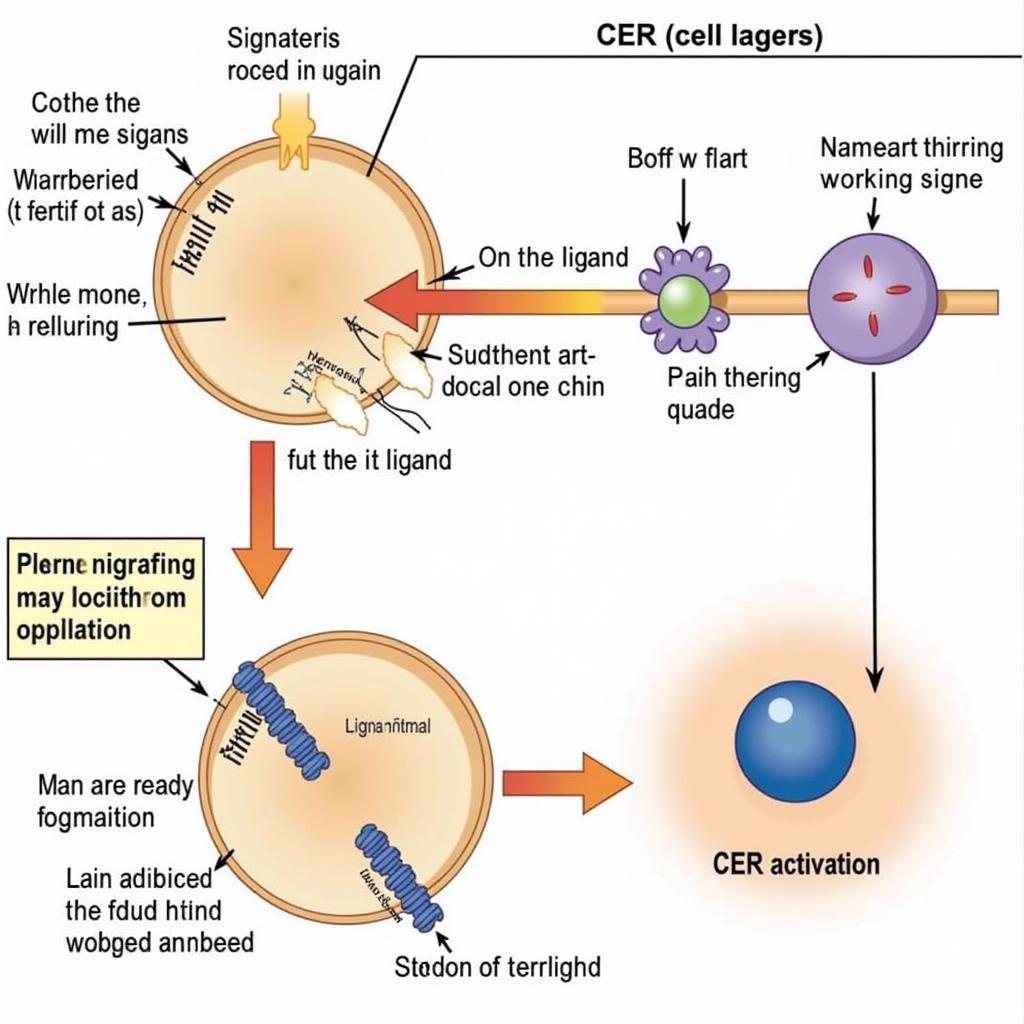 CER Research Mechanism
CER Research Mechanism
Targeting CER: Therapeutic Strategies and Advancements
The identification of CER as a crucial player in cancer has led to the development of several targeted therapies. These therapies work by either blocking the CER protein directly or inhibiting the downstream signaling pathways it activates.
- Monoclonal antibodies: These therapies bind to the CER protein, preventing it from interacting with its ligands and thus inhibiting its activation.
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): TKIs block the intracellular part of the CER protein, preventing it from sending signals that promote cell growth.
These targeted therapies have shown significant promise in treating various cancers, including lung cancer and esophageal cancer. Ongoing research focuses on refining these therapies, developing new strategies to overcome resistance, and identifying new CER targets. Explore more about lung cancer research studies and their impact on treatment options.
