Replacement theory in operation research addresses the optimal time to replace or maintain deteriorating equipment, machinery, or other assets. It helps businesses make informed decisions about when to retire aging assets and invest in new ones, balancing the costs of replacement against the increasing costs of maintenance and decreased efficiency of older equipment. This crucial aspect of operational efficiency can significantly impact a company’s bottom line by minimizing downtime and maximizing the lifespan of its investments.
Understanding the Basics of Replacement Theory
Replacement theory uses mathematical models to predict the optimal replacement cycle for assets. These models consider various factors, including the purchase price of new equipment, the operating costs of existing equipment, the salvage value of old equipment, and the rate at which equipment deteriorates. By analyzing these factors, businesses can determine the point at which the total cost of ownership for existing equipment exceeds the cost of acquiring and operating a new asset. This point represents the optimal time for replacement.
Different Types of Replacement Problems
Several types of replacement problems exist, each requiring a unique approach. These include:
- Replacement of items that fail suddenly: This applies to items with a random lifespan, such as light bulbs or electronic components. The optimal replacement policy often involves a combination of preventative maintenance and replacement upon failure.
- Replacement of items that deteriorate gradually: This applies to items that lose efficiency or incur higher maintenance costs over time, such as machinery or vehicles. The optimal replacement time balances the increasing maintenance costs with the cost of a new asset.
- Replacement with technological advancements: This involves replacing existing equipment with newer, more efficient technology, even if the current equipment is still functioning. The decision is based on the potential cost savings and improved performance offered by the new technology.
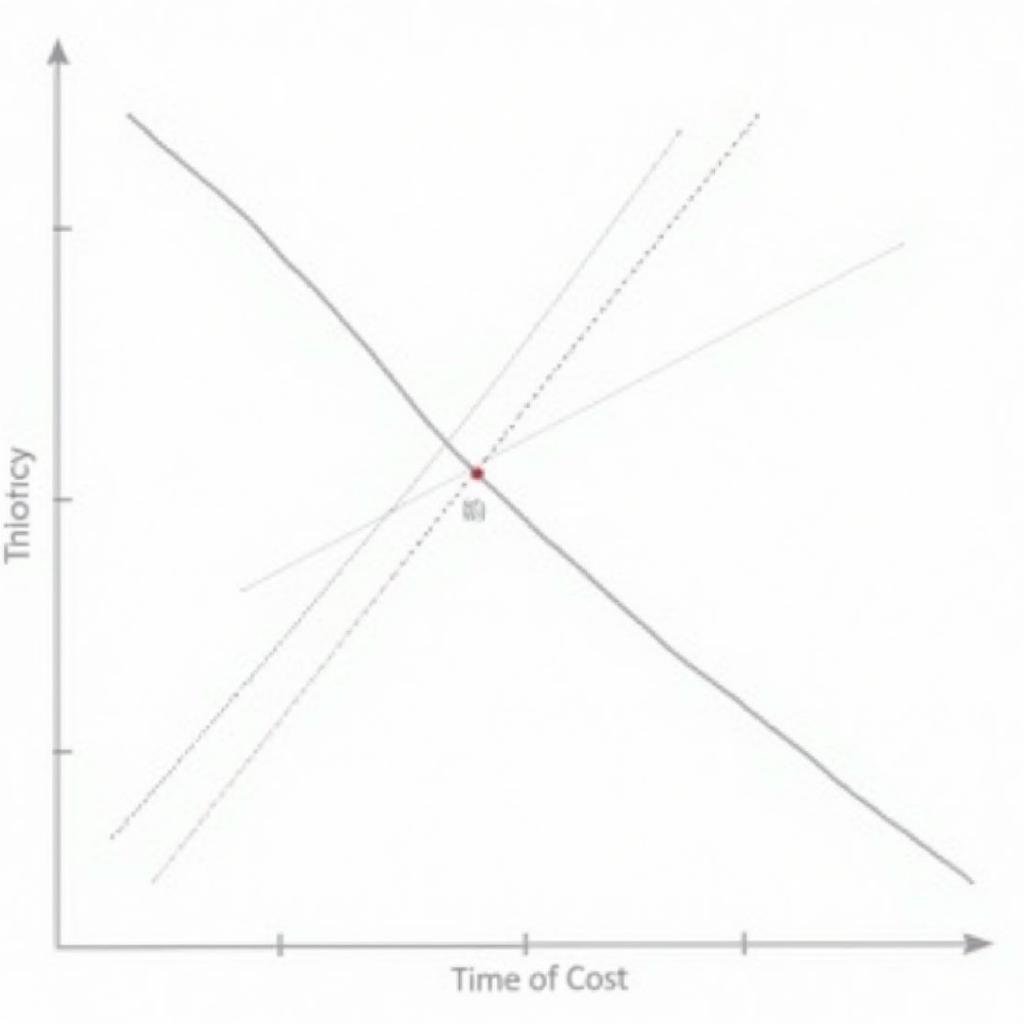 Graph illustrating optimal replacement time based on cost analysis
Graph illustrating optimal replacement time based on cost analysis
Key Factors Influencing Replacement Decisions
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the optimal replacement time:
- Purchase price of new equipment: This is a significant upfront cost that must be considered.
