Applied research is a powerful tool used to solve specific, practical problems and develop innovative solutions. It’s about taking the theoretical knowledge gained from basic research and putting it to work in the real world. Unlike basic research, which seeks to expand our understanding of fundamental principles, applied research focuses on addressing immediate challenges and improving existing products, processes, or technologies.
Understanding Applied Research and Its Significance
To fully grasp the concept of applied research, let’s delve deeper into its definition, explore its key characteristics, and examine its importance in various fields.
Applied research aims to find practical solutions to defined problems by applying existing knowledge to real-world situations. It focuses on:
- Problem-solving: Identifying and addressing specific issues or challenges.
- Practical Applications: Translating theoretical knowledge into tangible solutions.
- Innovation and Improvement: Developing new technologies, products, or processes, or enhancing existing ones.
This type of research plays a crucial role in numerous sectors, including:
- Business and Marketing: Understanding consumer behavior, improving marketing strategies, and developing new products.
- Healthcare: Discovering new treatments, developing medical devices, and improving patient care.
- Technology: Creating new software, hardware, and technological advancements.
- Education: Enhancing teaching methods, developing effective learning materials, and improving educational outcomes.
Distinguishing Applied Research from Basic Research
While both applied and basic research contribute significantly to the advancement of knowledge, they differ in their objectives, methodologies, and outcomes.
Basic research expands fundamental knowledge and understanding of the world. It is:
- Curiosity-driven: Motivated by a desire to explore and understand fundamental principles.
- Theoretical: Focused on developing or refining theories and models.
- Exploratory: Often open-ended, without a specific application in mind.
On the other hand, applied research is:
- Problem-oriented: Driven by a specific problem or challenge.
- Practical: Focused on finding solutions and developing practical applications.
- Goal-directed: Aims to achieve specific, measurable outcomes.
 Applied Research Examples
Applied Research Examples
Exploring Examples of Applied Research
To illustrate the concept further, let’s consider some concrete examples of applied research:
- Developing a new drug to treat a specific disease: This involves conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the drug in humans.
- Improving the efficiency of solar panels: Researchers might experiment with different materials and designs to increase the amount of sunlight converted into electricity.
- Creating a marketing campaign to target a specific demographic: This might involve conducting surveys and focus groups to understand the preferences and behaviors of the target audience.
- Developing a new teaching method to improve student engagement: This could involve implementing the method in a classroom setting and measuring its impact on student learning and motivation.
The Process of Conducting Applied Research
The process of conducting applied research typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the problem or opportunity: Clearly define the specific issue to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Examine existing research and data related to the problem.
- Formulate a hypothesis or research question: Develop a testable statement or question that guides the research.
- Design and conduct the study: Choose an appropriate research design, collect data, and analyze the findings.
- Interpret the results: Draw conclusions based on the data analysis and relate them back to the original problem or opportunity.
- Communicate the findings: Share the research results through reports, presentations, or publications.
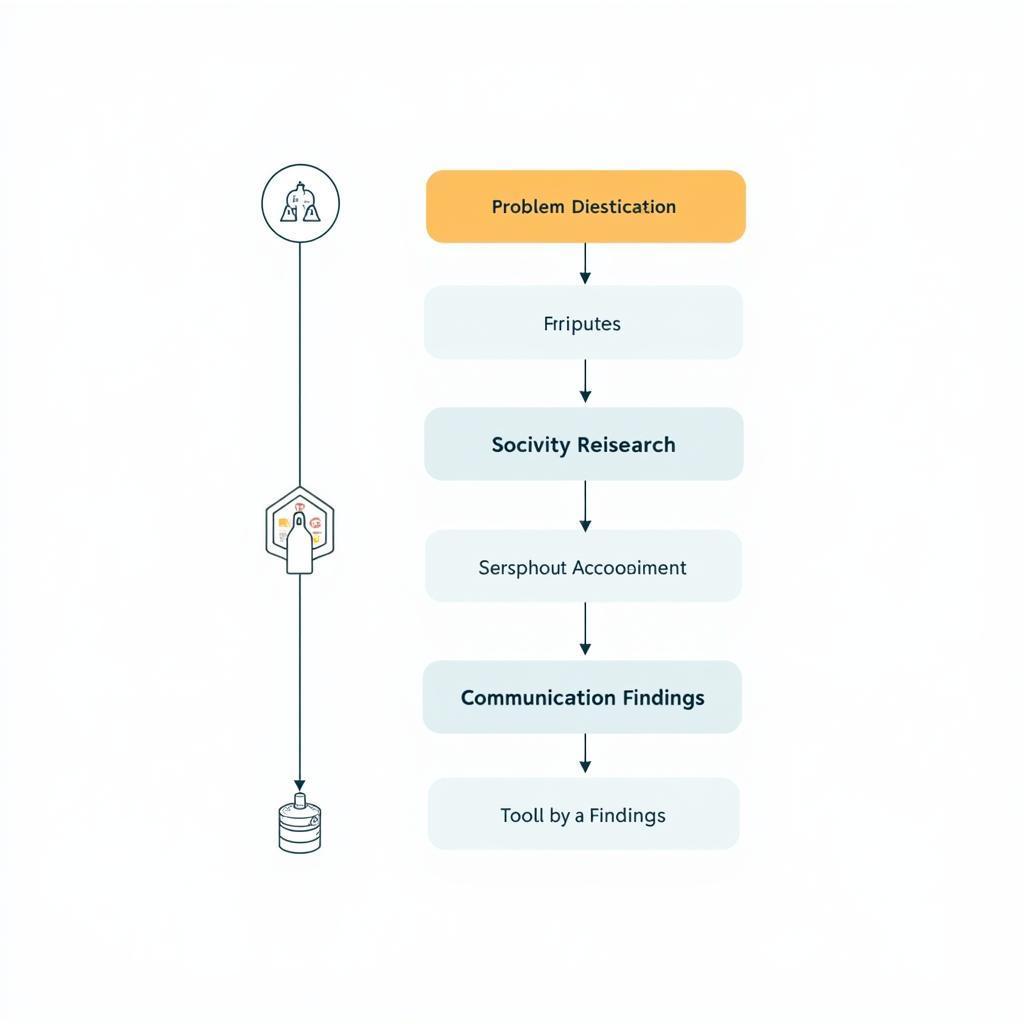 Applied Research Process
Applied Research Process
The Impact and Future of Applied Research
Applied research plays a vital role in driving progress and innovation across various sectors. It helps to:
- Solve real-world problems: Addressing critical issues in health, technology, business, and beyond.
- Improve existing products and processes: Enhancing efficiency, effectiveness, and user experience.
- Foster economic growth: Driving innovation and creating new markets and opportunities.
- Enhance quality of life: Developing solutions that improve health, education, and overall well-being.
As technology advances and global challenges become more complex, the importance of applied research will only continue to grow. Researchers will need to collaborate across disciplines to develop innovative solutions to pressing issues such as climate change, food security, and healthcare accessibility.
Conclusion
Applied research is a crucial driver of progress and innovation, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications. By focusing on solving specific problems and developing practical solutions, applied research continues to shape our world and improve our lives in countless ways. From developing life-saving medical treatments to creating groundbreaking technologies, applied research is essential for addressing the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
sociological research is based on which of the following offers a fascinating look at a specific type of applied research. For more on research in general, you can explore what is proprietary research](https://midatlanticparanormalresearch.com/what-is-proprietary-research/). If you’re interested in the nuances of academic writing, we also have a guide on can you use pronouns in a research paper.