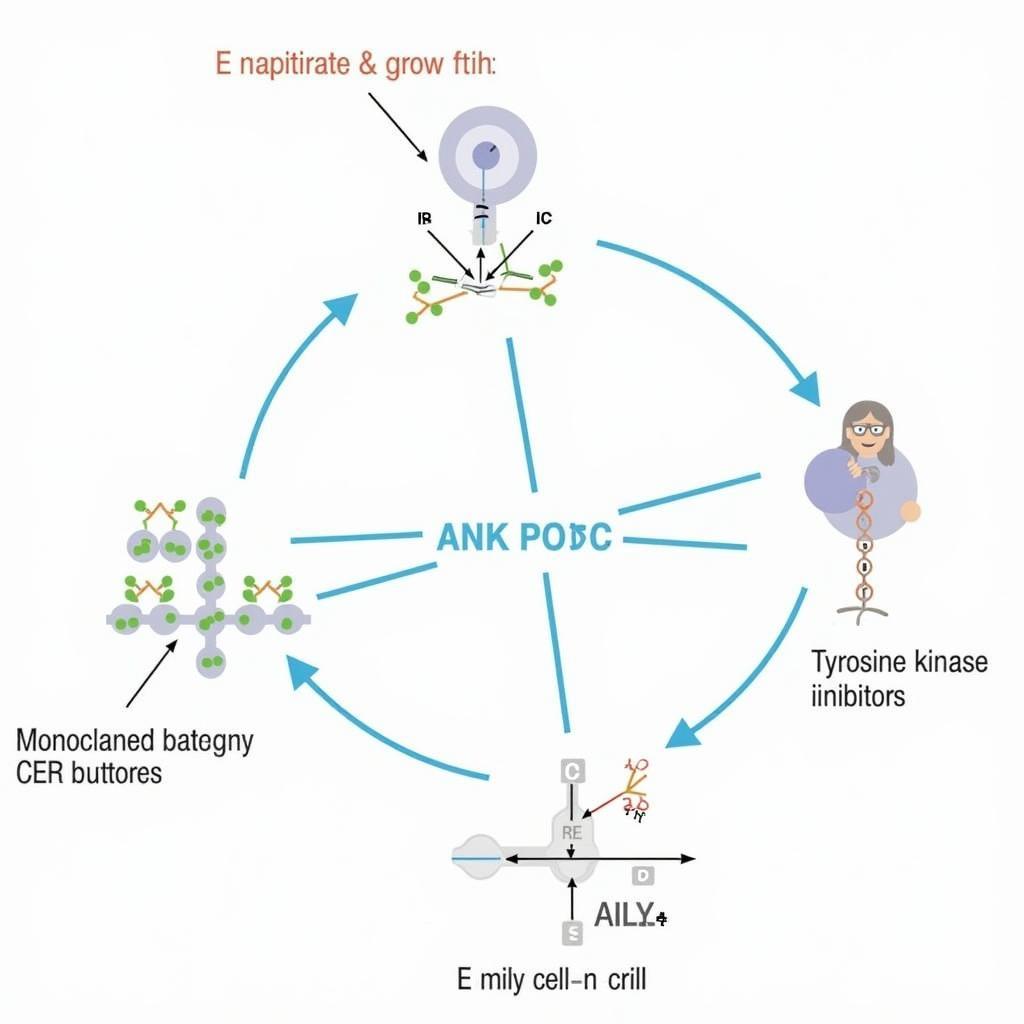 CER Targeted Therapies
CER Targeted Therapies
The Future of CER Research: Personalized Medicine and Beyond
CER research continues to evolve, paving the way for more effective and personalized cancer treatments. One of the most promising areas of research is the development of companion diagnostics. These tests help determine which patients are most likely to benefit from specific CER-targeted therapies, ensuring that treatment is tailored to the individual’s unique cancer profile. For more on cancer research foundations making an impact, visit The Hope Foundation for Cancer Research.
Further research is also exploring the role of CER in combination therapies, using multiple drugs to target different aspects of cancer development. This approach aims to enhance treatment efficacy and overcome drug resistance. Researchers are also investigating the potential of immunotherapy in combination with CER-targeted therapies to harness the power of the immune system in fighting cancer. Are you interested in understanding the impact of cancer research? You can explore the Mol Cancer Research Impact Factor.
 Future of CER Research
Future of CER Research
Conclusion
CER research has revolutionized our understanding of cancer and its treatment. From the identification of CER as a key driver in cancer development to the development of targeted therapies, this field has significantly advanced cancer care. Ongoing research promises to further refine these therapies, paving the way for more personalized and effective cancer treatment strategies. CER research continues to offer hope for improved outcomes and a brighter future for those affected by cancer.
FAQ
- What is CER? CER stands for Cancer Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, a protein involved in cell growth and differentiation.
- How is CER related to cancer? When CER malfunctions, it can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and contribute to cancer development.
- What are CER-targeted therapies? These therapies are designed to specifically block CER activity and inhibit cancer cell growth.
- How do CER-targeted therapies work? They work by either blocking CER directly or inhibiting its downstream signaling pathways.
- What is the future of CER research? Research focuses on personalized medicine, combination therapies, and immunotherapy.
- Where can I find more information on cancer research? Explore our articles on esophageal cancer research.
- Are there foundations dedicated to cancer research? Yes, consider visiting The Hope Foundation for Cancer Research.
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone Number: 0904826292, Email: [email protected], or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.