- Operating and maintenance costs: These costs typically increase as equipment ages.
- Salvage value of old equipment: The resale value of the old equipment can offset the cost of new equipment.
- Rate of deterioration: This reflects how quickly the equipment loses efficiency or requires more maintenance.
- Technological advancements: New technologies can offer significant improvements in efficiency and cost savings.
- Interest rates and inflation: These economic factors can influence the overall cost of replacement.
Applying Replacement Theory in Real-World Scenarios
Replacement theory finds application in various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. Examples include:
- Replacing a fleet of delivery trucks: A logistics company can use replacement theory to determine when to replace its aging trucks, balancing the increasing maintenance costs with the cost of purchasing new, more fuel-efficient vehicles.
- Replacing machinery in a manufacturing plant: A manufacturing company can use replacement theory to optimize the replacement cycle for its machinery, minimizing downtime and maximizing production efficiency.
- Replacing medical equipment in a hospital: A hospital can use replacement theory to determine the optimal time to replace medical equipment, ensuring patient safety and minimizing costs.
Why is Replacement Theory Important?
Implementing effective replacement policies based on replacement theory offers several benefits:
- Cost reduction: By optimizing the replacement cycle, businesses can minimize total cost of ownership over the asset’s lifespan.
- Improved efficiency: Replacing older equipment with newer, more efficient models can enhance productivity and reduce operating costs.
- Reduced downtime: Planned replacements minimize unexpected breakdowns and associated downtime, leading to smoother operations.
- Enhanced safety: Replacing worn-out equipment can improve workplace safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Better resource allocation: Replacement theory helps businesses allocate resources effectively by identifying the optimal time for capital investments.
“Replacement theory is not simply about minimizing costs; it’s about maximizing value over the entire lifecycle of an asset,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in operations research. “A well-executed replacement strategy can significantly contribute to a company’s overall profitability and competitiveness.”
Conclusion
What Is Replacement Theory In Operation Research? It’s a valuable tool for businesses seeking to optimize the lifecycle of their assets. By applying the principles of replacement theory, organizations can make informed decisions about when to replace deteriorating equipment, balancing the costs of replacement against the increasing costs of maintenance and decreased efficiency. This proactive approach can lead to significant cost savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness. By understanding and applying replacement theory, businesses can ensure they are getting the most value out of their investments and maximizing their long-term profitability.
FAQs
- What is the primary goal of replacement theory? To minimize the total cost of ownership over an asset’s lifespan.
- What factors are considered in replacement theory models? Purchase price, operating costs, salvage value, and deterioration rate.
- What are the different types of replacement problems? Sudden failure, gradual deterioration, and technological advancements.
- How can replacement theory benefit businesses? Cost reduction, improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety.
- What industries can benefit from replacement theory? Manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and many others.
- Is replacement theory only about cost? No, it’s about maximizing value over the asset’s lifecycle.
- How can I learn more about applying replacement theory in my business? Consult with an operations research expert.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 0904826292, Email: research@gmail.com or visit us at No. 31, Alley 142/7, P. Phú Viên, Bồ Đề, Long Biên, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.